DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
File Based Storage
Solutions for File Based Storage
In this guide, we explore Azure’s file-based storage offerings, including Storage Accounts, Microsoft Purview for governance, file categorization strategies, performance tiers, and geo-redundant storage for disaster recovery. You’ll learn how to optimize for cost, performance, and compliance.
Azure Storage Accounts
Azure Storage Accounts provide a unified namespace for storing multiple data types. Choose the right service based on your workload:
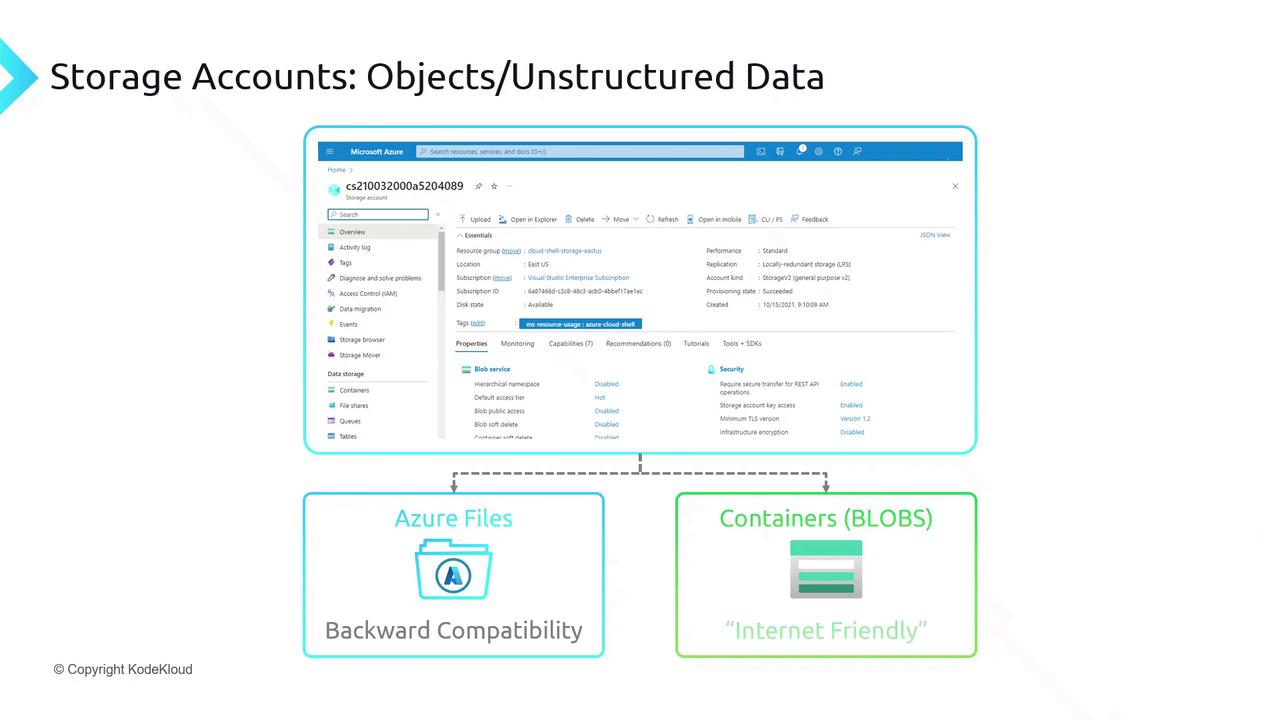
Azure Files
Fully managed SMB/NFS file shares—ideal for lift-and-shift migrations and legacy apps.Blob Storage (Containers)
Scalable object storage for unstructured data (images, videos, logs) with HTTP/HTTPS access and integration with big data analytics.
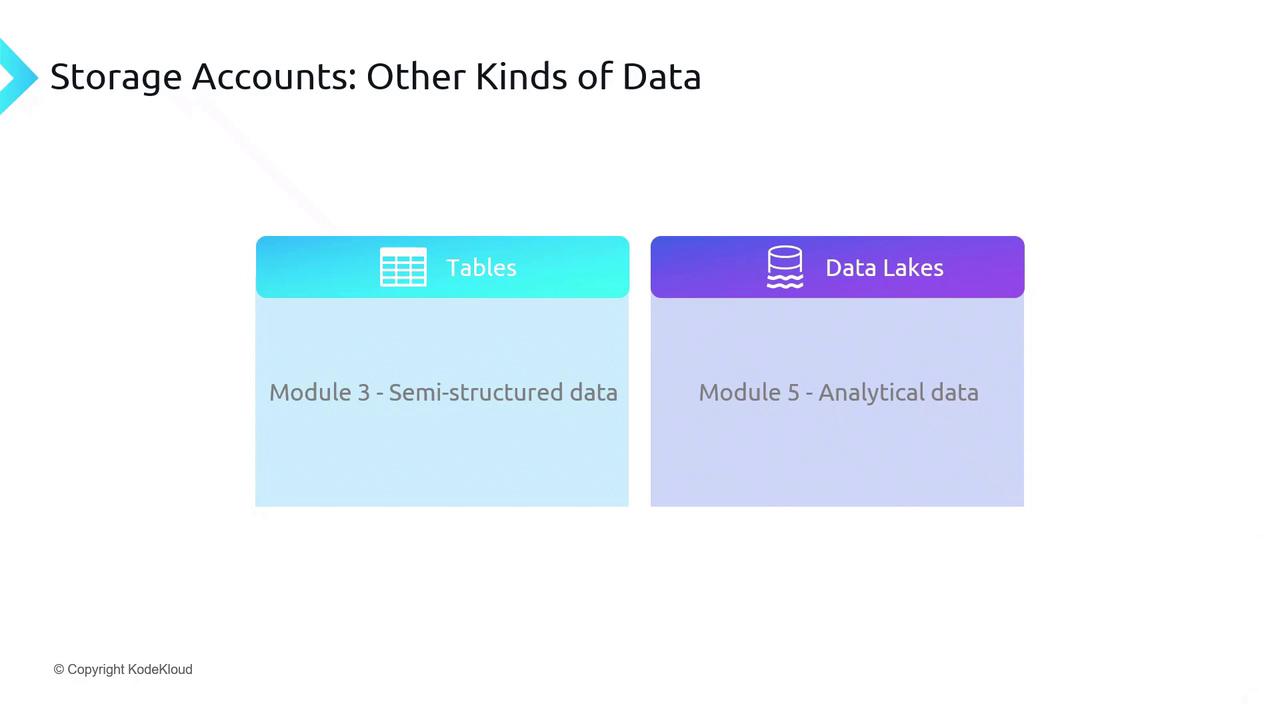
Other Data Services in a Storage Account
| Resource Type | Ideal For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Files | Enterprise file shares | SMB/NFS protocol support |
| Blob Storage (Containers) | Unstructured objects | Lifecycle management, tiering |
| Azure Tables | Semi-structured NoSQL data | Fast key/attribute lookups |
| Data Lake Storage Gen2 | Big data analytics | Hierarchical namespace, POSIX-compliant |
Tip
For analytics, use Data Lake Storage Gen2 on top of Blob Storage to leverage Hadoop, Spark, and Azure Synapse workloads.
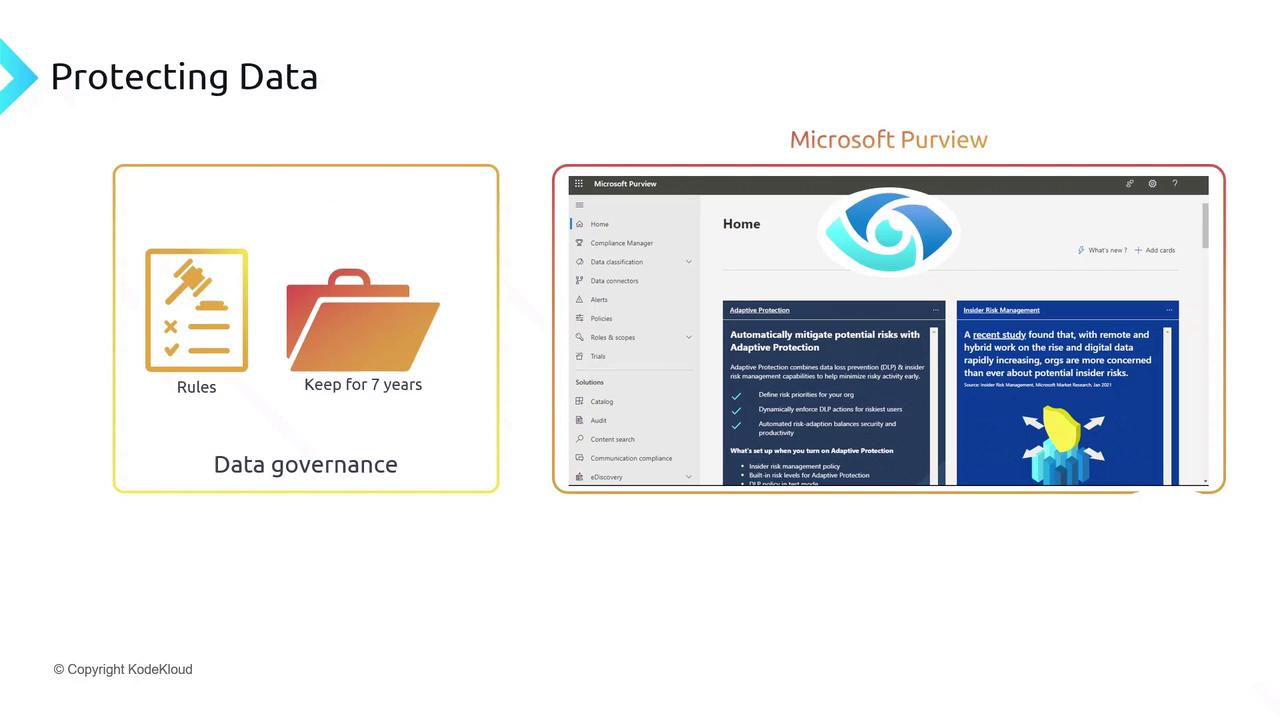
Microsoft Purview for Data Governance
Microsoft Purview centralizes data governance, classification, and discovery:
Governance Policies
Define retention schedules and lifecycle rules (e.g., retain logs for 7 years).Data Protection
Apply sensitivity labels and prevent unauthorized sharing of confidential files.Catalog & Discoverability
Index enterprise data for search, lineage, and compliance reporting.

Warning
Without proper governance, you risk non-compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
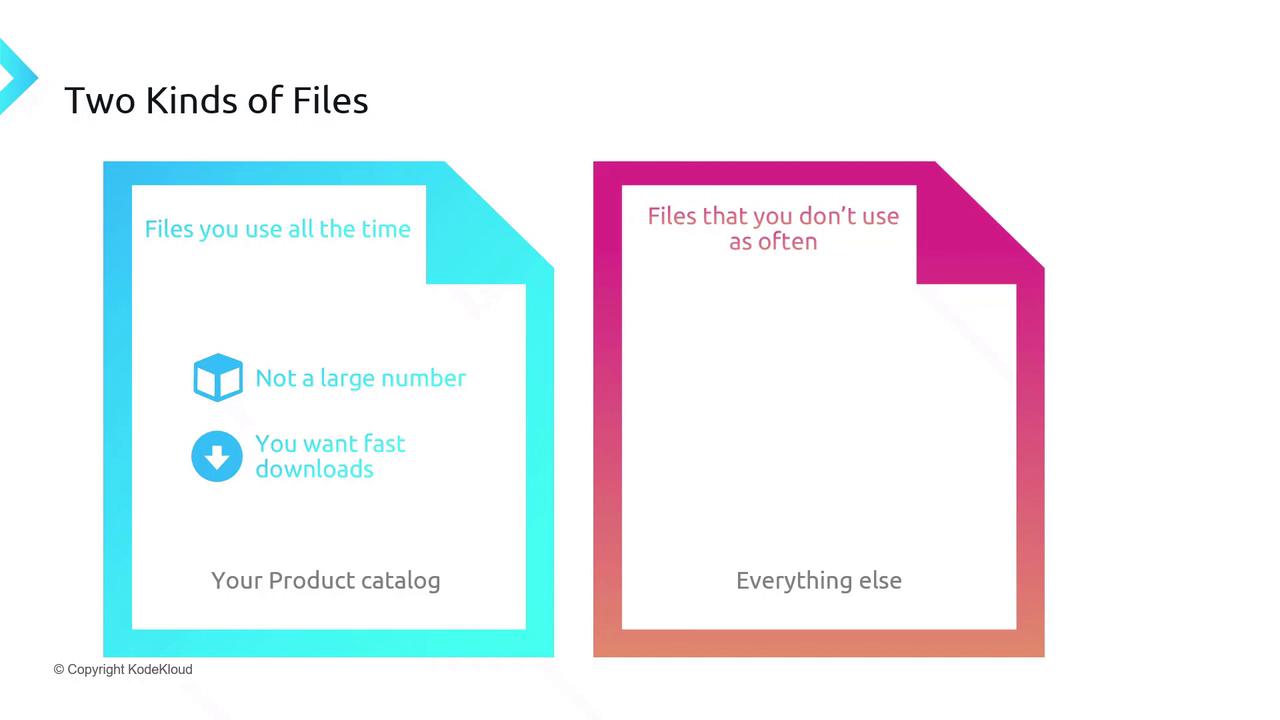
File Categorization: Hot vs. Cold
Segment your files based on access frequency to control costs:
Hot Data
Frequently accessed files, e.g., product catalogs requiring low latency.Cold Data
Infrequently accessed archives and backups where access speed is less critical.
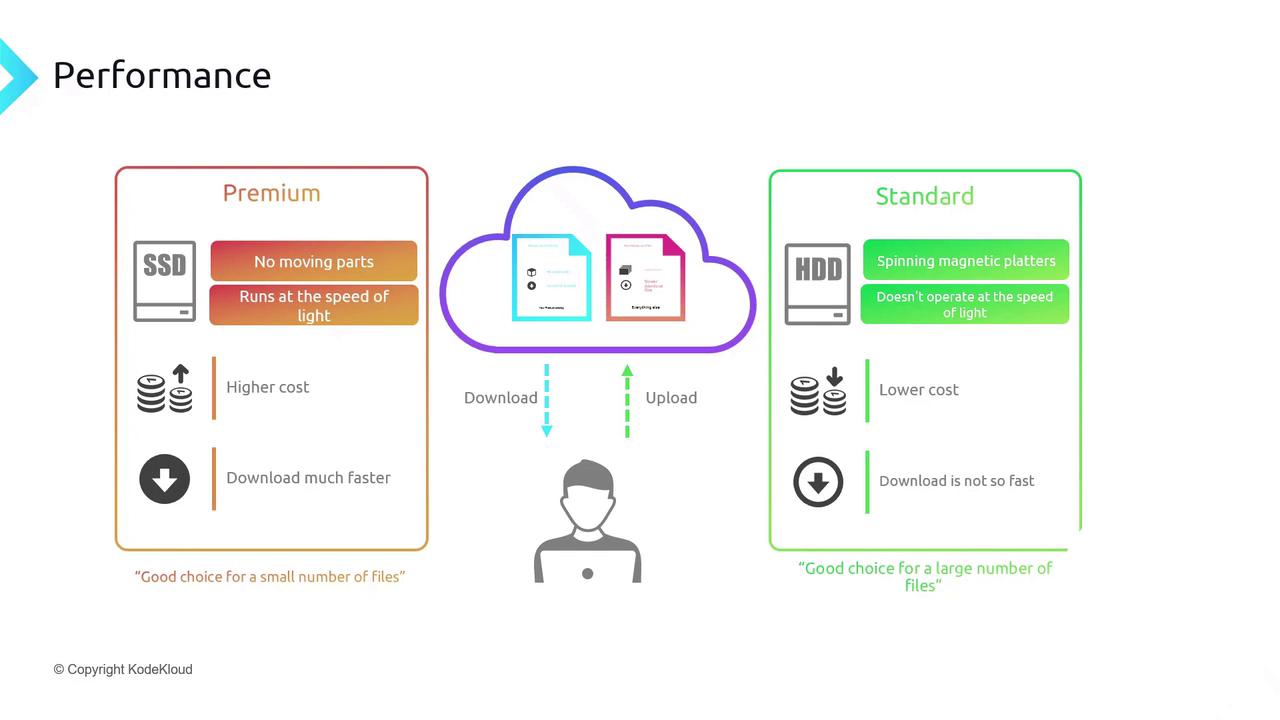
Performance Tiers: Standard vs. Premium
Balance cost and performance by selecting the appropriate tier:
| Tier | Storage Medium | Best For | Latency | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premium | SSD | Hot data, high IOPS | Millisecond-scale | Higher |
| Standard | HDD | Cold data, large archives | Higher milliseconds | Lower |
Pro Tip
Use Azure Storage lifecycle policies to transition blobs automatically between hot, cool, and archive tiers.
Geo-Redundant Storage (GRS)
Ensure business continuity with Geo-Redundant Storage:
- Asynchronously replicate data to a paired region (>300 miles apart).
- Automatic failover in the event of a regional outage.
- Optionally enable read-only access in the secondary region (Read-Access GRS).
![]()
Best Practice
Pair GRS with Azure Backup and Azure Site Recovery for end-to-end disaster recovery.
Next, we’ll demonstrate how to create and configure an Azure Storage Account using the Azure Portal and Azure CLI.
Watch Video
Watch video content