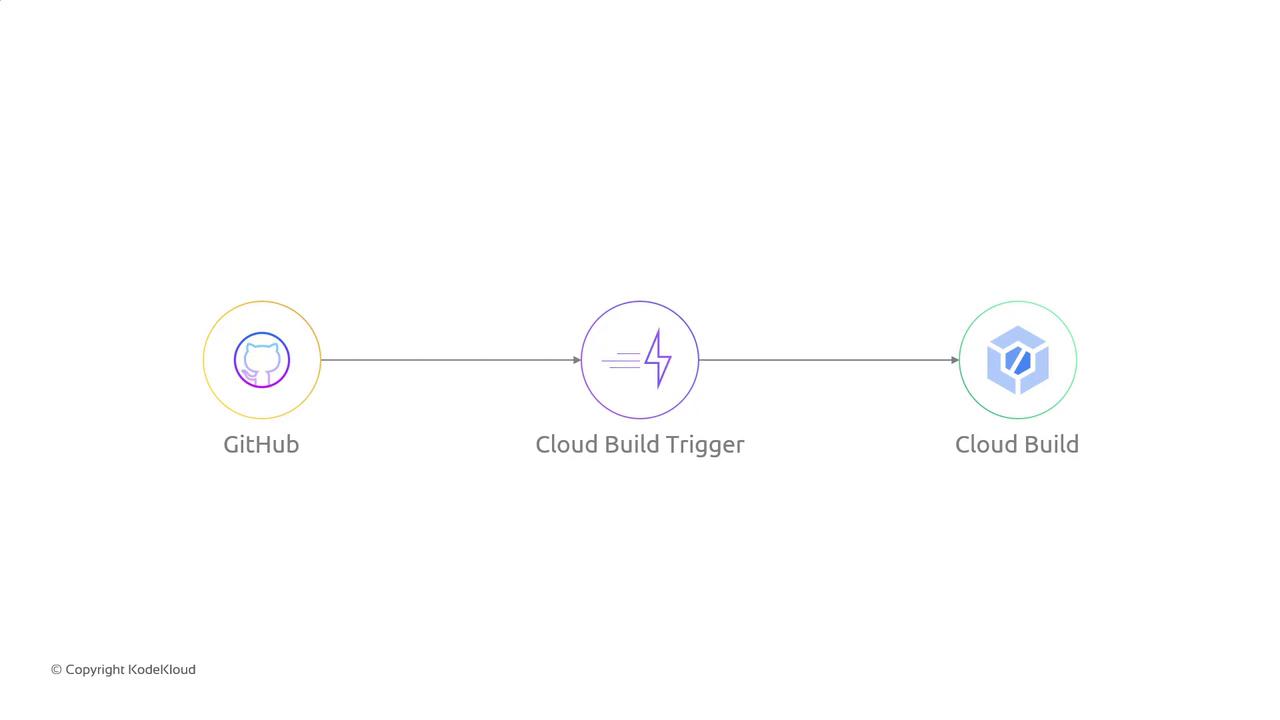
Why Use a Cloud Build Trigger?
In Jenkins, you configure webhooks to detect pushes or pull requests in GitHub. Cloud Build provides the same capability natively with Cloud Build triggers, which listen for repository events and kick off builds defined in yourcloudbuild.yaml.
Before you begin, make sure you’ve granted Cloud Build access to your GitHub repository. See Create and Manage Triggers for detailed steps.
Common Trigger Events
When creating a trigger, you specify which events should start a build. Typical events include:| Event Type | Description |
|---|---|
Push to main or master | Ideal for deploying from the primary branch |
| Push to a specific branch | Build feature or release branches on demand |
| Pull request creation/update | Test code before merging changes into protected branches |
How It Works
-
Define the trigger
In the Cloud Console or viagcloud, link your GitHub repo and select the event and branch filters. -
Provide your build configuration
Cloud Build looks for acloudbuild.yamlat the repo root. Each step runs in its own container image, in sequence: -
Trigger execution
When GitHub detects your specified event (e.g.,pushtomain), it notifies Cloud Build, which then runs your pipeline automatically.
Ensure your
cloudbuild.yaml is valid and located at the repository root. Otherwise, triggers will fail with a configuration error.Next Steps
- Configure and test your Cloud Build trigger.
- Monitor build history in the Cloud Console under Cloud Build > History.
- Integrate additional notifications or approvals as needed.