| Step | Action | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create IAM role | Attach AmazonSSMFullAccess |
| 2 | Launch EC2 instance | t2.medium, 16 GiB root, attach IAM role |
| 3 | Connect via Session Manager | No SSH keys needed |
| 4 | Install Java & Kafka | Java 8 (Corretto), Kafka 3.0.0 |
| 5 | Configure Kafka in KRaft mode | Edit server.properties |
| 6 | Open port 9092 | Inbound rule in security group |
| 7 | Start broker & create a demo topic | kafka-server-start.sh, kafka-topics.sh |
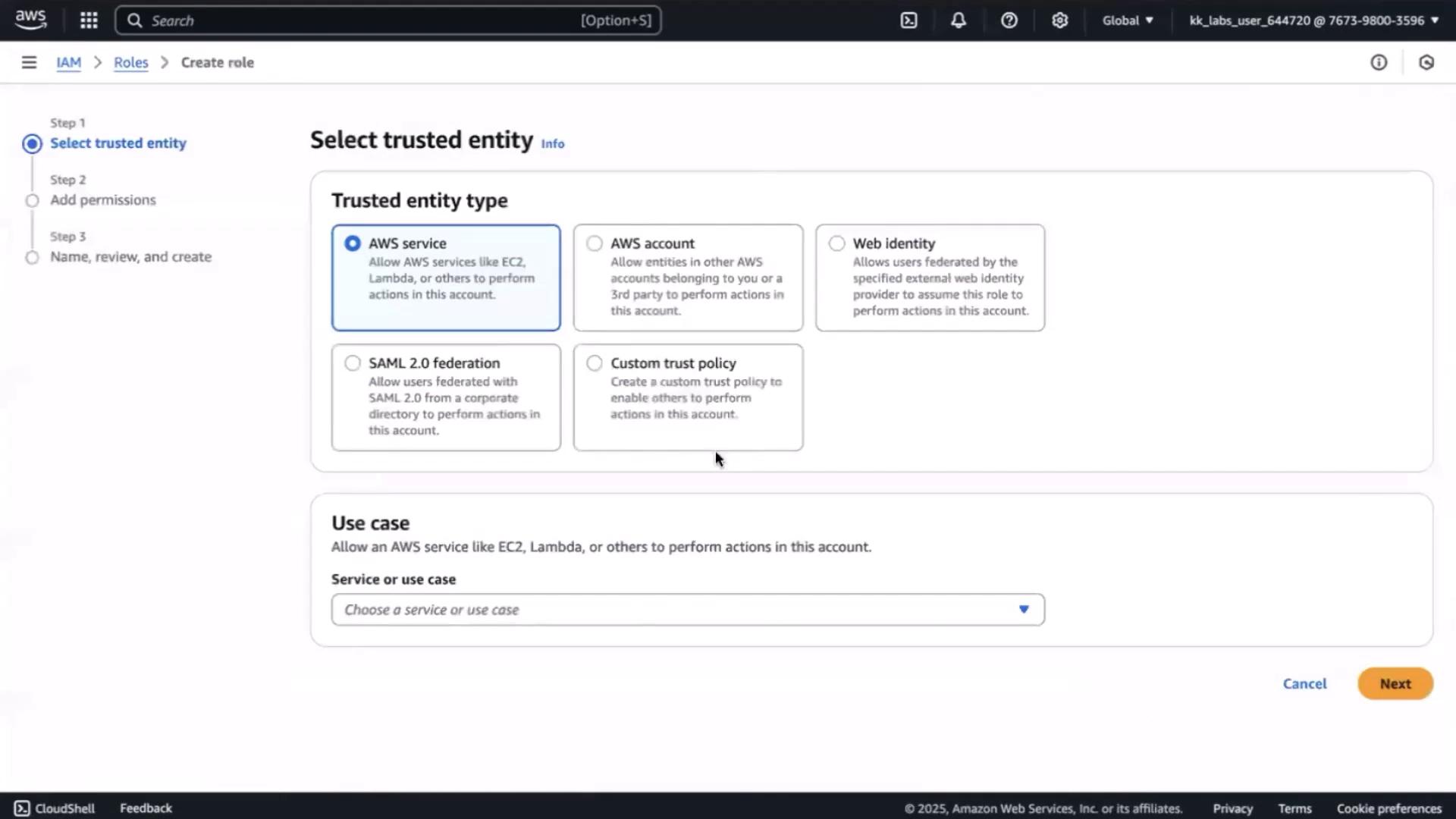
1. Create an IAM Role for EC2 with SSM Access
- In the AWS Console, go to IAM → Roles → Create role.
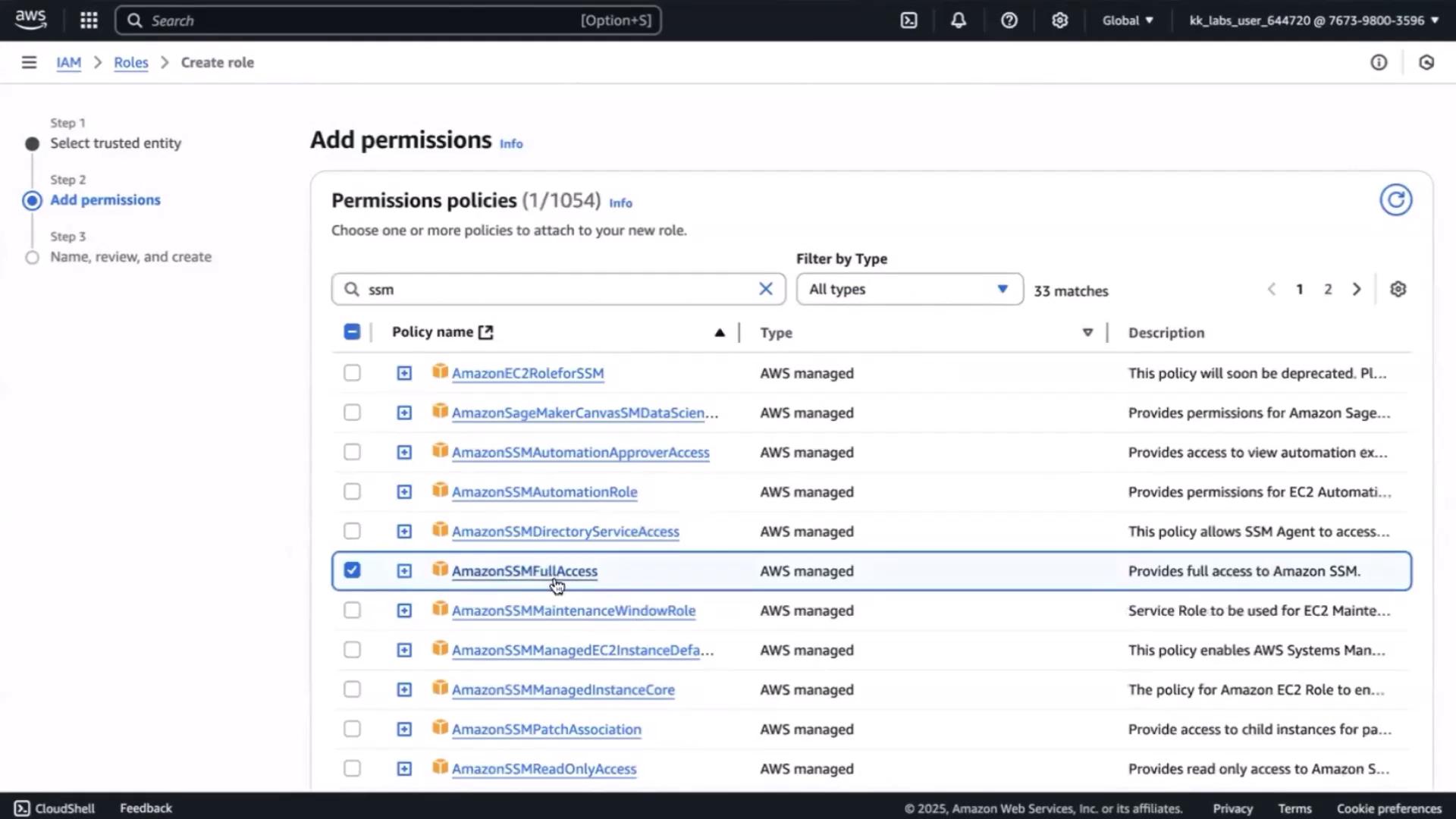
- Choose AWS service → EC2, then click Next.
- Search for SSM and attach the AmazonSSMFullAccess policy.
- Name the role KafkaDemo, then Create role.
2. Launch the EC2 Instance
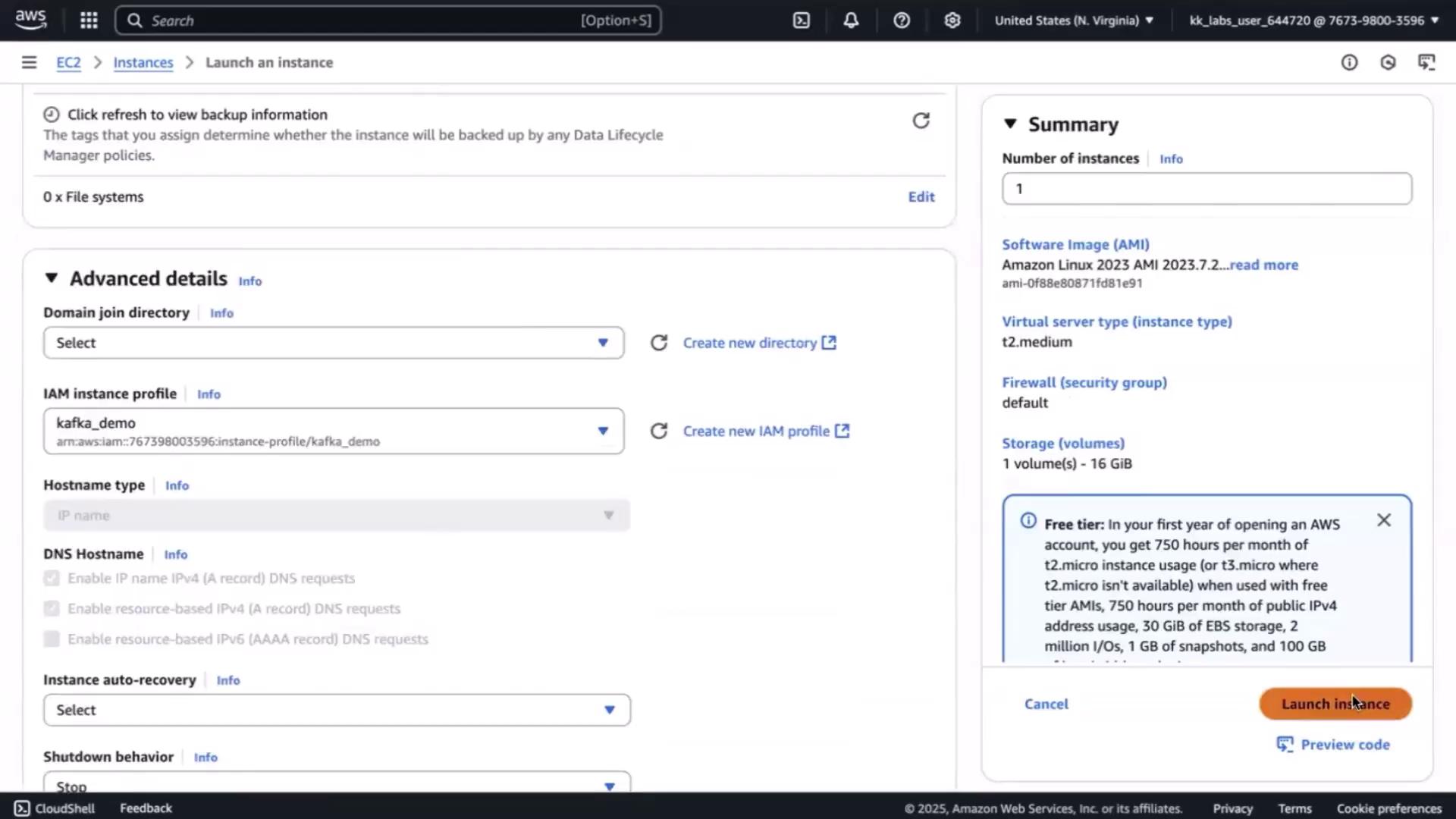
- Open the EC2 Console → Launch instance.
- Configure:
- Name: kafka-demo
- Instance type: t2.medium
- Root volume: increase to 16 GiB
- IAM role: KafkaDemo
- Skip key pair selection (SSM will handle connectivity).
- Keep the default security group for now.
- Click Launch.
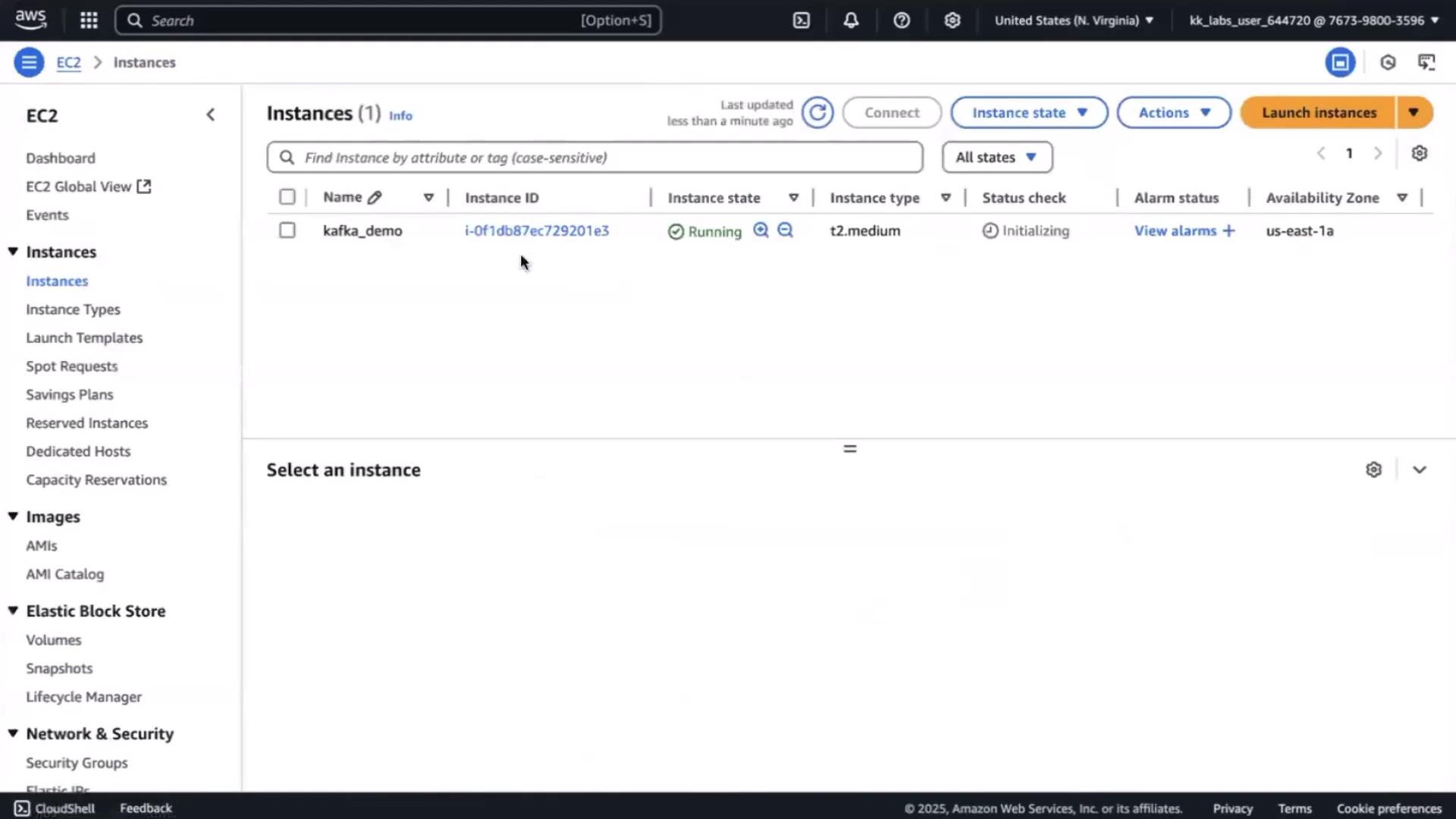
3. Connect via Session Manager
Wait until the instance state reads running. Then:- Go to Instances, select kafka-demo → Connect → Session Manager → Connect.
4. Install Java and Kafka
In the Session Manager terminal, elevate privileges and install:5. Configure Kafka in KRaft Mode
Kafka 3.x’s KRaft protocol removes the need for ZooKeeper. Perform these steps:-
Generate a cluster ID
Copy the returned UUID (e.g.,
BMKCKvMMT64yxEZSmnTQ). -
Format the storage directory
-
Edit
config/kraft/server.propertiesand update:
Make sure to replace
<YOUR_EC2_PUBLIC_IP> with your EC2 instance’s actual public IP.6. Open Port 9092 in the Security Group
Allow external clients to reach Kafka’s default port:- In EC2 Console, select the instance → Security → Security groups.
- Under Inbound rules, click Edit inbound rules → Add rule:
- Type: Custom TCP
- Port: 9092
- Source: 0.0.0.0/0 (or restrict to your subnet)
- Description: Kafka broker
- Save rules.
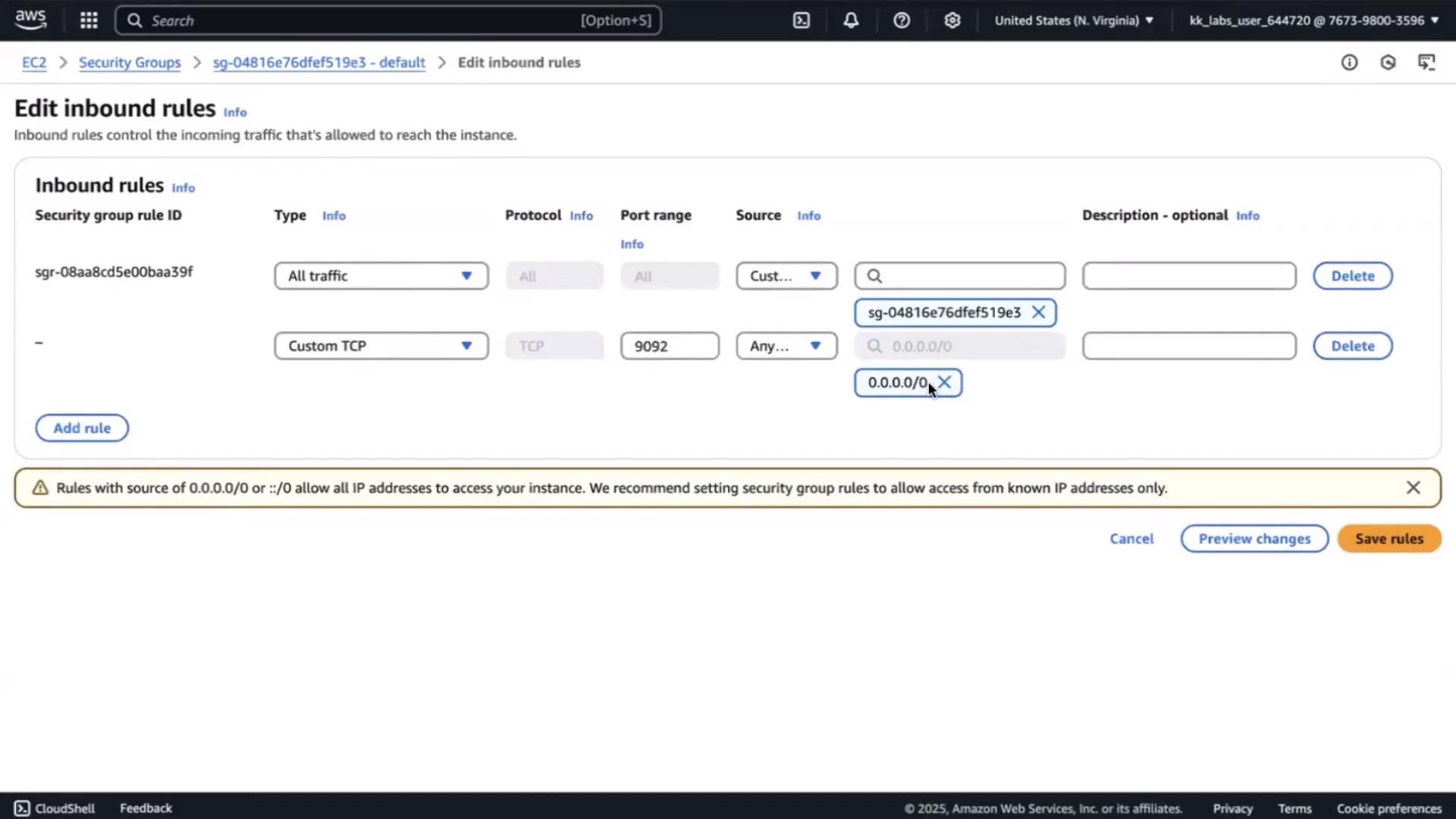
Opening port 9092 to
0.0.0.0/0 exposes your broker to the Internet. Limit the source to only trusted IP ranges when possible.7. Start Kafka and Create a Topic
Start the Kafka broker
Create a demo topic
Open a new Session Manager shell (keep the broker running):Congratulations! Your single-node Kafka broker on EC2 is now online and ready to accept messages.