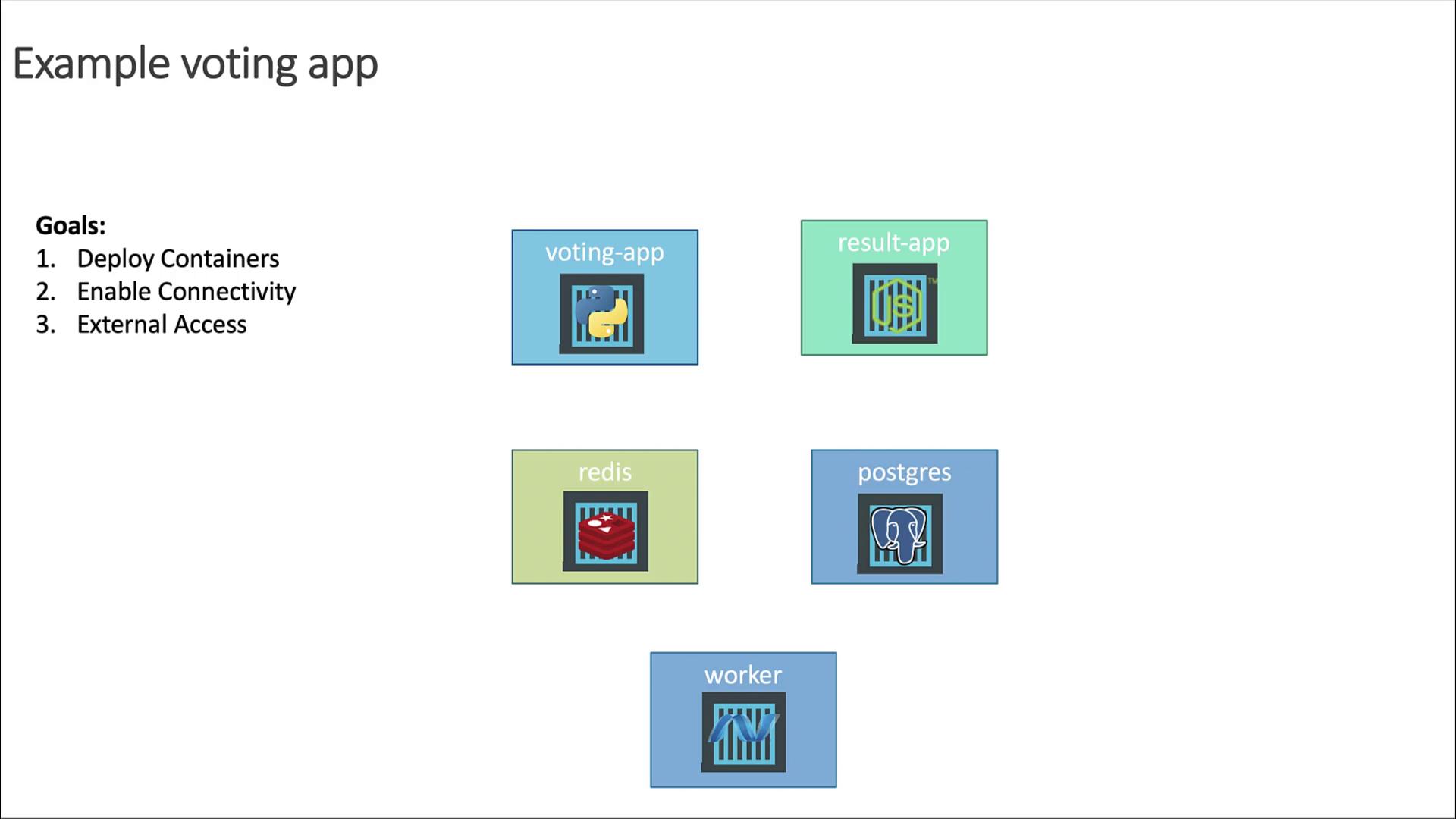
Objectives
- Deploy each service as containers on a Kubernetes cluster
- Enable reliable connectivity so services can communicate
- Expose the Voting and Result apps externally via web browser
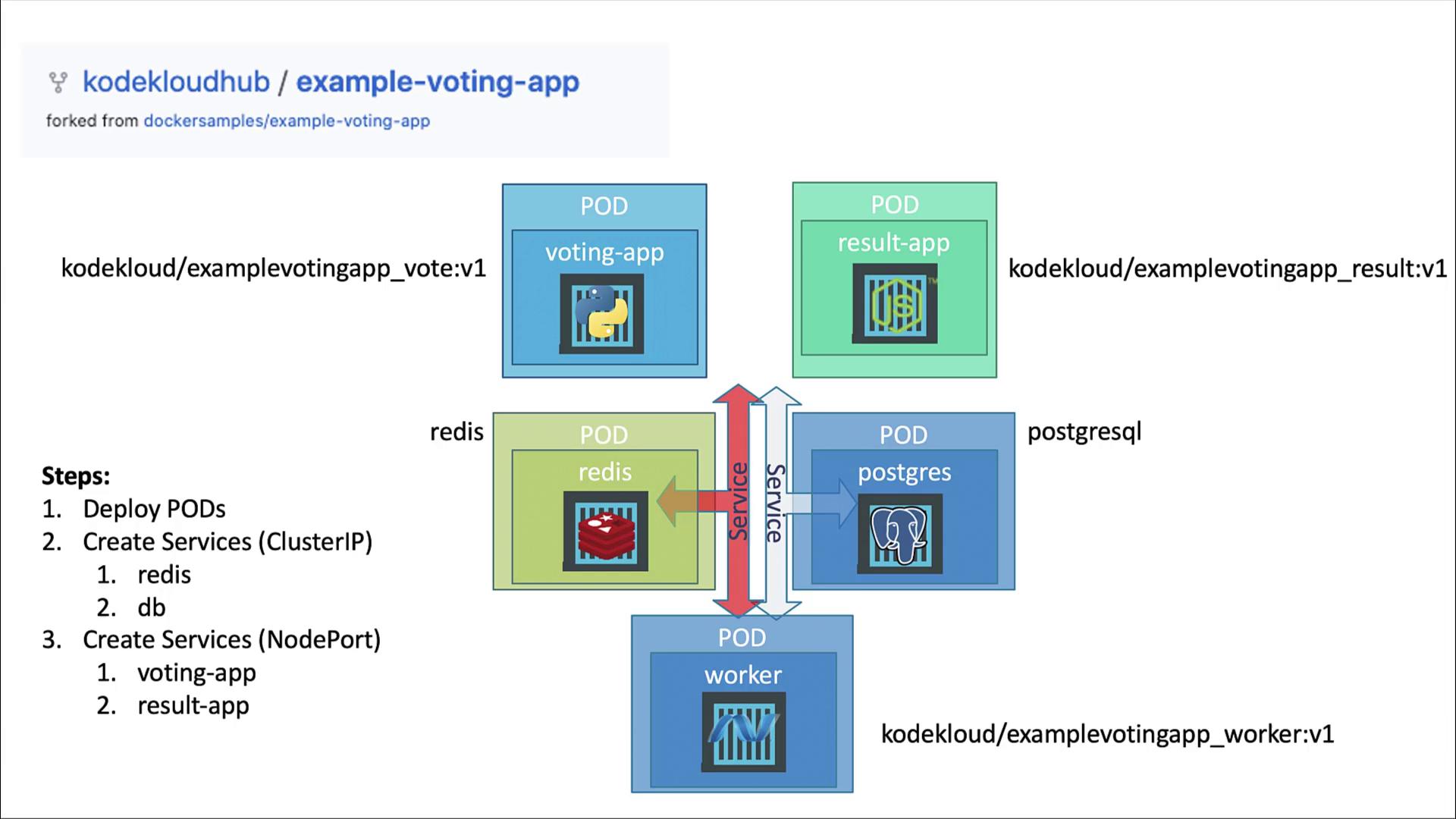
High-Level Plan
- Deploy each application as a standalone Pod (we’ll convert them to Deployments later).
- Create Services for internal connectivity:
- redis (ClusterIP)
- db (ClusterIP)
- Expose the frontends using NodePort Services:
- voting-app
- result-app
- Skip a Service for the worker (it’s only a background job).
Connectivity Requirements
- voting-app writes votes to Redis.
- worker reads votes from Redis and writes aggregates to PostgreSQL.
- result-app reads results from PostgreSQL to display.
- voting-app and result-app are user-facing.
- worker runs in the background and doesn’t receive external traffic.
- voting-app: 80
- result-app: 80
- redis: 6379
- postgres: 5432
- worker: no external port
Why Use a Service?
Pod IPs are ephemeral. Kubernetes Services provide a stable DNS name and virtual IP. For example, the Python app connects to Redis at hostredis:
Database Credentials
- Username: postgres
- Password: postgres
Service Types
- ClusterIP: Internal-only (redis, db)
- NodePort: External access (voting-app, result-app) – ports > 30000
Summary of Resources
| Resource | Type | Service Type | Port |
|---|---|---|---|
| voting-app | Pod | NodePort | 80 |
| result-app | Pod | NodePort | 80 |
| redis | Pod | ClusterIP | 6379 |
| postgres | Pod | ClusterIP | 5432 |
| worker | Pod | (none) | — |
The worker Pod has no Service because it does not receive traffic from other components.
Docker Images
We’ll use the following container images:kodekloud/example-voting-app_vote:v1kodekloud/example-voting-app_worker:v1kodekloud/example-voting-app_result:v1redis:latestpostgres:latest