Example: EV Charging Network
Consider an EV charging network where each charging station publishes events—status updates, metrics, and more—to two topics:charging-station-topicstation-metrics-topic
station-metrics-topic to display live station status.
In this example, we assume three brokers (
broker1, broker2, broker3) and three partitions per topic.Topic Creation Example
1, each partition only exists on a single broker.
Imagine broker2 fails. The partition it hosts becomes unavailable, and dashboards go dark.
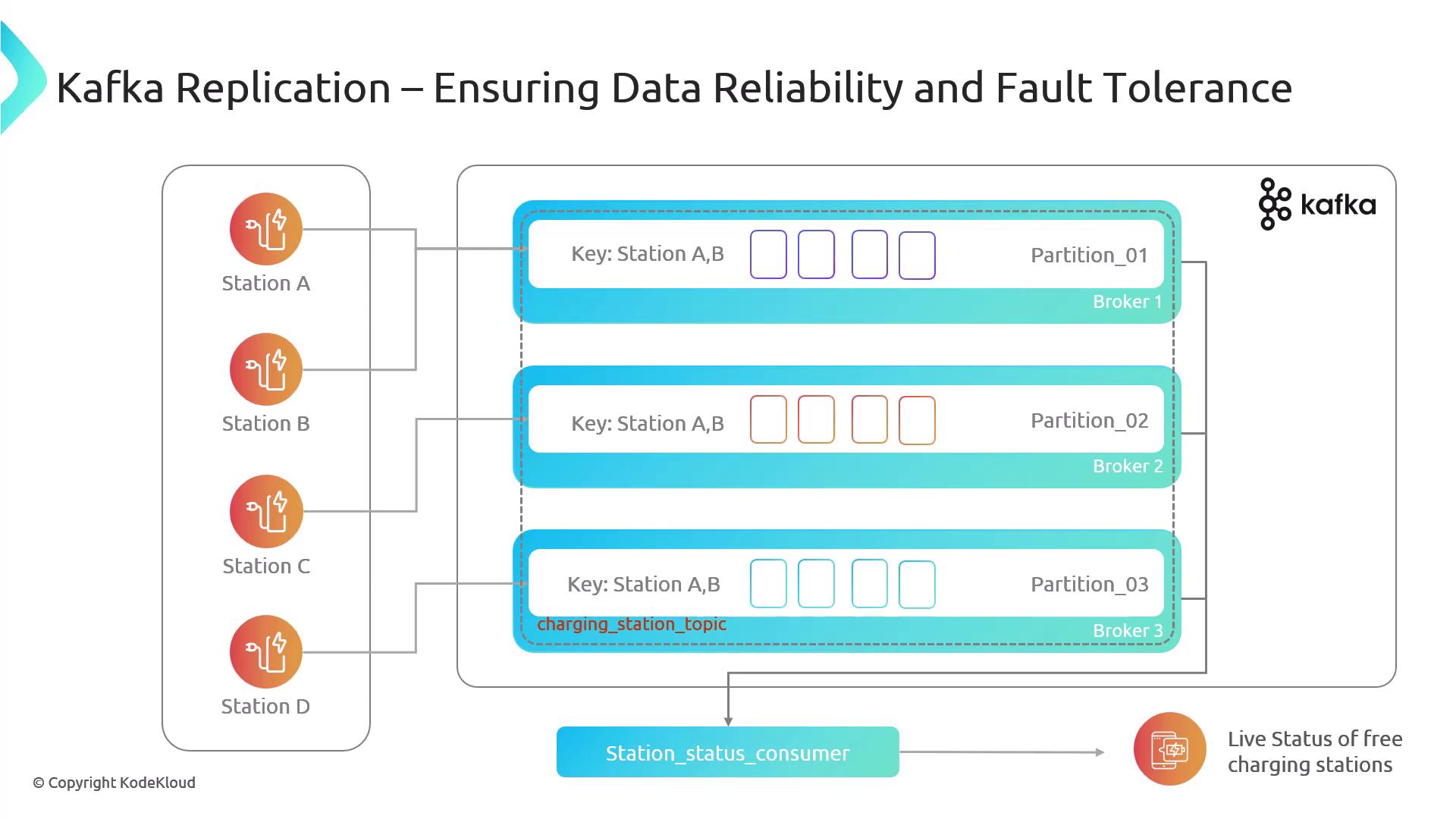
Without replication, any single broker failure leads to data unavailability for the partitions it hosts.
Why Replication Matters
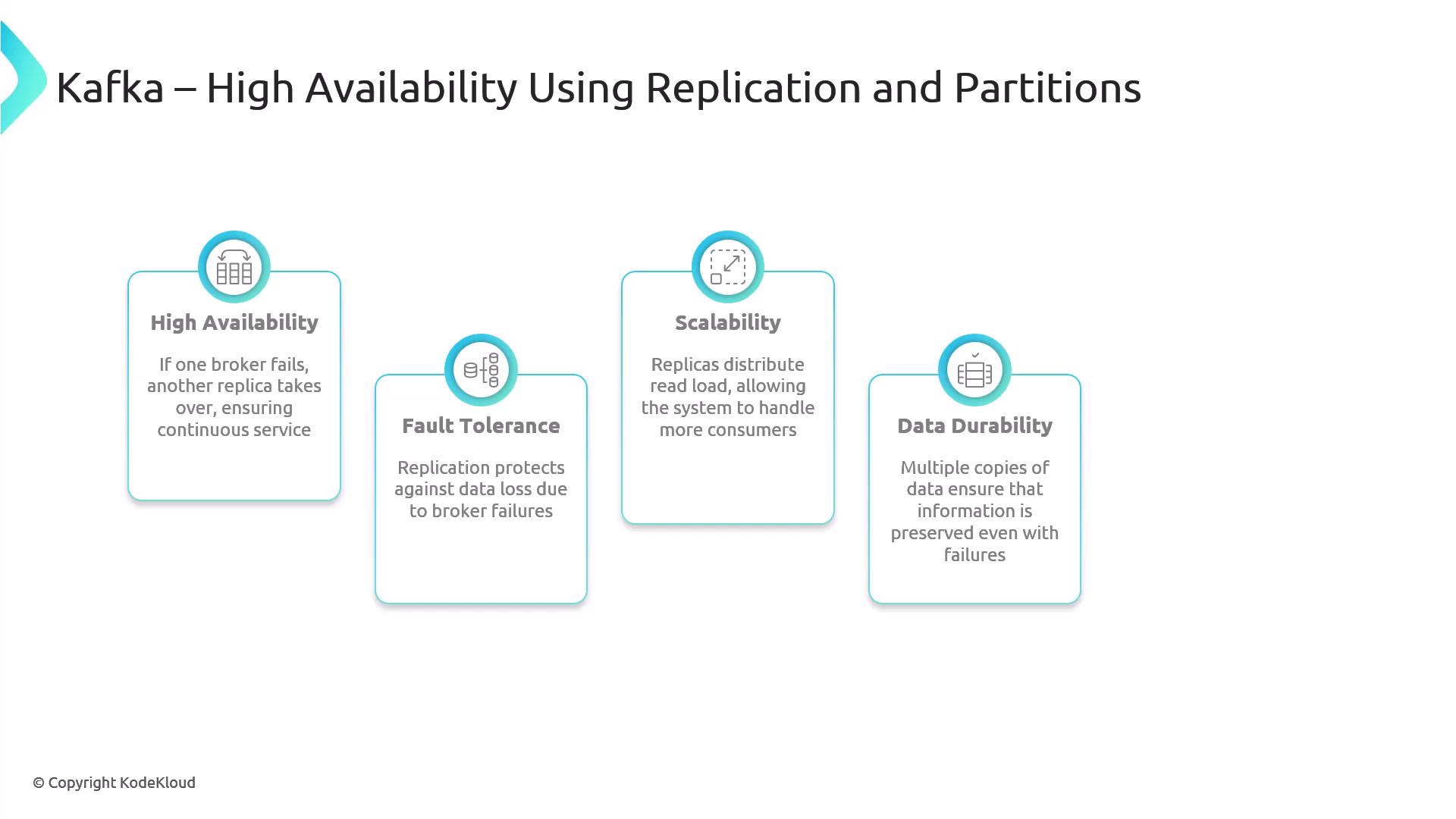
Replication copies each partition across multiple brokers. This ensures:| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| High Availability | On broker failure, an in-sync replica is promoted to leader automatically. |
| Fault Tolerance | Multiple copies prevent data loss if a broker crashes or hardware fails. |
| Scalability | Consumers can read from replicas, distributing the load and improving read throughput. |
| Data Durability | Messages are only acknowledged to producers once written to all in-sync replicas. |
| Increased Throughput | Parallel reads and writes across replicas boost overall system throughput. |
Replication in Action
Let’s update our topic to use a replication factor of 3:- Leader on
broker1 - Followers on
broker2andbroker3
-
Broker Failure (Non-Leader):
Ifbroker3goes offline, the partition continues serving reads/writes from the leader and the remaining in-sync follower. Kafka will automatically replicate to restore the desired replication factor. -
Leader Failure:
Ifbroker1(leader) fails, one of the in-sync followers (e.g.,broker2) is elected leader. Producers and consumers transparently reconnect, minimizing downtime.