Kubernetes Cluster Overview
A Kubernetes cluster has two main parts:- Control Plane: Manages the cluster’s state and schedules workloads.
- Worker Nodes: Run containerized applications in Pods.
Control Plane Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud Controller Manager | Integrates cloud-provider APIs and isolates cloud-specific logic from Kubernetes. |
| Kube Controller Manager | Runs controllers like Node, Job, EndpointSlice, and ServiceAccount controllers. |
| Kube API Server | Exposes the Kubernetes API and serves as the control plane’s front end. |
| etcd | A distributed, highly available key-value store holding all cluster data. |
| Kube Scheduler | Assigns newly created Pods to appropriate nodes based on resource requirements. |
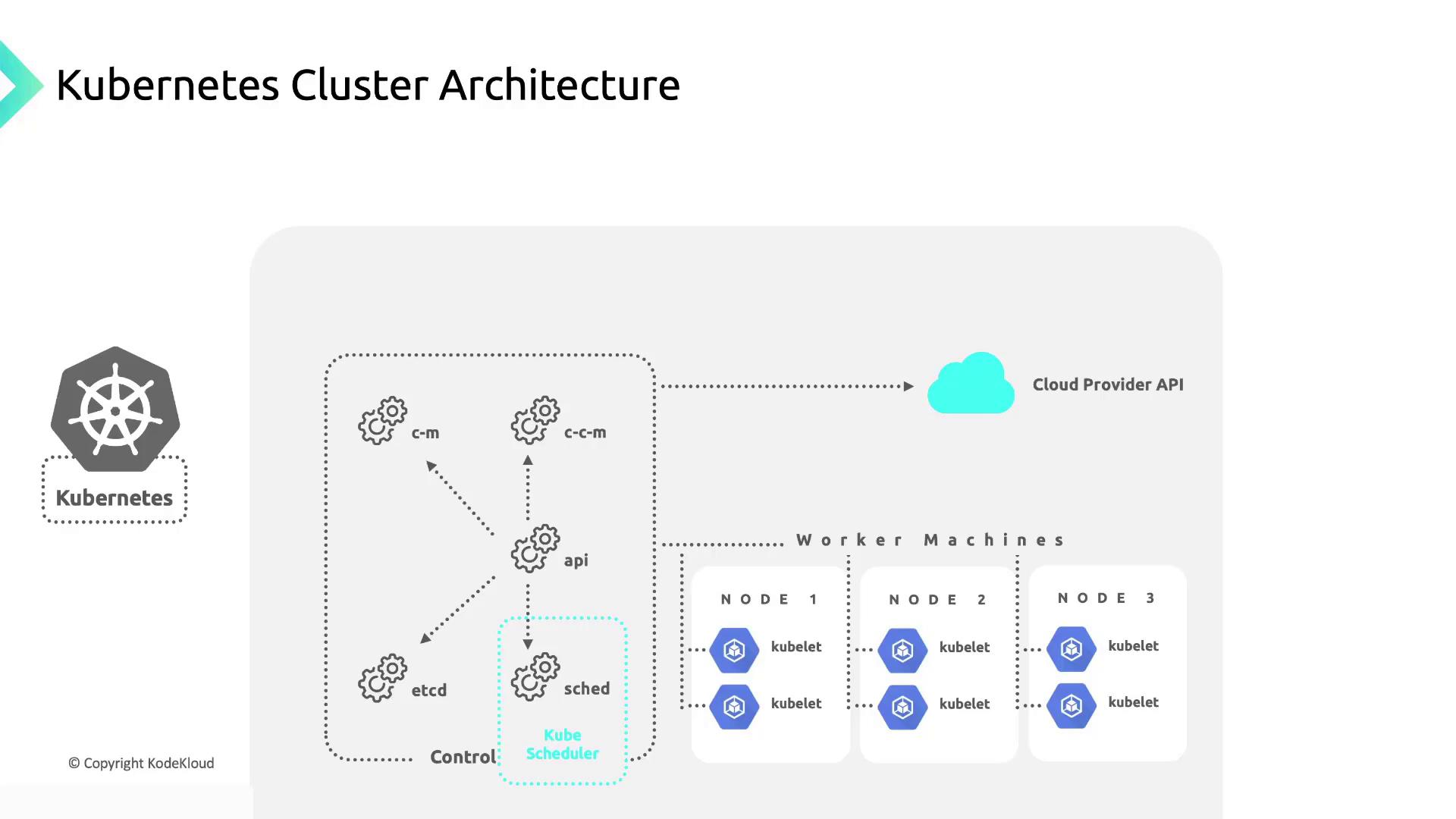
In a vanilla Kubernetes setup, you must provision and manage your own worker nodes—Kubernetes does not handle node creation.
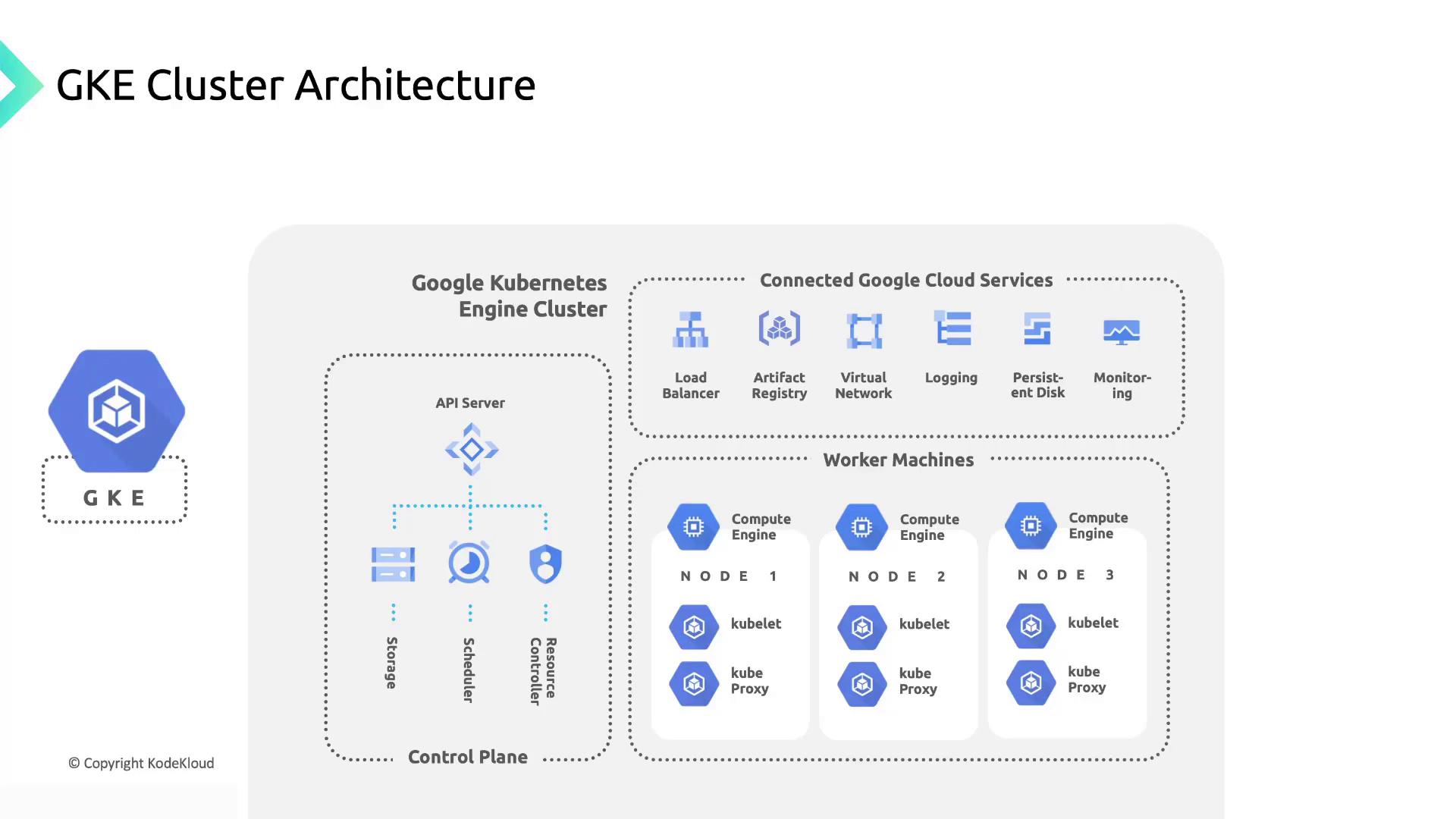
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Cluster Architecture
GKE simplifies cluster operations by managing both the control plane and worker nodes. It handles provisioning, upgrades, and system component maintenance.Managed Control Plane
GKE provisions and operates your control plane components on Google Cloud. You get a stable API endpoint forkubectl operations while GKE handles:
- Automatic upgrades for security patches and version updates
- High availability configuration across zones
- Monitoring and logging integration
Automated Node Management
GKE launches Google Compute Engine VMs as worker nodes and configures:- kubelet: Node agent that ensures containers are running
- kube-proxy: Maintains network rules for Pod communication
- DaemonSet Pods: System containers for logging, monitoring, and networking
Node Pools
Node pools are groups of nodes sharing the same machine type, labels, and autoscaling settings. Use multiple node pools to:- Optimize cost by mixing CPU-optimized and memory-optimized VMs
- Run specialized workloads on nodes with GPU or high-memory instances
- Roll out updates with minimal disruption
In Standard mode, you’re responsible for node upgrades and autoscaling. Plan your maintenance windows and cluster autoscaler settings accordingly.
Integration with Google Cloud Services
GKE seamlessly connects to other Google Cloud services:- Pulls system container images from Google Cloud Artifact Registry
- Exports logs to Cloud Logging and metrics to Cloud Monitoring
- Leverages VPC-native networking for Pod-to-Pod and Pod-to-service communication
Cluster Modes: Autopilot vs. Standard
| Mode | Control Plane Management | Node Management |
|---|---|---|
| Autopilot | Fully managed by GKE | Nodes provisioned & scaled automatically |
| Standard | Managed by GKE | Nodes provisioned by user |