Service Definition Parameters
You can customize a service definition with the following fields:| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| id | Unique identifier for this service instance (defaults to name) | web-server-01 |
| name | Logical service name (DNS-compliant) [required] | front-end-ecommerce |
| tags | Optional metadata to filter queries (e.g., version, environment) | ["v7.05","production"] |
| address | IP address where the service listens (defaults to agent’s bind address) | 10.3.13.112 |
| port | Port on which the service is running | 8080 |
| checks | Array of health checks (script, HTTP, TCP, etc.) | See below |
Only the
name field is required. If you omit id, Consul uses the value of name. Explicitly setting id helps avoid collisions when running multiple instances.Example Service Definition
Field Breakdown
- id: Unique per instance (e.g.,
web-server-01,web-server-02). - name: Service identifier for discovery (e.g.,
front-end-ecommerce). - tags: Filterable attributes like
v7.05orproduction. - address: Interface IP for the service (agent bind address if omitted).
- port: Network port (e.g.,
8080for HTTP). - checks: Health checks; here, a memory-check script running every 30 seconds.
If health checks continually fail, the service remains in the catalog but marked unhealthy—it will not receive traffic until the check passes.
Discovery via DNS
Consul exposes services under theservice.consul domain. Only healthy instances are returned:
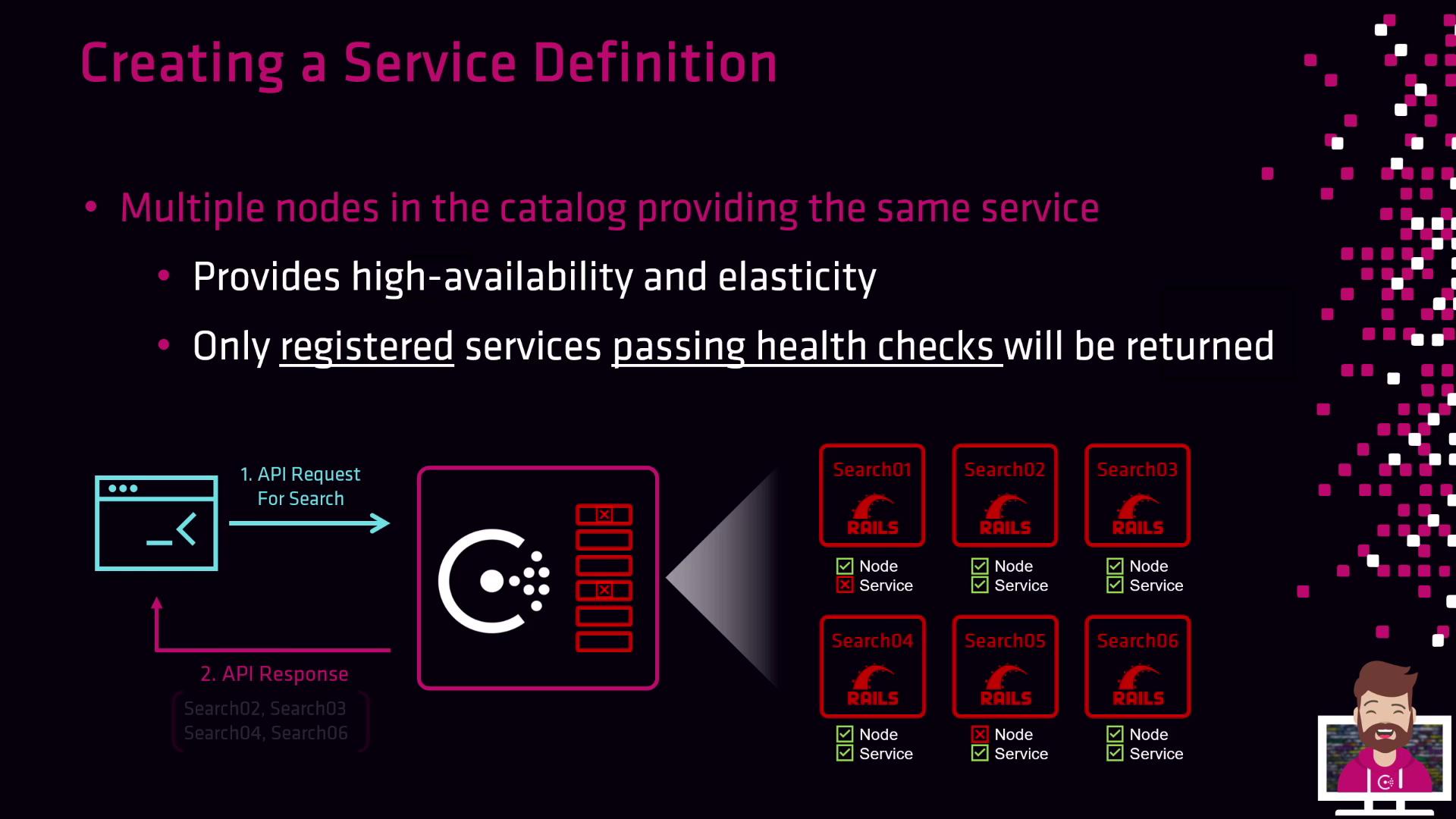
High Availability and Elasticity
Registering multiple instances under the samename delivers:
- High availability: Traffic shifts to other healthy nodes if one fails.
- Elasticity: Scale instances up or down to match load and optimize resource usage.
Next Steps
- Save your JSON definition in the Consul agent’s configuration directory (e.g.,
/etc/consul.d/). - Reload or restart the Consul agent:
- Verify registration and health status: