GitOps with FluxCD
Helm Controller and OCI Registry
DEMO Push Kubernetes Manifest to OCI Registry
In this walkthrough, we’ll package Kubernetes manifests as an OCI artifact and push them to GitHub Container Registry (GHCR). Flux can then pull and deploy these manifests directly.
Prerequisites
You need a GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT) with permissions to manage packages and your repository:
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
repo | Full control of private repositories |
write:packages | Upload and publish packages |
delete:packages | Remove packages from GHCR |
Note
If you already have a PAT, update it to include repo, write:packages, and delete:packages.
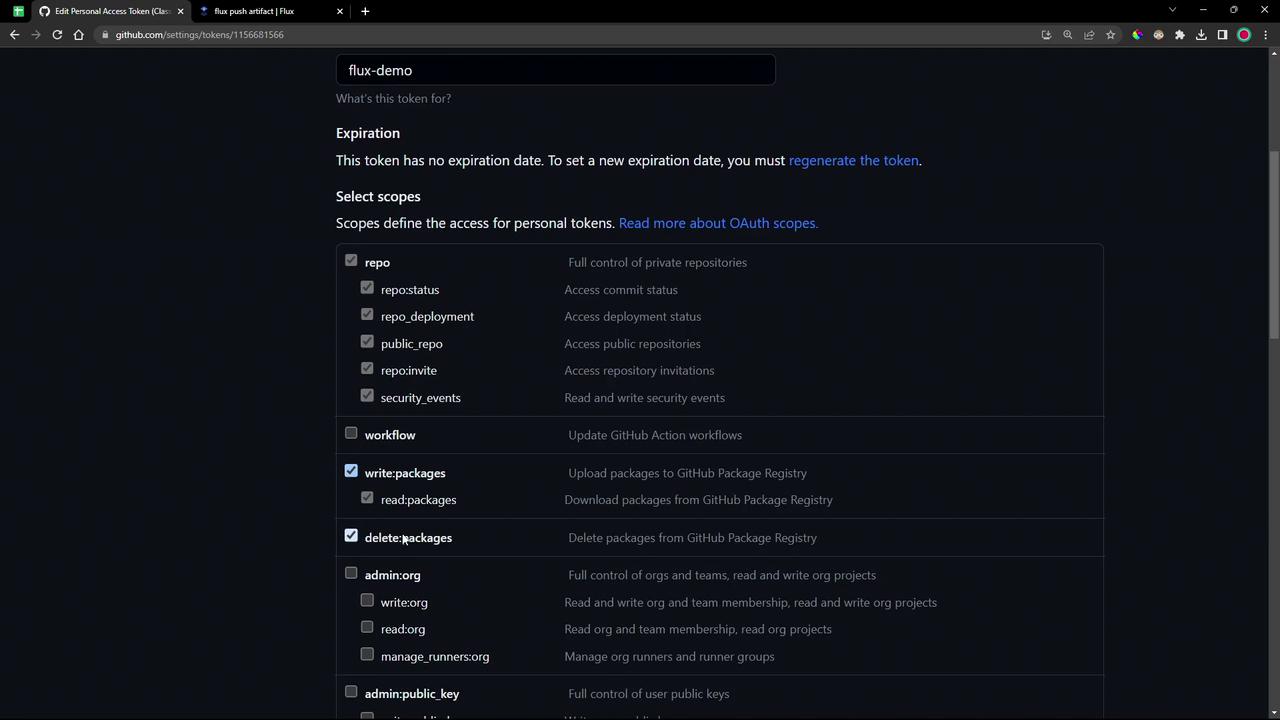
Once the correct scopes are selected, click Update Token and save the token value securely.
1. Prepare the Local Repository
Navigate to your source directory and switch to the demo branch:
cd ~/bb-app-source git checkout 7-demoIf you see a “dubious ownership” error on Ubuntu, mark it as safe:
git config --global --add safe.directory "$(pwd)" git checkout 7-demoEnter the versioned folder and inspect its contents:
cd 7.7.0 sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y tree treeYou should see the
manifests/directory alongside YAML files.
2. Log in to GHCR
Use Docker to authenticate against GHCR. Replace <username> with your GitHub handle:
docker login ghcr.io --username <username>
# When prompted, paste your PAT
On success, you’ll see:
Login succeeded
3. Push the OCI Artifact
Flux’s push artifact command packages a directory (or file) as an OCI artifact and uploads it to a registry.
First, set reusable variables and then run:
# Generate tags and metadata
REF=$(git rev-parse --short HEAD)
SRC=$(git config --get remote.origin.url)
TAG="7.7.0-${REF}"
REPO="oci://ghcr.io/<username>/bb-app:${TAG}"
# Push manifests as an OCI artifact
flux push artifact "${REPO}" \
--path="./manifests" \
--source="${SRC}" \
--revision="${TAG}"
What happens:
- Flux reads your GHCR credentials from
~/.docker/config.json - It tars up
./manifests - Uploads to
ghcr.io/<username>/bb-app:7.7.0-<short-git-sha> - Attaches the Git remote URL and revision metadata
A successful push shows:
pushing artifact to ghcr.io/<username>/bb-app@sha256:<digest>
artifact successfully pushed to ghcr
4. Verify the Package
- Go to your GitHub repo’s Packages tab and refresh.
- You should see
bb-applisted under private packages.
You can also confirm locally:
docker pull ghcr.io/<username>/bb-app:7.7.0-<short-git-sha>
Note
Flux requires a Kubernetes imagePullSecret to authenticate when pulling OCI artifacts. We’ll cover secret creation in a later module.
Next Steps
In the following lesson, we will package and push Helm charts to an OCI registry.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content