In this tutorial, you’ll configure the Flux Notification Controller to automatically send GitOps alerts to a Slack channel. By the end, you will have a working Slack App, Flux provider, and alert definitions driving real-time notifications.
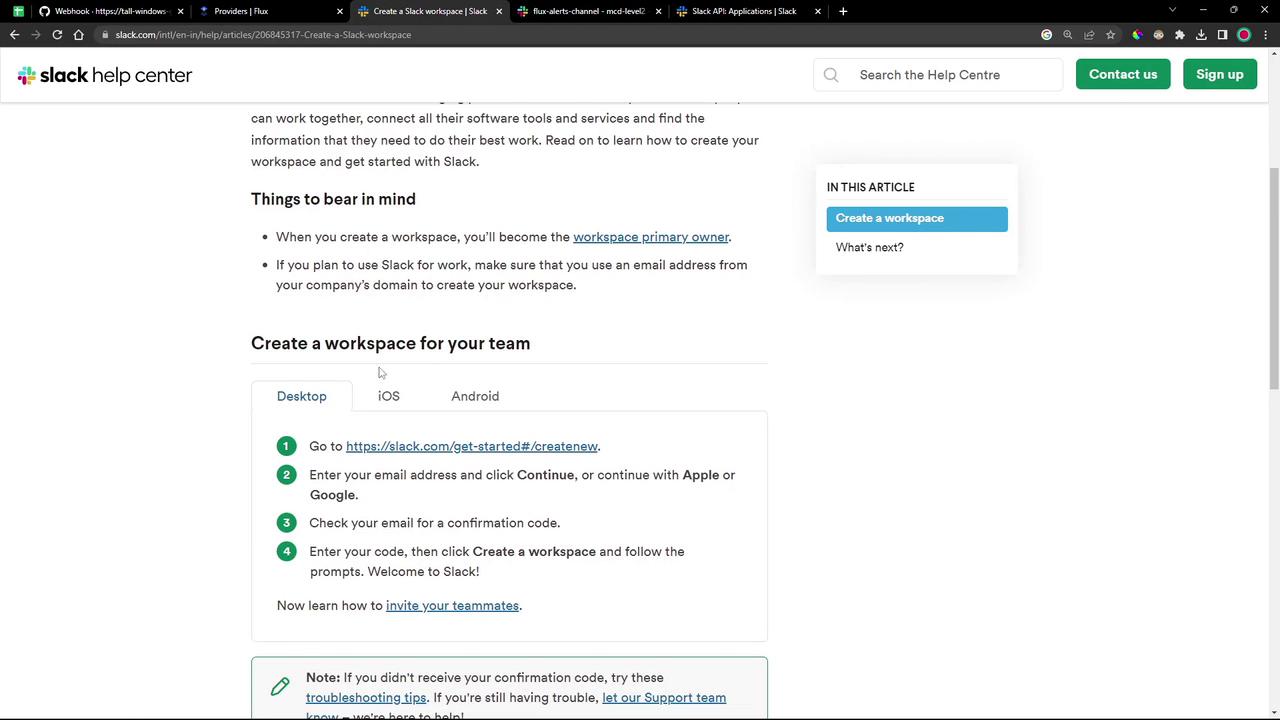
1. Prepare Your Slack Workspace and Channel If you don’t have a Slack workspace yet, create one by following Slack’s Help Center instructions :
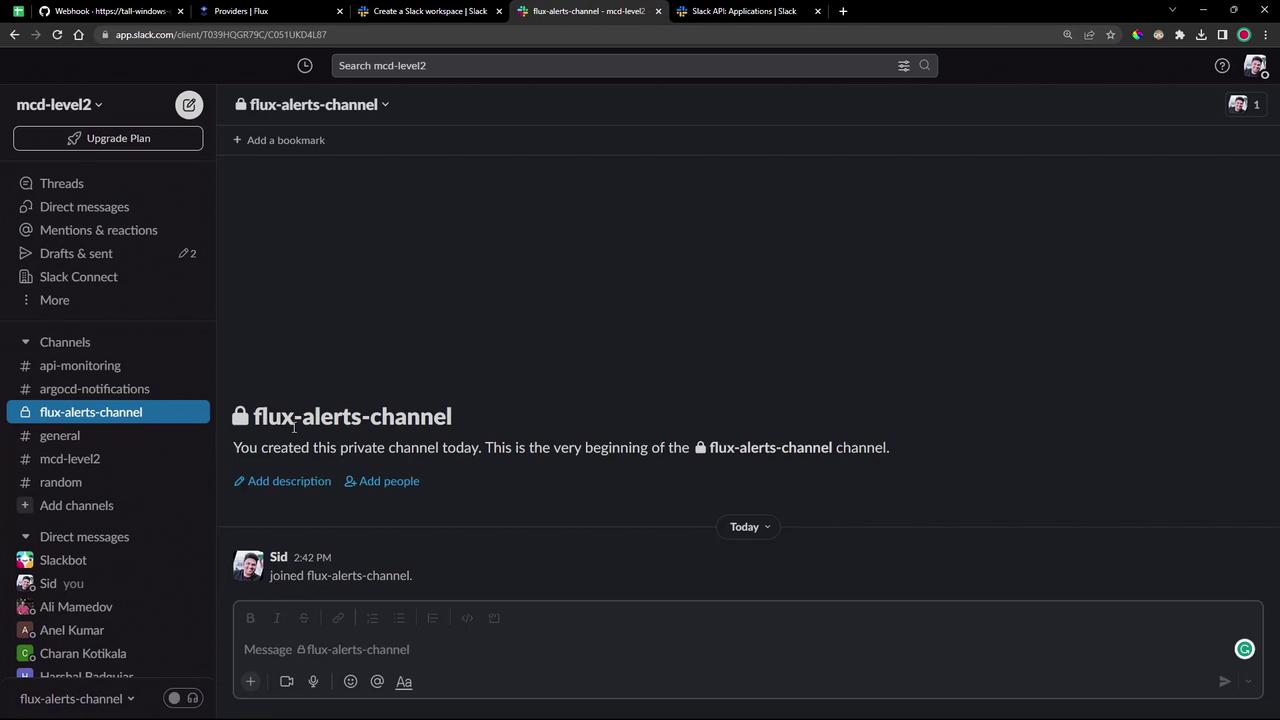
Once your workspace is ready, create a new channel (public or private) for Flux alerts. In this demo, we’ll use flux-alerts-channel:
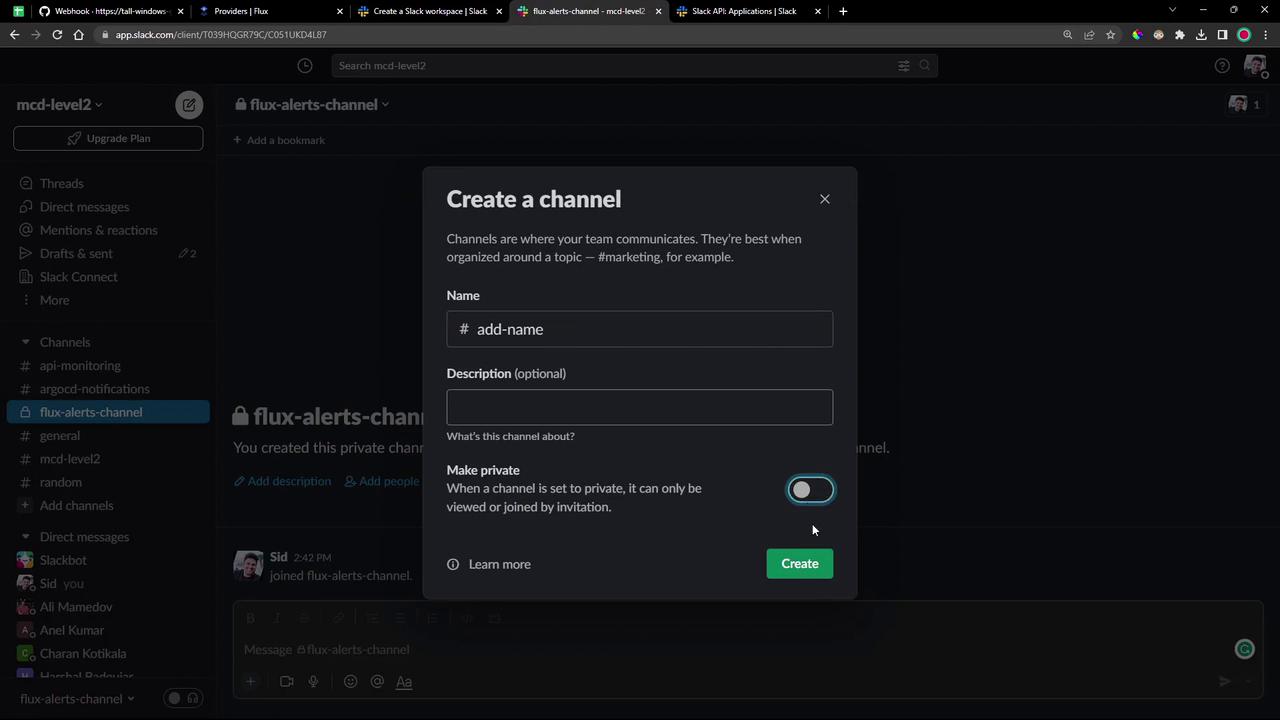
If you need to customize the channel settings, use the channel-creation pop-up:
2.1 Create the Slack App
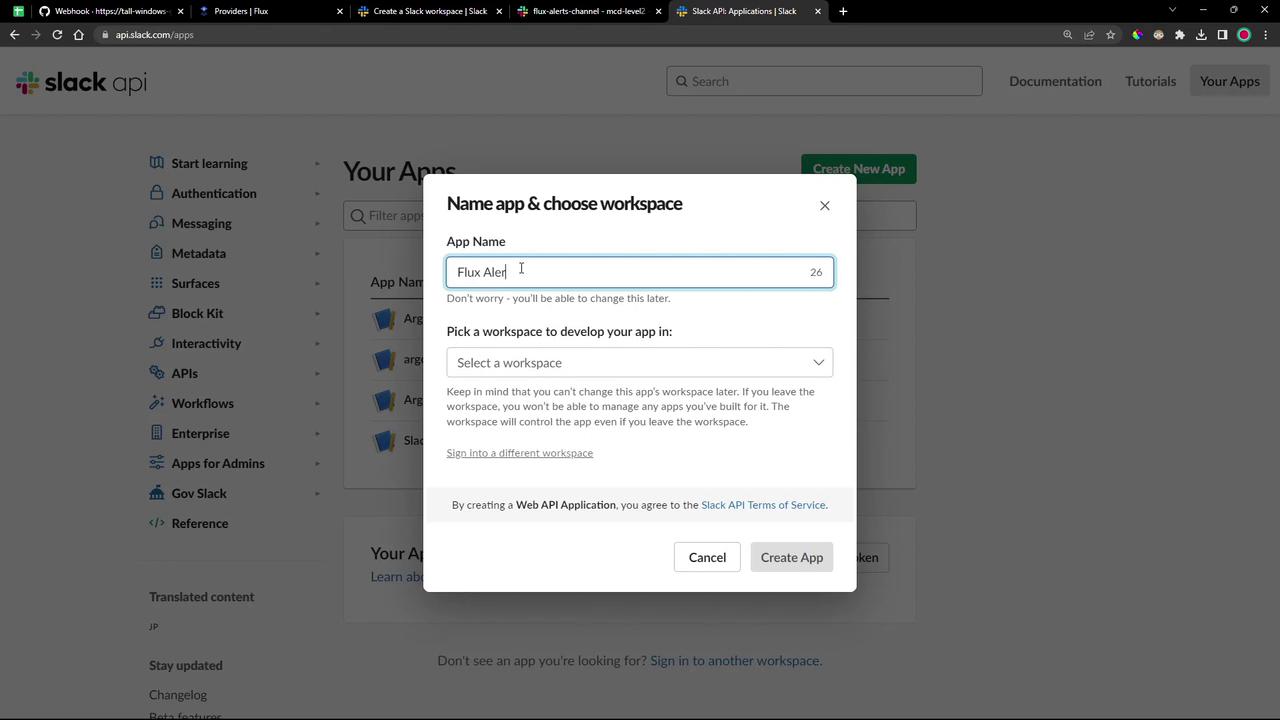
Go to the Slack API dashboard .
Click Create an App , give it a name (e.g., Flux Alerts Application ), and select your workspace.
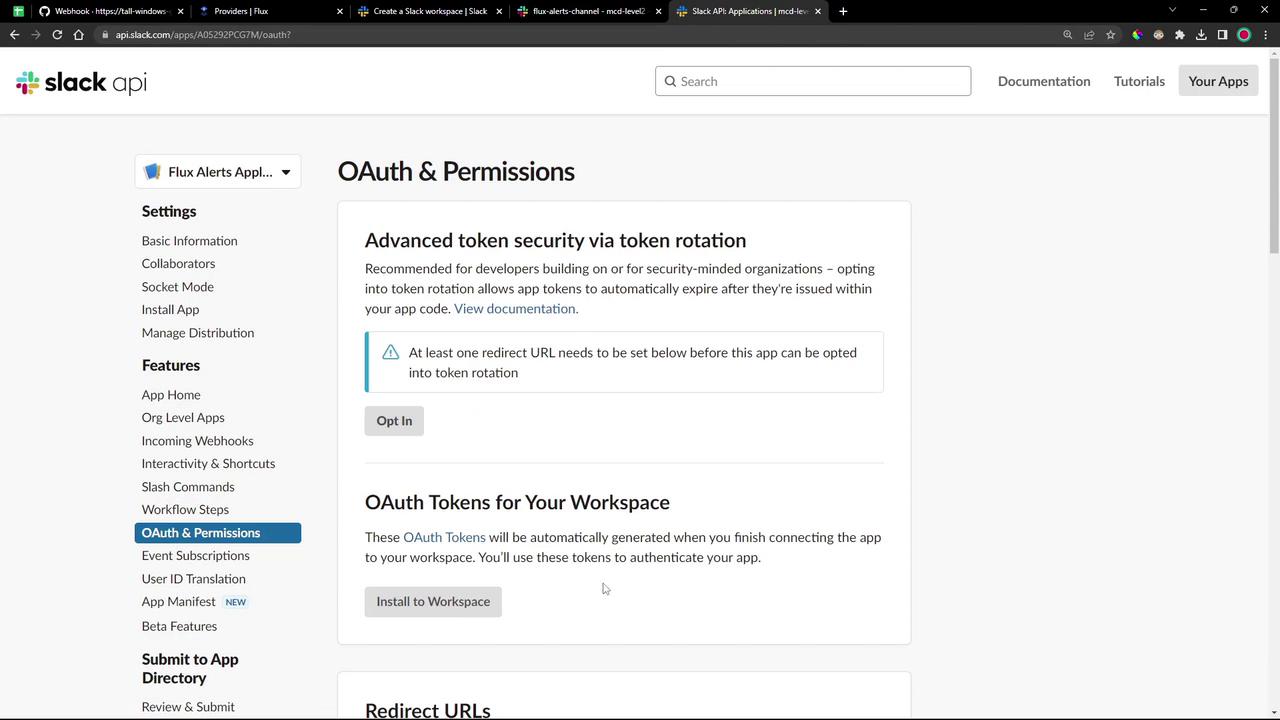
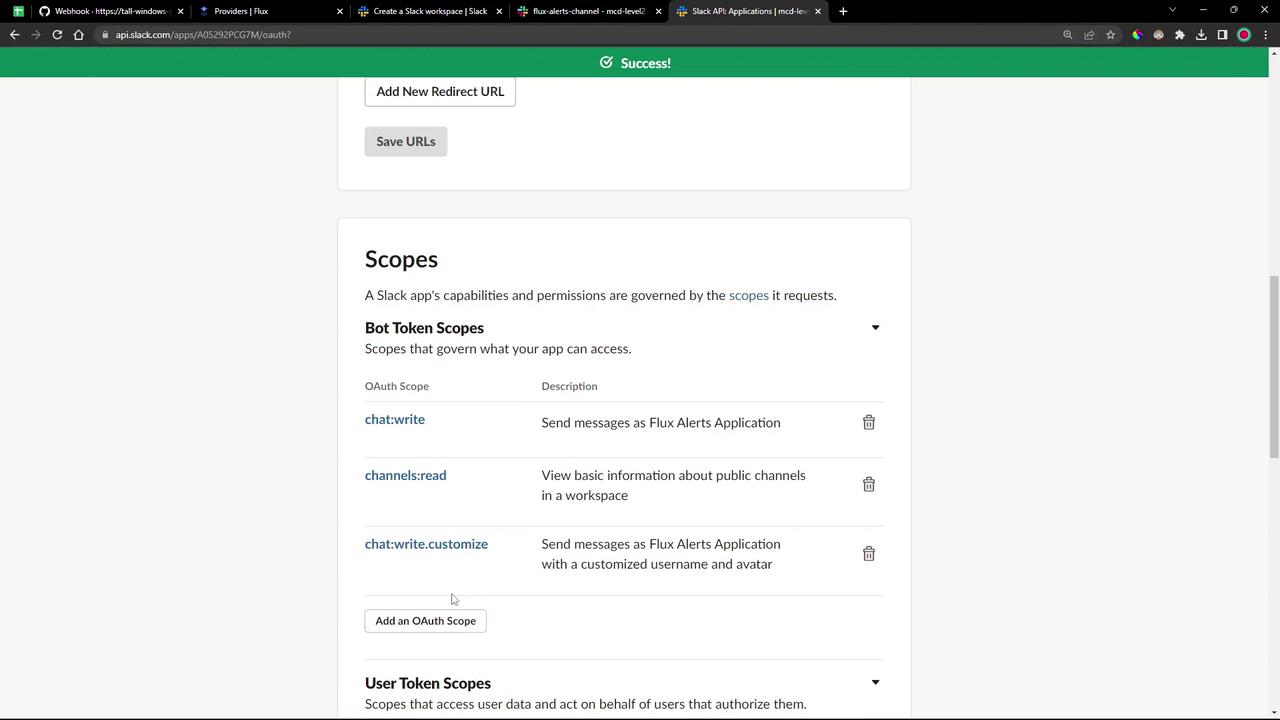
Under Features → OAuth & Permissions , add the following Bot Token Scopes :
Scope Description chat:write Send messages as the app channels:read Read public channel information chat:write.customize Send messages with a custom avatar
After adding the scopes, install the app:
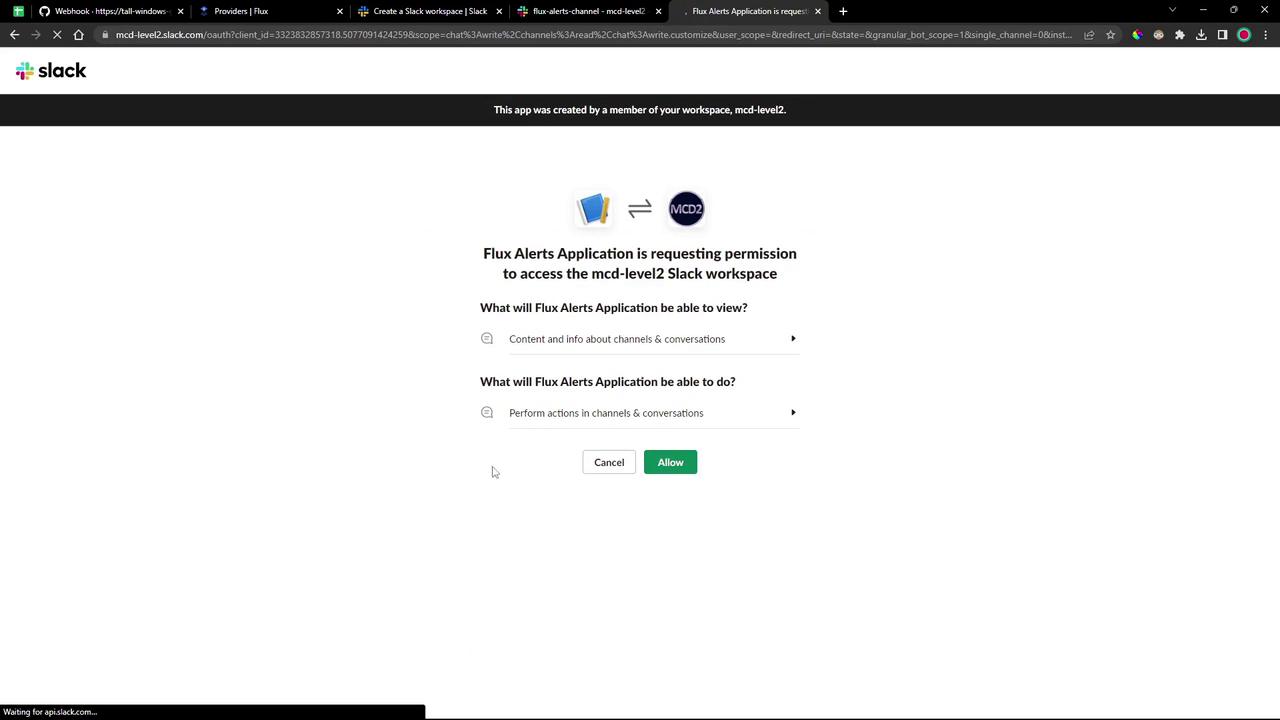
On the authorization screen, click Allow :
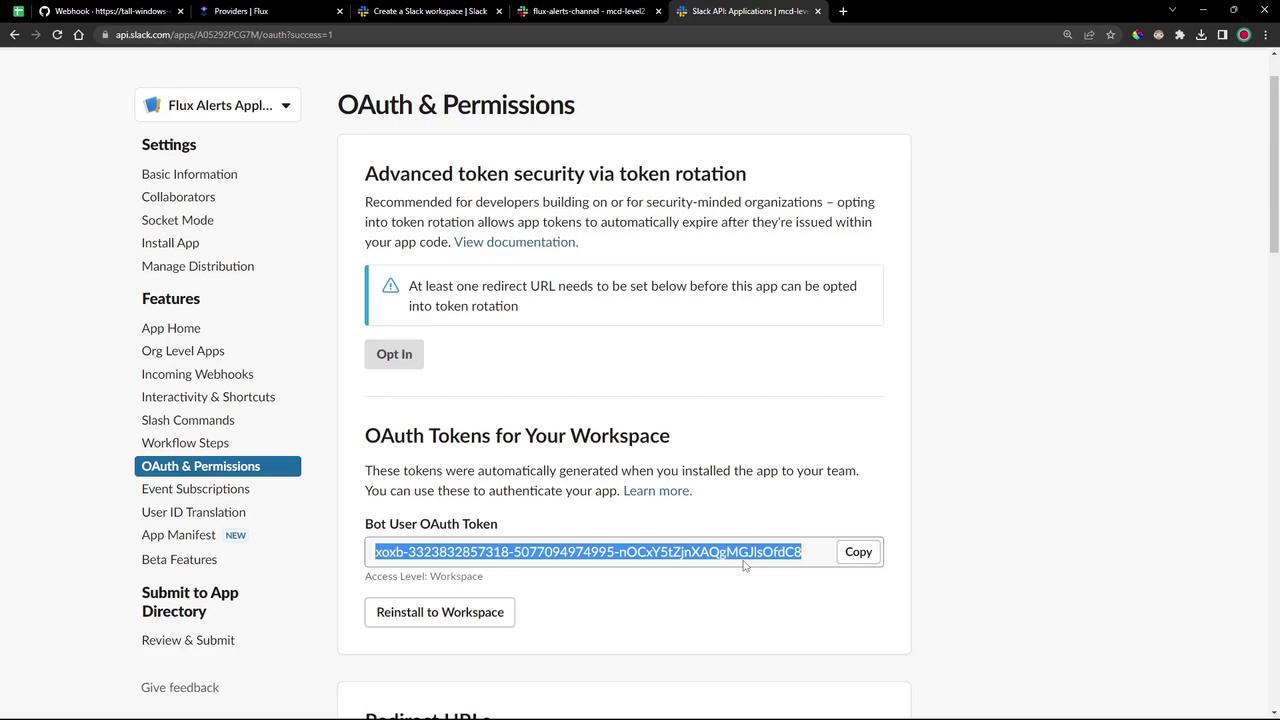
Once installed, copy the Bot User OAuth Token from the OAuth & Permissions page.
Keep your Bot User OAuth Token secure. Treat it like any sensitive credential.
2.3 Invite the Bot to Your Alert Channel If your alerts channel is private, you must add the app as a member:
Once invited, you’ll see a confirmation in the channel:
3.1 Create the Slack Bot Token Secret Store your Slack Bot Token in the flux-system namespace:
kubectl -n flux-system create secret generic slack-bot-token \ --from-literal=token=xoxb-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Replace xoxb-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx with your actual Bot User OAuth Token.
3.2 Define the Slack Provider Flux’s Provider API lets you specify how notifications are sent. See Flux Notification Providers :
Option A: Apply a YAML manifest notification-provider-slack.yaml:apiVersion : notification.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2 kind : Provider metadata : name : notification-provider-slack namespace : flux-system spec : type : slack channel : flux-alerts-channel address : https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage secretRef : name : slack-bot-token username : flux-bot
Apply it:
kubectl -n flux-system apply -f notification-provider-slack.yaml
Option B: Generate with the Flux CLI flux create provider notification slack notification-provider-slack \ --channel flux-alerts-channel \ --username flux-bot \ --secret-ref slack-bot-token \ --address https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage \ --export > notification-provider-slack.yaml
3.3 Define an Alert Alerts let you filter events by severity and resource type before sending them via your provider.
Create notification-alert-slack.yaml:
apiVersion : notification.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2 kind : Alert metadata : name : notification-alert-slack namespace : flux-system spec : eventSeverity : info eventSources : - kind : Kustomization; name : "*" - kind : GitRepository; name : "*" - kind : Bucket; name : "*" - kind : OCIRepository; name : "*" - kind : HelmChart; name : "*" - kind : HelmRepository; name : "*" - kind : HelmRelease; name : "*" - kind : ImageRepository; name : "*" - kind : ImagePolicy; name : "*" - kind : ImageUpdateAutomation; name : "*" providerRef : name : notification-provider-slack
Or generate with the Flux CLI:
flux create alert notification-alert-slack \ --event-severity info \ --provider-ref notification-provider-slack \ --event-source Kustomization/ * \ --event-source GitRepository/ * \ --event-source Bucket/ * \ --event-source OCIRepository/ * \ --event-source HelmChart/ * \ --event-source HelmRepository/ * \ --event-source HelmRelease/ * \ --event-source ImageRepository/ * \ --event-source ImagePolicy/ * \ --event-source ImageUpdateAutomation/ * \ --export > notification-alert-slack.yaml
Apply your Alert:
kubectl -n flux-system apply -f notification-alert-slack.yaml
4. Confirm Setup Make sure Flux picks up your changes and that both the provider and alert are READY:
flux reconcile source git flux-system flux get alert flux get providers notification
5. Trigger and Observe Notifications Change something in your Git repository—for example, reduce the replica count in your deployment:
# in bb-app-source/2-demo/deployment.yaml spec : replicas : 1
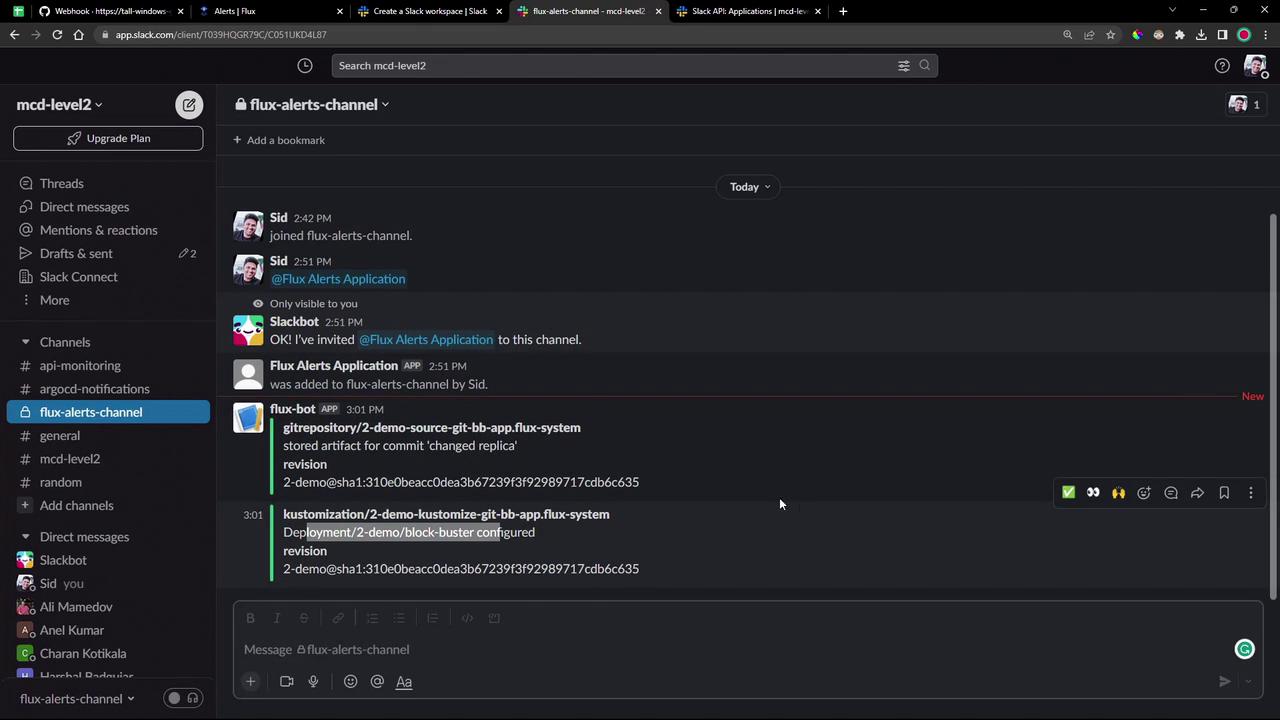
Commit and push the update. Once Flux reconciles, you will see a notification in flux-alerts-channel :
6. Verify the Update in Kubernetes Confirm that your deployment reflects the new replica count:
kubectl -n 2-demo get pods
Congratulations! You have successfully configured Flux Notification Controller to deliver Slack alerts for all your Flux events.
Links and References