- Architect and provision GKE clusters
- Configure networking and integrate with Cloud services
- Deploy applications, manage secrets, and optimize resource usage
- Monitor, log, and perform cluster upgrades
- Implement autoscaling, load balancing, and high availability
Key Topics
-
GKE Architecture & Cluster Creation
Examine the control plane versus data plane components, and create clusters via thegcloudCLI or Cloud Console. -
Networking & Service Integration
Configure VPCs, subnets, and firewall rules; integrate with Cloud Load Balancing, Cloud DNS, and other managed services. -
Application Deployment & Management
Explore rolling updates, canary releases, Secrets, ConfigMaps, and best practices for resource requests and limits. -
Administration & Maintenance
Use Cloud Monitoring for resource metrics, Cloud Logging for logs aggregation, and automate cluster upgrades.
Scaling & Load Balancing
GKE provides multiple strategies to handle varying workloads and traffic patterns:| Feature | Purpose | Example Command |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) | Scales pods based on CPU, memory, or custom metrics | kubectl autoscale deployment webapp --cpu-percent=75 --min=2 --max=10 |
| Cluster Autoscaler | Adjusts node pool size according to pending pod demands | gcloud container clusters update my-cluster --enable-autoscaling --min-nodes=1 --max-nodes=5 --node-pool default-pool |
| Cloud Load Balancing | Distributes traffic globally or regionally across pods | Configure an HTTP(S) load balancer in the Console or with gcloud compute url-maps and backend services |
Delivery Framework
This lesson is divided into modules, each covering a core GKE topic. To deepen your understanding, refer to:- GKE Documentation for official guides
- Google Cloud Community: GKE for Q&A and discussions
- Community blogs and tutorials on advanced patterns and use cases
Hands-on practice is crucial. We recommend following along in a Google Cloud project with billing enabled and the Google Cloud SDK installed.
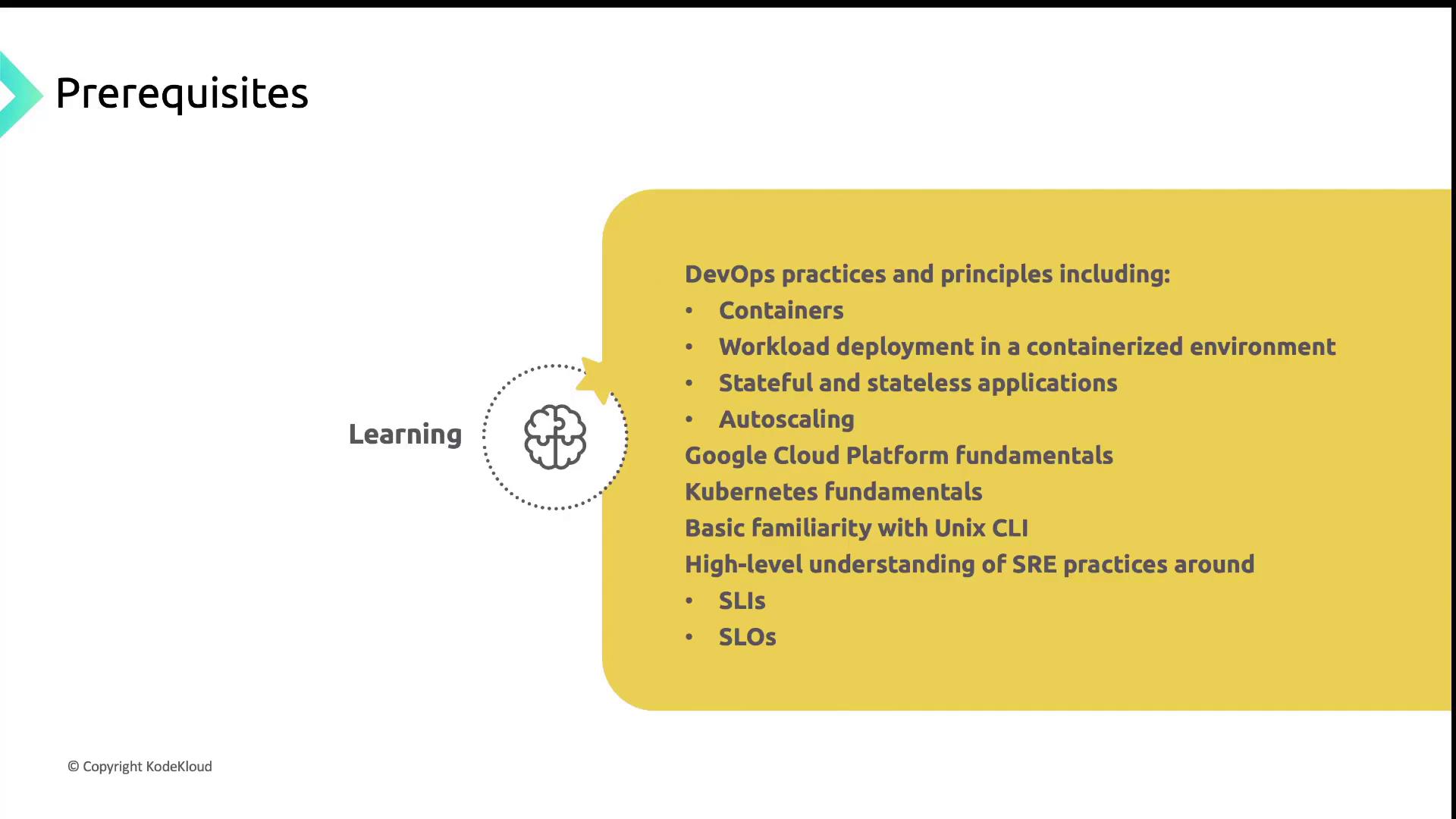
Prerequisites
Ensure you have the following before starting:- Strong grasp of DevOps principles (CI/CD, containers, deployments)
- Experience with Google Cloud Platform core services (Compute Engine, Networking)
- Familiarity with Kubernetes basics (Pods, Deployments, Services)
- Comfort using the Unix/Linux CLI and shell scripting
- Understanding of SRE concepts such as SLIs, SLOs, and error budgets
Skipping these prerequisites may slow your progress when tackling advanced GKE features.
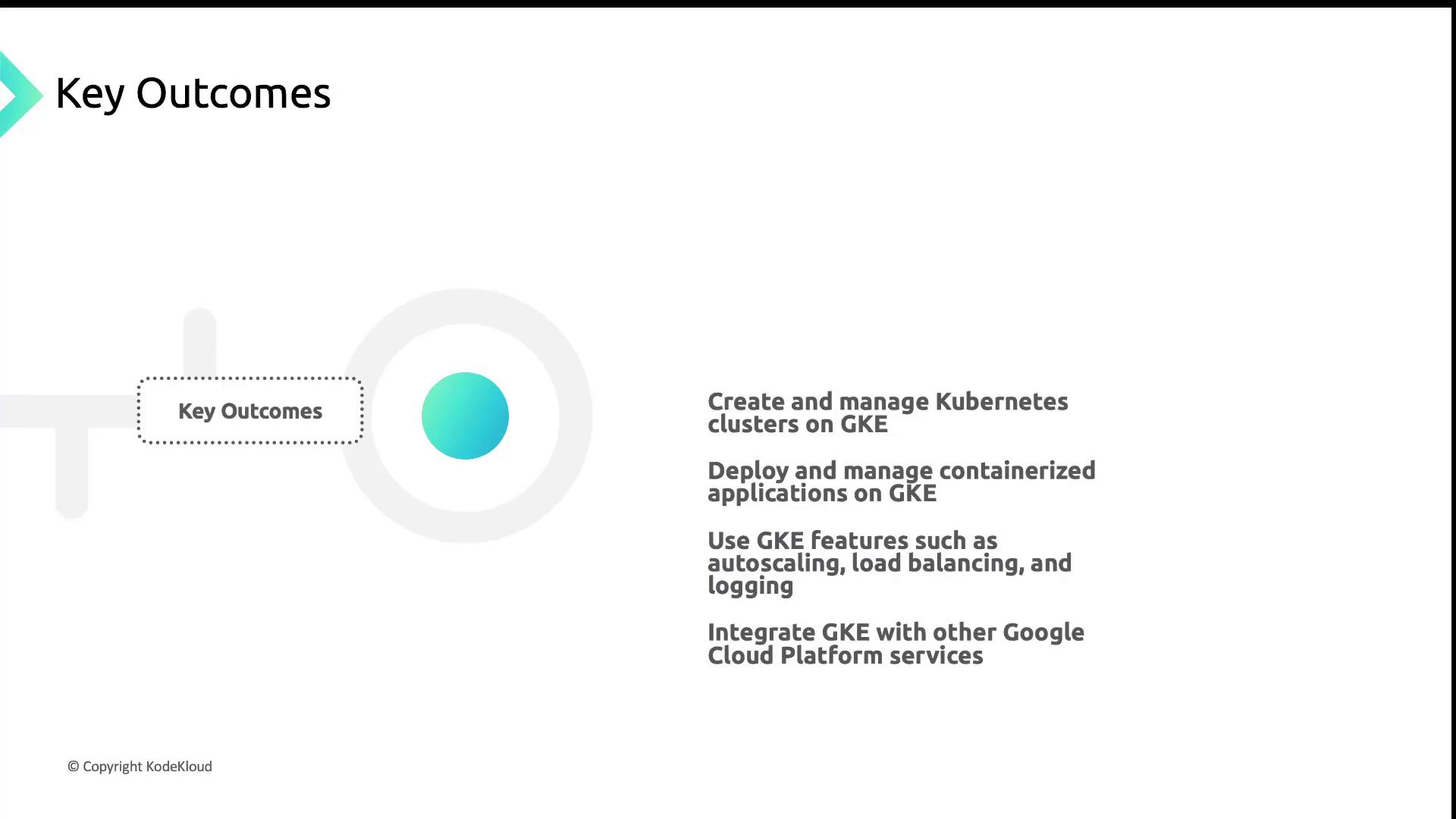
Expected Outcomes
After completing this lesson, you will be able to:- Provision and manage GKE clusters via CLI and Console
- Deploy, update, and observe containerized workloads
- Configure autoscaling, load balancing, and centralized logging
- Integrate applications with Google Cloud services like Pub/Sub and Cloud SQL
- Design a secure, highly available, and cost-effective GKE environment