EFK Stack: Enterprise-Grade Logging and Monitoring
Fluent Bit
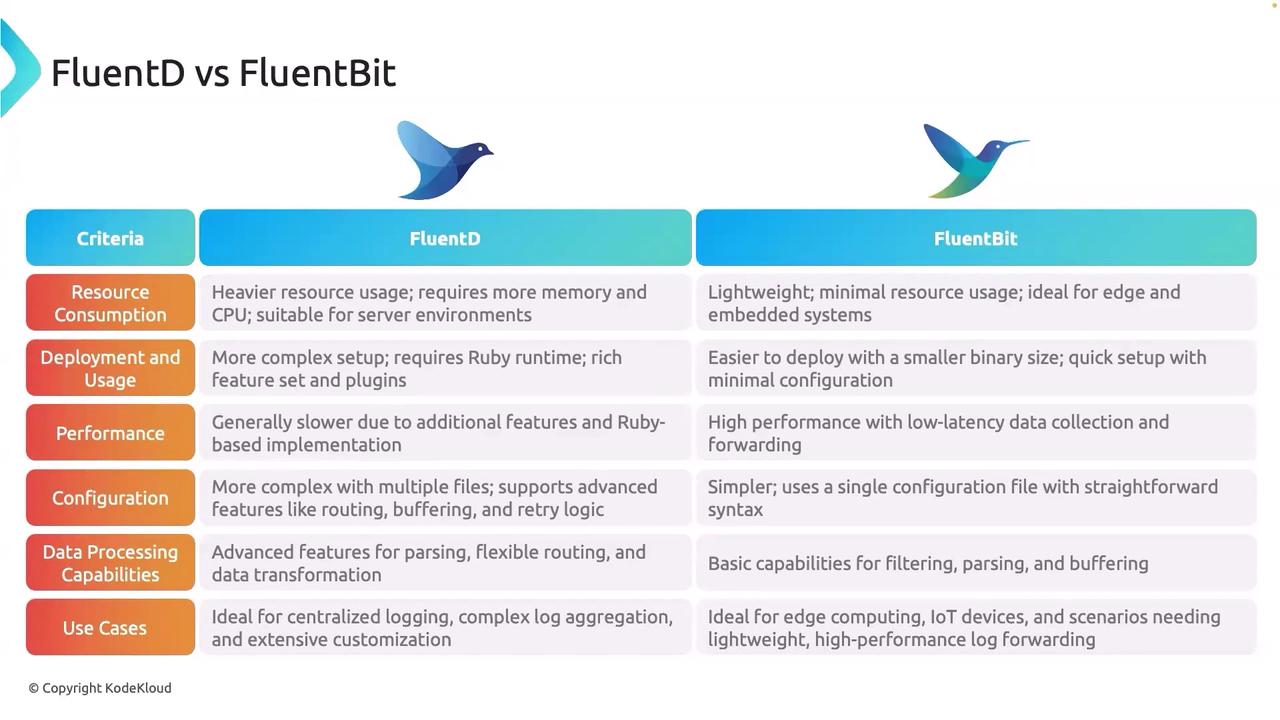
FluentD vs FluentBit
Welcome to this comprehensive guide comparing FluentD and FluentBit. In this lesson, we will highlight the key differences between the two log processors, helping you decide which solution best fits your application's needs. Both FluentD and FluentBit have evolved as superior alternatives to Logstash, offering varied benefits depending on your infrastructure requirements.
Resource Consumption
FluentD delivers a rich feature set but consumes more resources due to its architecture, which requires additional memory and CPU. This makes it a suitable choice for server environments where ample resources are available. In contrast, FluentBit is designed for minimal footprint applications, making it ideal for edge devices or embedded systems where every byte and millisecond counts—for example, in IoT devices.
Resource Tip
When planning your deployment, consider the resource limitations of your environment. Choose FluentBit for resource-constrained systems and FluentD for more robust setups.
Deployment and Usage
Setting up FluentD can be complex as it depends on the Ruby runtime and supports a wide array of plugins for data transformation and routing. This slanted complexity is advantageous when intricate data manipulation is required. On the other hand, FluentBit offers a quick and straightforward deployment, thanks to its lightweight binary and simple configuration. This makes FluentBit particularly attractive in Kubernetes environments and microservices architectures where rapid scaling is essential.
Performance
FluentD's comprehensive architecture can sometimes result in slower performance compared to the streamlined FluentBit. Designed for high-speed log collection with low latency, FluentBit excels in scenarios demanding quick log processing and forwarding. This performance edge makes it a go-to solution for real-time monitoring systems and fast-paced logging environments.
Configuration
The configuration approach is another significant differentiator. FluentD often requires multiple configuration files to handle complex routing rules and setups, making it highly customizable. FluentBit, conversely, simplifies configuration by using a single, concise file. This streamlined configuration is particularly beneficial when deploying on platforms like Kubernetes, where simplicity and manageability are key.
Data Processing Capabilities
FluentD provides advanced data processing features, including robust parsing, flexible routing, and extensive transformation capabilities. These features are ideal for enterprises requiring thorough log analysis and customization. FluentBit, while offering a more basic set of functionalities, still provides effective filtering, parsing, and buffering, making it a reliable choice in scenarios such as smart home setups where efficient log management from multiple sensors is required.
Use Cases
Below is a comparison table that outlines scenarios for both FluentD and FluentBit:
| Feature | FluentD | FluentBit |
|---|---|---|
| Use Case | Centralized logging and comprehensive customization | Edge computing and resource-constrained deployments |
| Ideal Environment | Large-scale enterprise systems with diverse log sources | IoT devices and microservice architectures |
| Deployment Complexity | Higher due to Ruby runtime and multi-file configurations | Minimal due to the single configuration file and lightweight design |
| Performance | May experience slower performance in high-speed scenarios | Excels in rapid log forwarding with low latency |
Visual Comparison
Making the Right Choice
Choosing between FluentD and FluentBit largely depends on your specific requirements:
- If you need a lightweight solution with low memory usage for efficient log input, parsing, and output, FluentBit is the ideal candidate.
- If your infrastructure demands complex data transformation and routing, FluentD's advanced features may be more appropriate.
Both tools have increasingly replaced Logstash in modern logging architectures, commonly referred to as the EFK stack (Elasticsearch, FluentD or FluentBit, and Kibana).
Final Insight
Evaluate your system's requirements carefully to determine the best fit. For further reading on centralized logging and scalable deployments, explore additional resources on Kubernetes Documentation and the Elasticsearch documentation.
We hope this guide clarifies the distinctions between FluentD and FluentBit, aiding you in making an informed decision for your logging infrastructure. Thank you for reading.
Watch Video
Watch video content