DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
Semi Structured Data
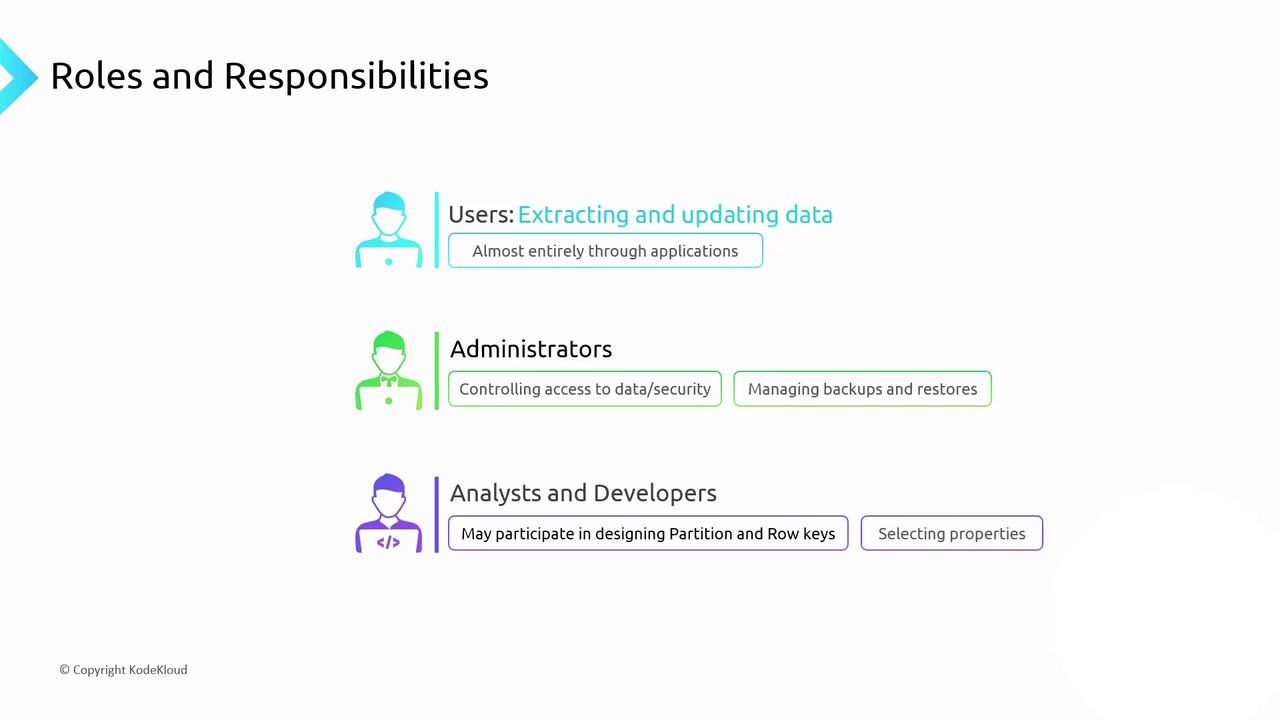
Roles and Responsibilities
In this final section, we explore the primary roles and responsibilities required to manage Azure Table Storage effectively. Understanding these roles helps ensure secure access, optimal performance, and maintainable schema design.
| Role | Primary Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Users | - Interact with Table Storage through applications rather than direct access<br>- Require assigned permissions for both user accounts and service principals |
| Administrators | - Also known as Database Administrators (DBAs)<br>- Grant and revoke access rights to control who can perform specific actions<br>- Perform backups and restores for recovery |
| Analysts & Developers | - Determine optimal PartitionKey and RowKey values to distribute data and speed up queries<br>- Define entity properties to enforce a consistent schema<br>- Monitor performance and refine queries |
Schema Flexibility
Azure Table Storage supports a semi-structured schema: each entity can have different properties. However, aligning on a core set of attributes per row prevents uncontrolled schema growth and simplifies data handling.
Key Takeaways
- Deployment Options
- Native Azure Table Storage
- Azure Cosmos DB Table API for global distribution and low latency
- NoSQL Key–Value Model
- Each entity (row) holds all related data for a single transaction
- Required Keys
- Every row must include a
PartitionKey,RowKey, andTimestamp
- Every row must include a
- PartitionKey
- Determines how data is distributed across storage nodes
- Narrow your query to a single partition to limit scanned rows and improve performance
- RowKey
- Unique within its partition and automatically indexed for fast lookups
- Requires an exact
PartitionKeymatch to leverage the index
- Flexible Schema
- Store varying properties per row
- Maintain a baseline attribute set to ensure consistency and manageability
Performance Tip
An unbalanced partition strategy (e.g., “hot” partitions) can cause throttling. Monitor access patterns and adjust your PartitionKey design to distribute load evenly.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content