Enhancing Soft Skills for DevOps Engineers: Essential Non-Technical Skills to Thrive
Consulting and Client Management
Navigating Conflict
Welcome to this guide on mastering conflict resolution for DevOps professionals. I’m Michael Forrester, and here we’ll apply the FBI’s Behavioral Change Stairway Model—popularized by Chris Voss—to a DevOps context. Whether you’re managing deployments or collaborating on infrastructure-as-code, these non-technical skills will help you transform tension into productive outcomes.
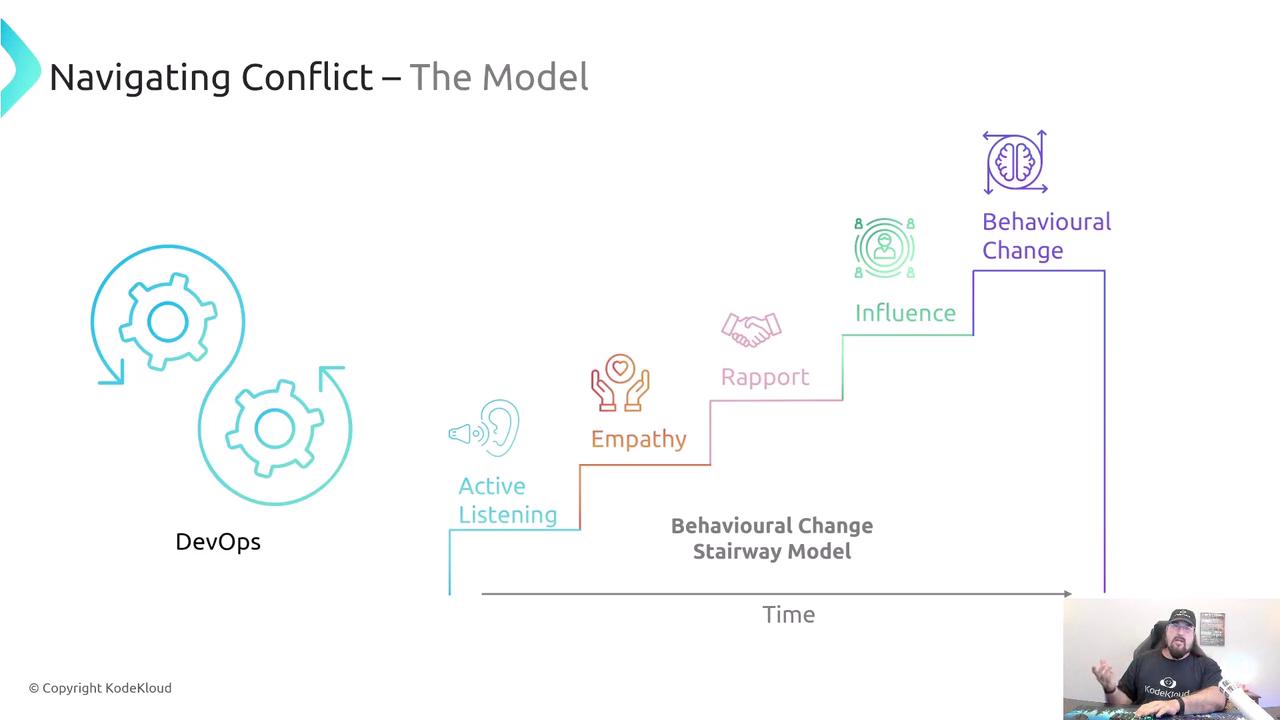
The Five-Step Framework
Below is an overview of the Behavioral Change Stairway Model adapted for DevOps:
| Step | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Active Listening | Capture both verbal and non-verbal cues to understand concerns |
| Empathy | Acknowledge emotions to build psychological safety |
| Rapport | Establish trust for ongoing collaboration |
| Influence | Guide stakeholders toward mutual goals |
| Behavioral Change | Achieve sustainable agreement and follow-through |
1. Active Listening
Active listening is the bedrock of conflict navigation. In a system outage or deadline dispute, pay attention to:
- Tone & Emotion: Are they frustrated, anxious, or neutral?
- Body Language: Posture, eye contact, and micro-expressions.
- Verbal Cues: Repetitions, hesitations, or abrupt topic changes.
Key techniques:
Mirroring
Repeat the last few words.
Example:
Speaker: “We lost production metrics last night.”
You: “Production metrics?”Paraphrasing
Restate in your own language.
“So you’re saying the monitoring alerts didn’t fire?”Emotional Labeling
Name the feeling you observe.
“It sounds like that was really stressful.”Effective Pauses
Use silence to prompt elaboration.
Note
Combine these techniques with genuine curiosity to foster psychological safety in your team.

2. Four Techniques for Active Listening
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Mirroring | Echo the speaker’s last words to show attentiveness |
| Paraphrasing | Summarize their point to confirm understanding |
| Emotional Labeling | Identify and verbalize emotions to demonstrate empathy |
| Effective Pauses | Allow space for deeper insights and reflection |
Use these methods iteratively to draw out hidden concerns and clarify priorities in high-pressure situations.
![]()
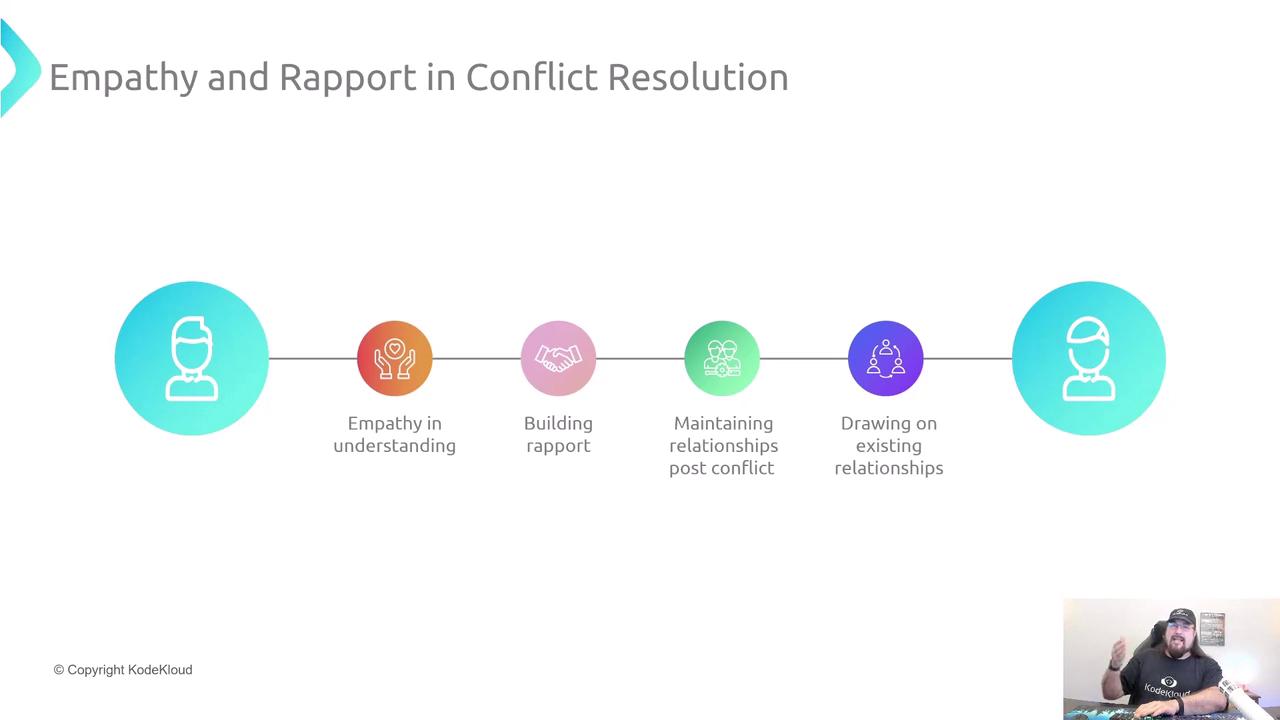
3. Empathy and Rapport
Once you’ve listened, validate emotions and cultivate trust:
- Label both your own and their feelings.
- Choose the right setting: one-on-one for sensitive topics.
- Model accountability by apologizing for any missteps.
Maintain rapport with regular check-ins:
- Schedule a follow-up meeting.
- Ask, “Does next Tuesday work for an update?”
This “social grease” prevents friction when priorities shift.
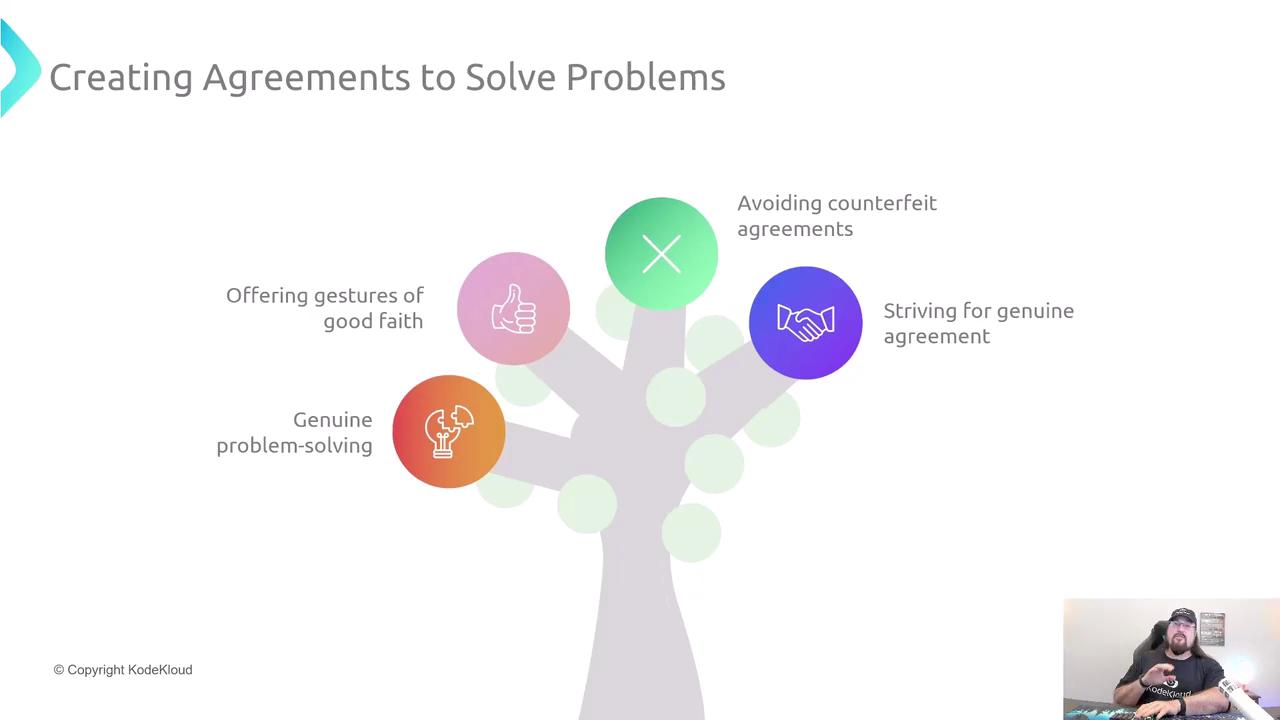
4. Creating Genuine Agreements
In DevOps, missed SLAs and changing specs often cause disputes. Forge reliable commitments by:
Offering gestures of good faith (e.g., daily status updates).
Distinguishing between different “yes” types:
Type of Yes Meaning Confirmation yes “Has this been decided?” Commitment yes “I will get this done by EOD.” Counterfeit yes Pretending to agree without intent
If uncertain, use a realistic timeline:
“Let me verify the details and get back to you by 3 PM tomorrow.”
Warning
Avoid counterfeit yeses—they erode trust and lead to scope creep.
5. Behavioral Change & Follow-Through
True resolution comes from consistent follow-through:
- Document agreements in a shared channel (e.g., Jira ticket, Confluence page).
- Set clear milestones and review dates.
- Celebrate wins to reinforce positive collaboration.
Further Reading & Resources
By integrating these five steps—Active Listening, Empathy, Rapport, Influence, and Behavioral Change—you’ll turn conflict into collaboration and drive continuous improvement across your DevOps teams.
Watch Video
Watch video content