- A dedicated
developmentGit branch - A customized
cloudbuild.yamlfor development - A Cloud Build trigger that reacts to pushes on
development - Verification steps to confirm your
-devimage lands in Container Registry
1. Create and Switch to the development Branch
First, make sure your local main branch is up to date:
Use descriptive branch names like
development to clearly separate lifecycle stages.development:
2. Customize cloudbuild.yaml for Development
Your production pipeline builds, pushes, and deploys the image gcpdevops to the gcp-devops-prod namespace:
-dev) and namespace (gcp-devops-dev):
Configuration Comparison
| Attribute | Production | Development |
|---|---|---|
| Docker Tag | gcpdevops | gcpdevops-dev |
| GKE Namespace | gcp-devops-prod | gcp-devops-dev |
| Cloud Build Trigger | Branch: main | Branch: development |
3. Commit and Push Your Changes
4. Configure a Cloud Build Trigger for development
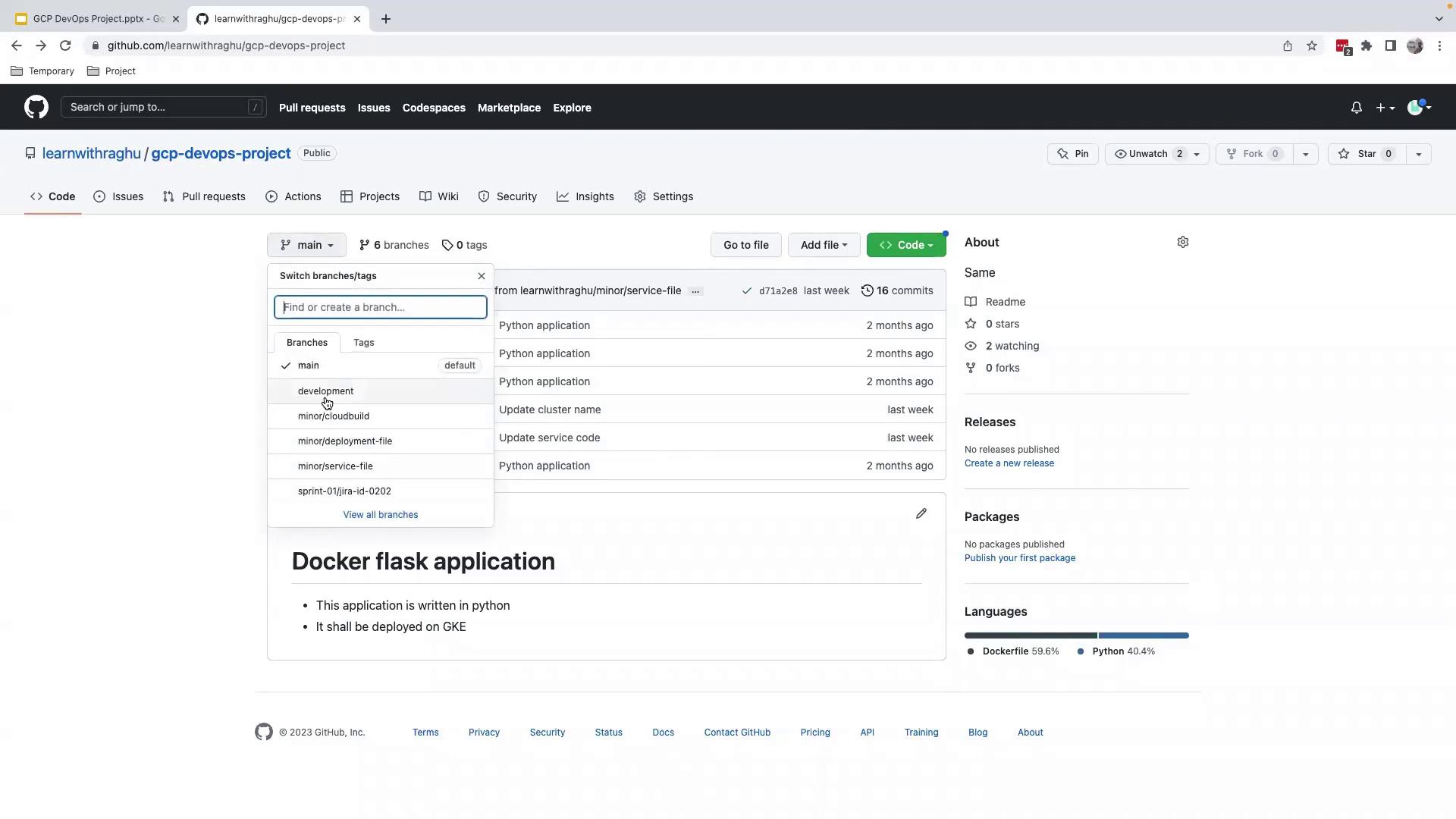
4.1 Select the development Branch in GitHub
- Go to your GitHub repository.
- Open the Branch dropdown and choose
development.
4.2 Create the Trigger in Google Cloud Build
- In the GCP Console, navigate to Cloud Build > Triggers.
- Click Create Trigger.
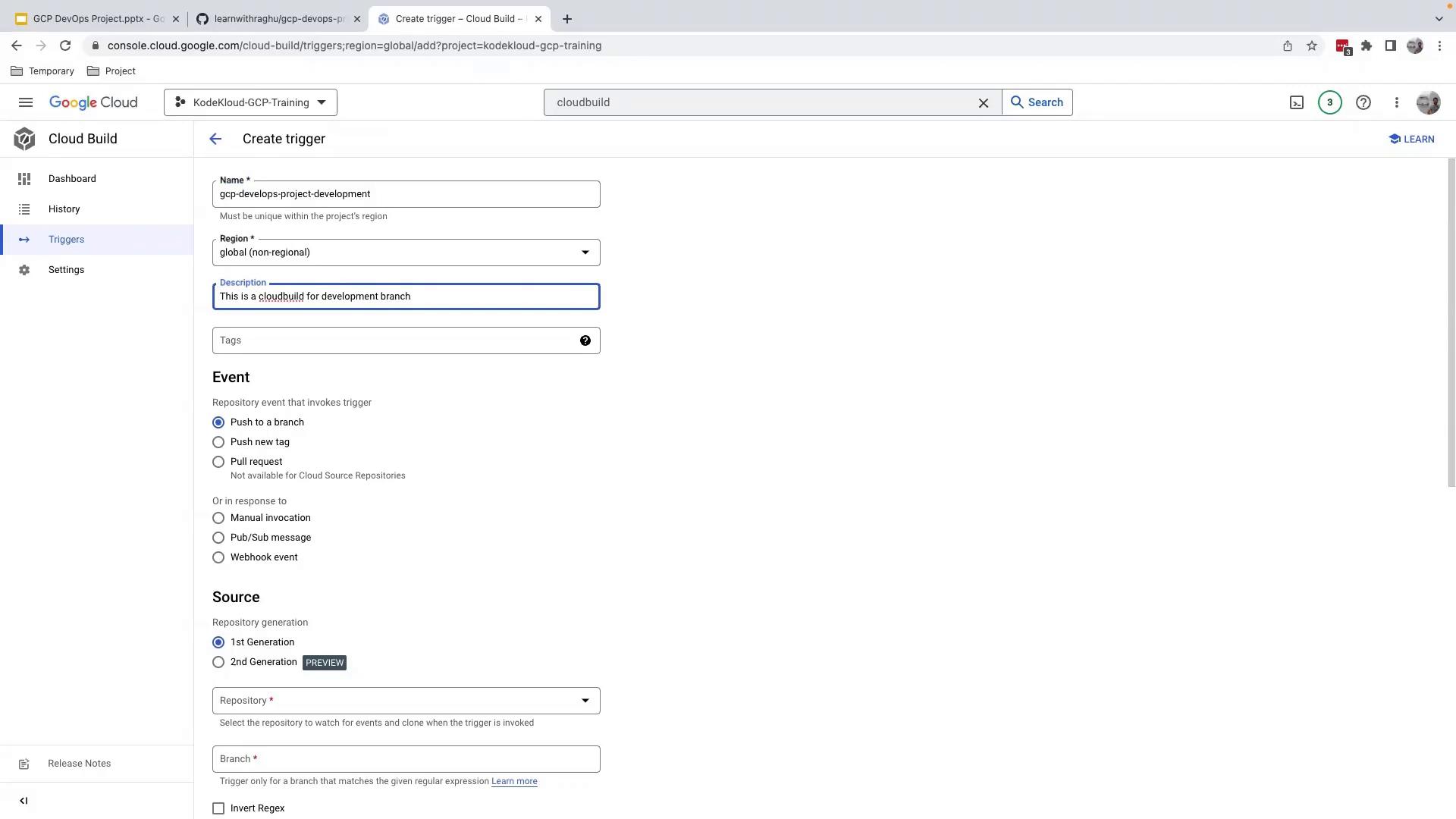
- Fill out the Create trigger form:
- Name:
gcp-devops-project-development - Event: Push to a branch
- Source repository: Your GitHub repo
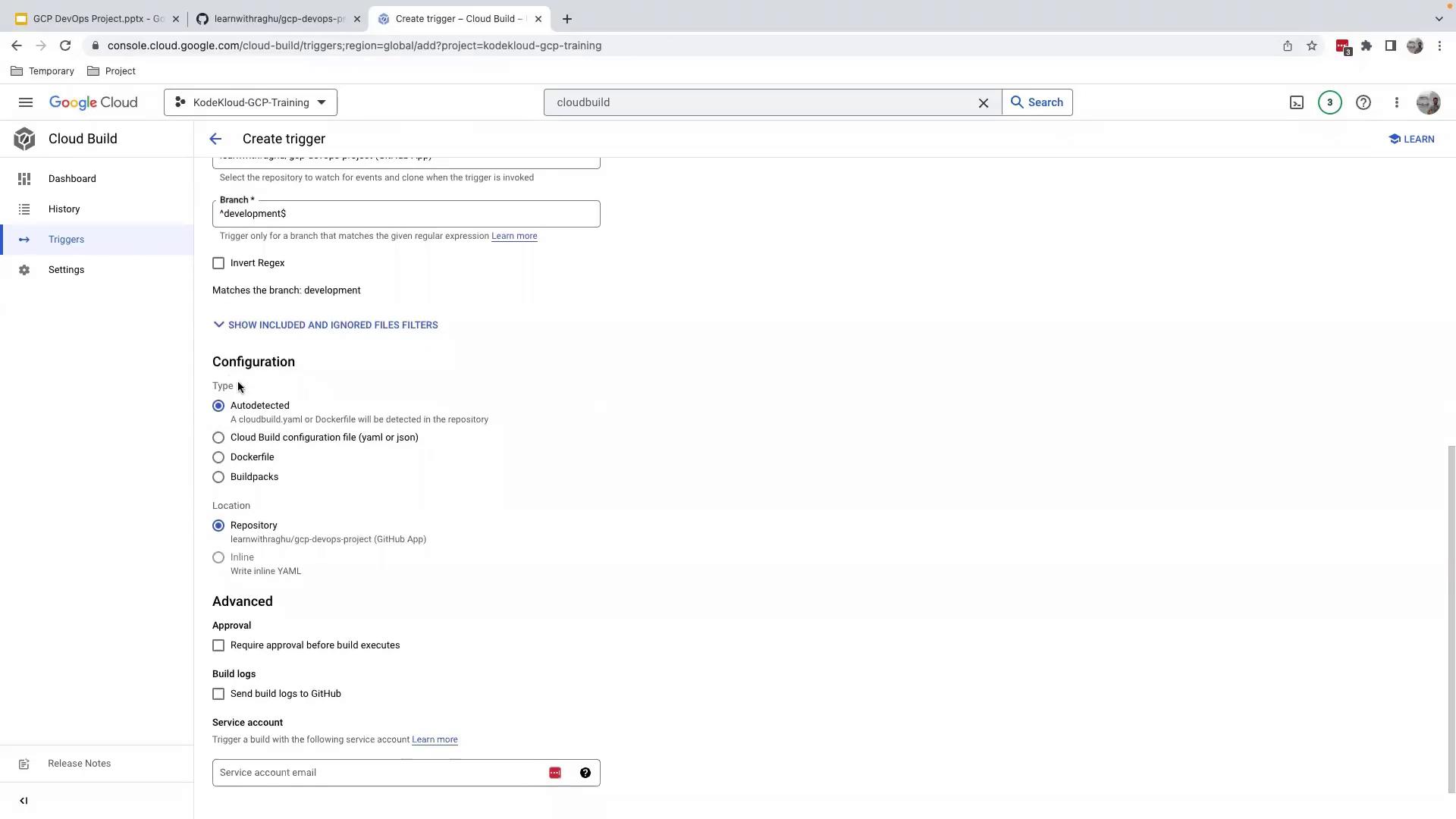
- Branch:
^development$ - Build configuration: Cloud Build configuration file (
cloudbuild.yaml)
- Name:
- (Optional) Expand Advanced settings to adjust substitutions, timeouts, or notifications.
- Click Create to finalize.
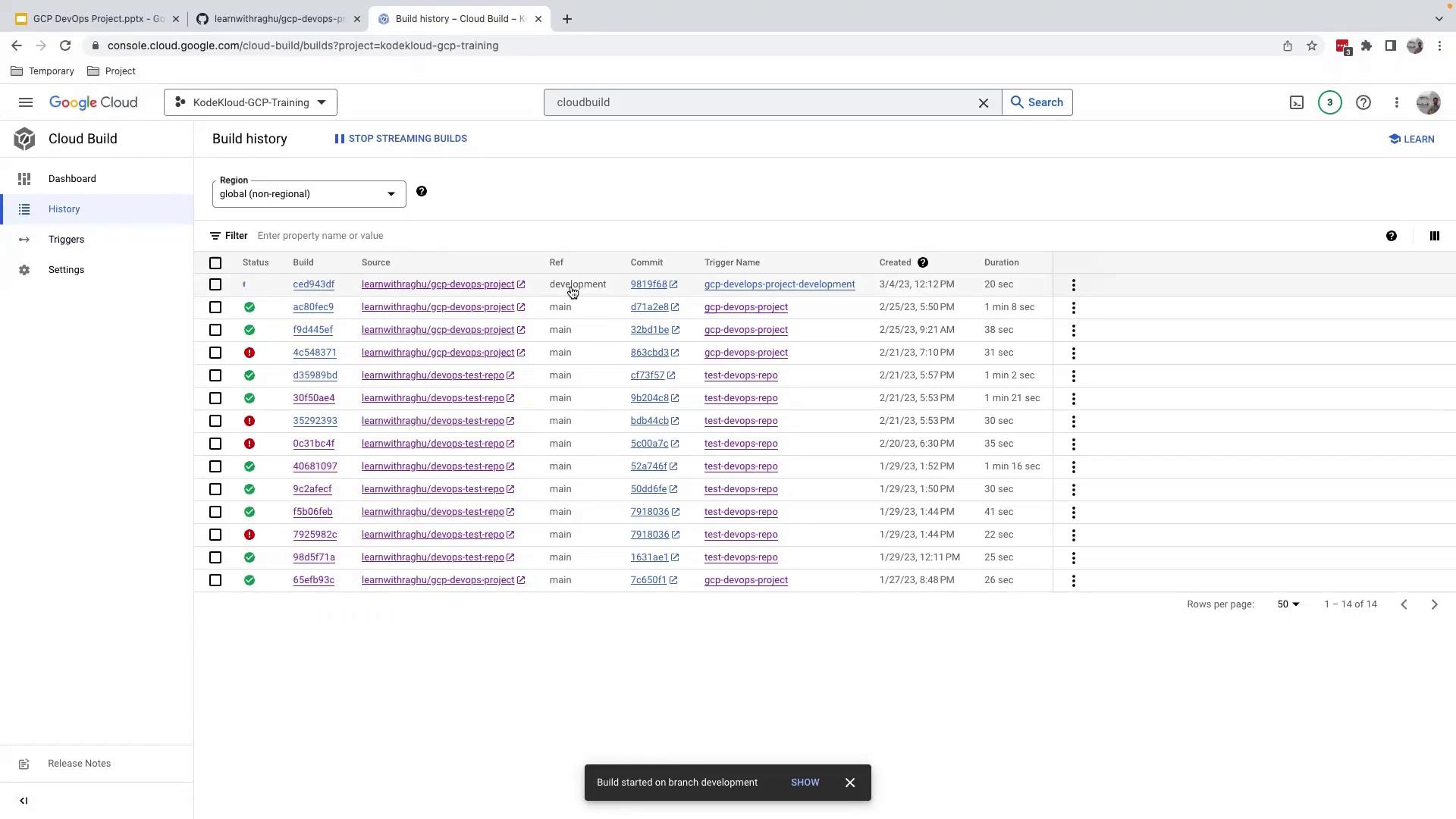
4.3 Run and Verify the Trigger
- Manual Trigger: In Cloud Build > Triggers, click Run next to
gcp-devops-project-development. - Monitor: Go to Cloud Build > History to see builds initiated by the
developmentbranch.
- Since the
gcp-devops-devnamespace likely doesn’t exist yet, the deploy step will report a failure (this is expected at this stage):

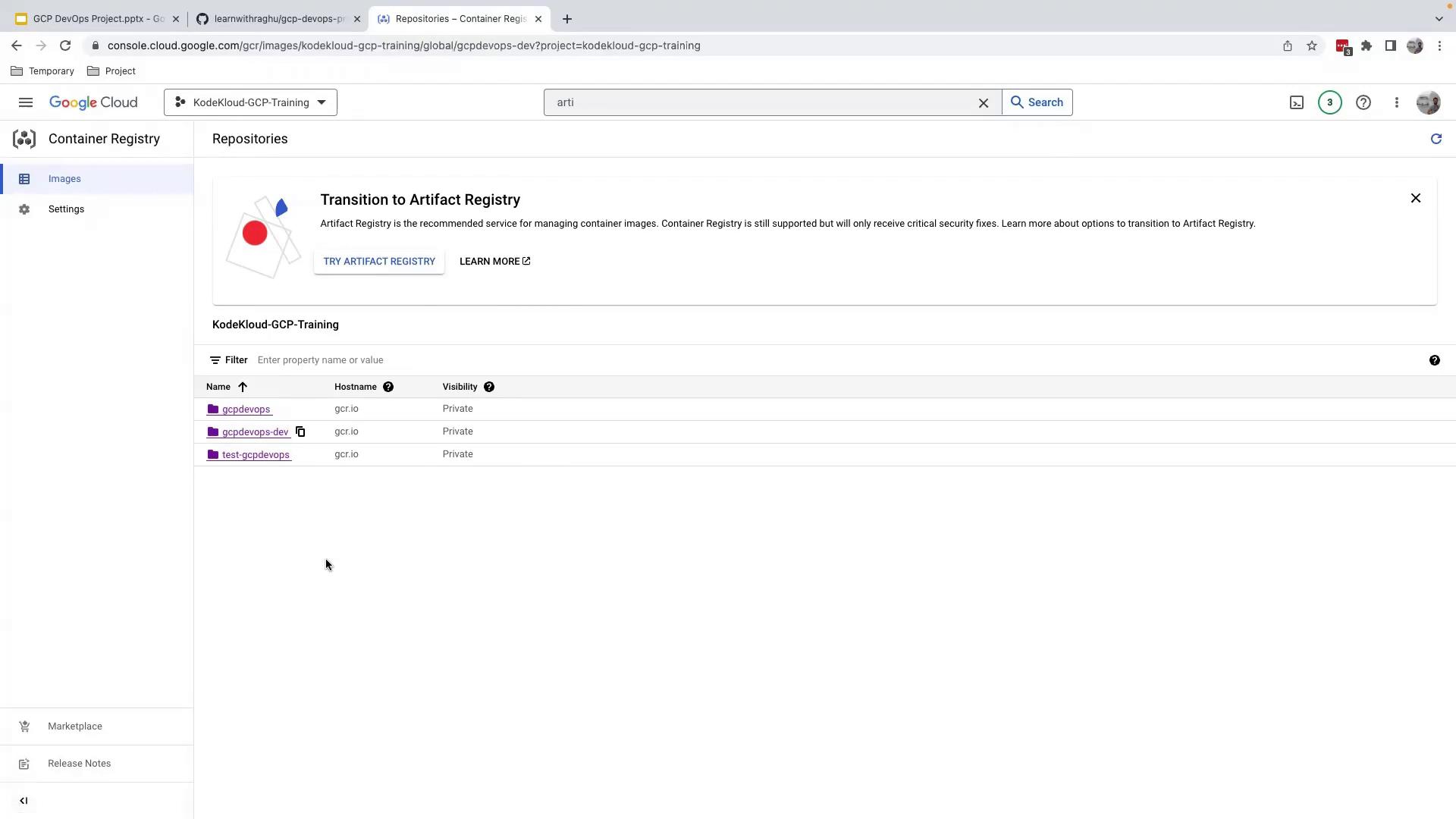
5. Verify the Development Image in Registry
Navigate to Artifact Registry or Container Registry in the GCP Console. Undergcr.io, confirm that gcpdevops-dev is present:
Congratulations! Your Cloud Build trigger for the
development branch is live. In the next lesson, you’ll learn how to create the dev namespace and finalize automatic deployments.