HashiCorp Certified: Consul Associate Certification
Explain Consul Architecture
Service Configuration
In this lesson, we’ll explore how to leverage Consul’s distributed Key/Value (K/V) store for dynamic service configuration. Consul automatically replicates all K/V data across every server in the cluster, delivering redundancy and high availability for your application settings.
Consul K/V Store: At a Glance
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Distributed & Replicated | Every write is propagated to all Consul servers, ensuring consistency across the cluster. |
| Flexible Storage | Store any configuration data—strings, JSON blobs, or serialized objects (≤512 KB per key). |
| Versioning & Atomic Ops | Supports atomic Compare-and-Set (CAS) operations and optimistic locking. |
| Not a Full Data Store | Designed for configuration and service discovery, not high-throughput persistence like DynamoDB. |
Warning
Always enable ACLs to restrict access to your K/V data. Without proper ACLs, unauthorized users could browse or delete critical entries.
Accessing the K/V Store
You can interact with Consul’s K/V store in several ways:
| Method | Usage Example |
|---|---|
| CLI | consul kv put key value |
| HTTP API | curl --request PUT http://localhost:8500/v1/kv/key |
| Web UI | Navigate to Key/Value in the Consul dashboard |
Key/Value Hierarchies & Limits
- Flat Namespace: Keys are simple strings; forward slashes (
/) only emulate folders (e.g.,app/config/db/connection_string). - Size Limit: Each value ▶ 512 KB.
- Any Object Type: Store text, JSON, or serialized binaries, up to the size cap.
Example: Managing Application Parameters
Suppose you have a “training” application deployed by a CI/CD pipeline (Jenkins, CircleCI, GitLab CI, etc.). You need to supply:
- Database connection string
- Application version
- Database name
- Database table name
First, store these in Consul:
# Store configuration in Consul K/V
consul kv put training/app/database/connection_string \
"Server=prod.db.local;Database=training;User Id=app;Password=secret"
consul kv put training/app/version "1.2.3"
consul kv put training/app/database/name "training_db"
consul kv put training/app/database/table "users"
During deployment, your pipeline retrieves the values:
# Fetch the application version
consul kv get training/app/version
# → 1.2.3
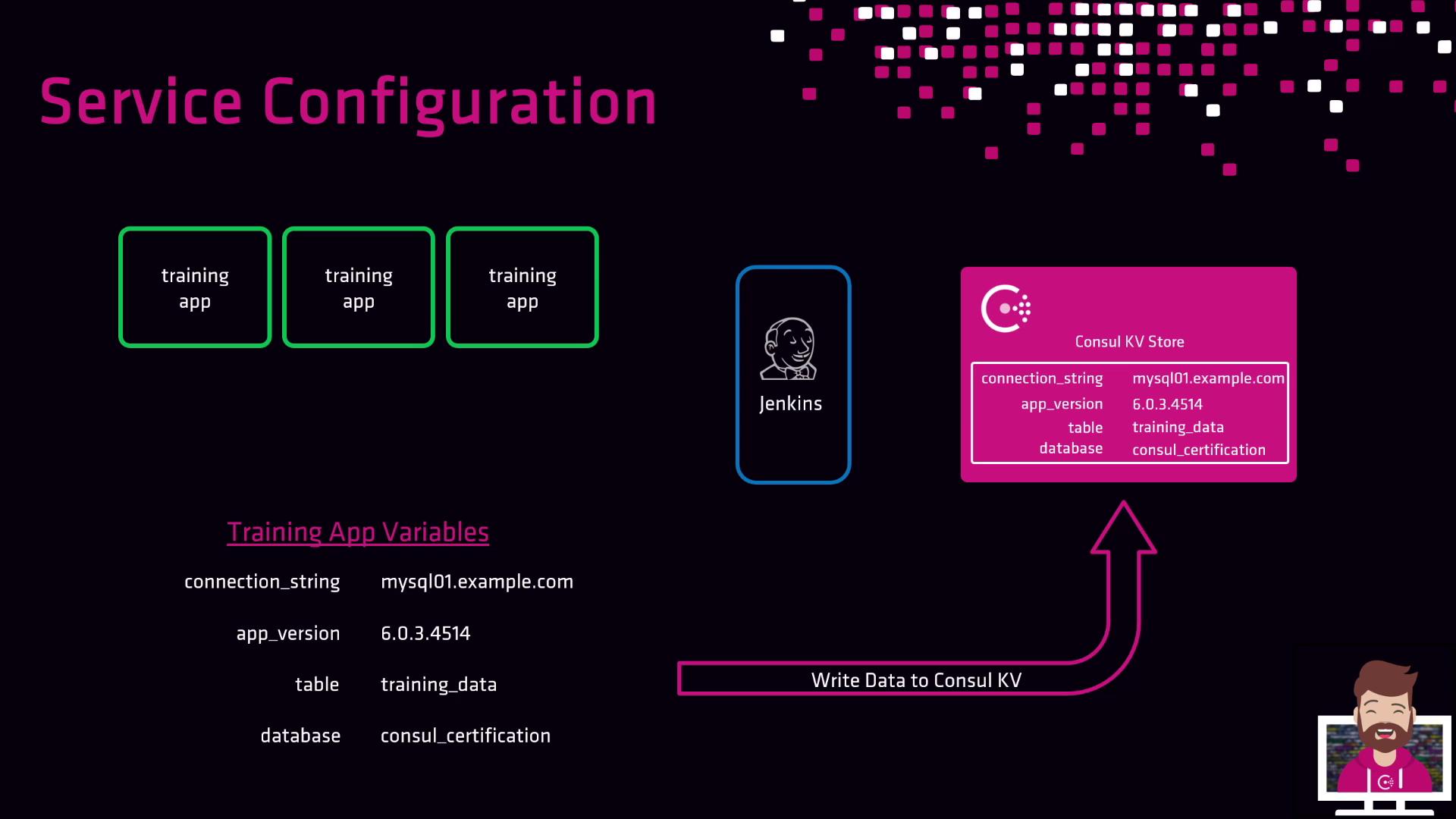
- CI/CD fetches configuration from Consul.
- Pipeline applies parameters at deploy time.
- Any update to Consul entries triggers new deployments with current settings.
Note
Updating K/V entries decouples configuration changes from pipeline scripts—your deployments always use up-to-date parameters.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content