HashiCorp Certified: Consul Associate Certification
Register Services and Use Service Discovery
Registering a Consul Service
What Is a Consul Service?
In HashiCorp Consul, a service represents any workload or application—web servers, microservices, databases, APIs, and more—that provides functionality within your infrastructure. Consul’s service discovery catalogs these services, enabling clients to locate them through DNS queries or HTTP API calls. Once registered, services can also discover their own dependencies.
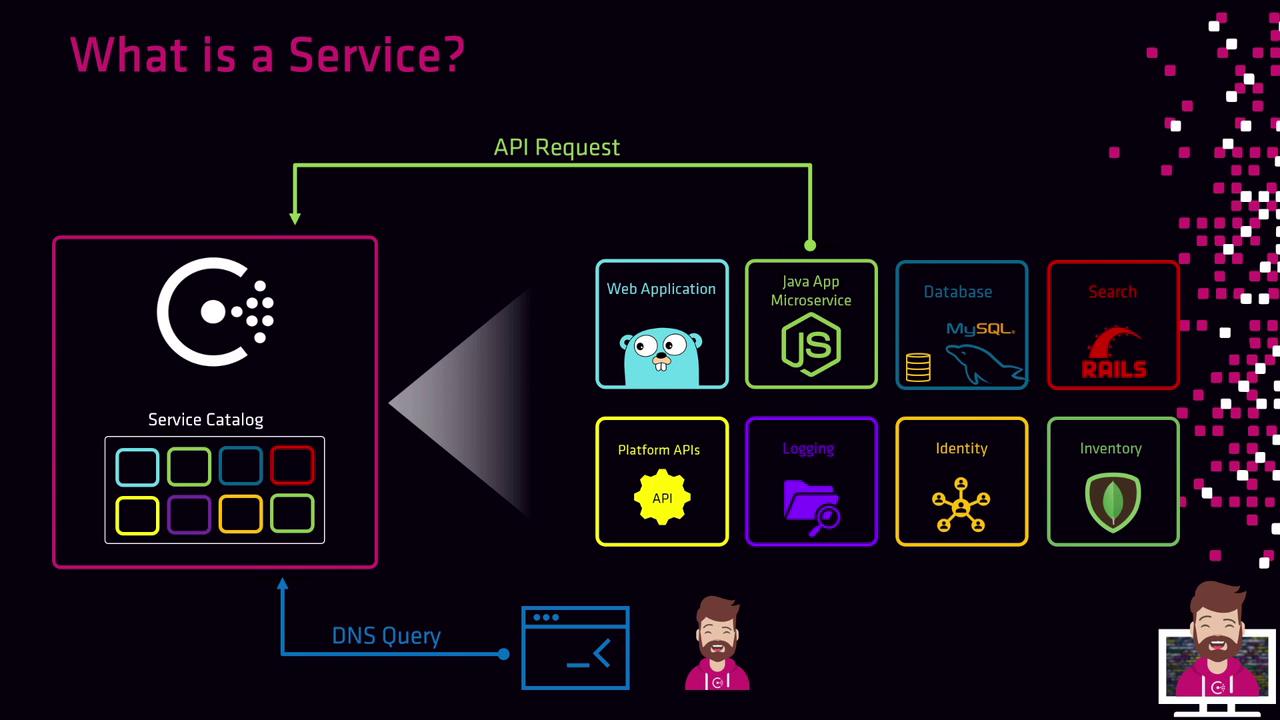
Service registration occurs on the local Consul agent running beside your application. You can register services by:
- Calling the Consul HTTP API
- Placing a service definition file on disk
Most deployments automate this step: containers in Kubernetes, Terraform provisioning, or configuration-management tools invoke registration as part of setup. After registration, Consul immediately starts health checks, and only healthy instances receive traffic.
Note
Consul automatically initiates health checks for each registered service. Ensure your checks are correctly configured to prevent unhealthy nodes from serving requests.
Service Registration Methods
Choose one of the following approaches to register services with your Consul agent:
| Method | Description | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP API | Register services programmatically via HTTP requests | curl -X PUT --data @payload.json https://consul.example.com:8500/v1/agent/service/register |
| Definition File | On-disk configuration in HCL or JSON | Drop files into /etc/consul.d/ or run consul services register /path/to/service.hcl |
| Agent Reload | Reload updated definitions without restarting agent | consul reload |
1. Register via the HTTP API
Send a PUT request to the agent’s registration endpoint with your service definition:
curl --request PUT \
--data @payload.json \
https://consul.example.com:8500/v1/agent/service/register
Example payload (payload.json):
{
"Name": "retail-web",
"Port": 8080
}
- Name: A unique identifier for the service in Consul’s catalog.
- Port: The TCP port on which the service listens on localhost.
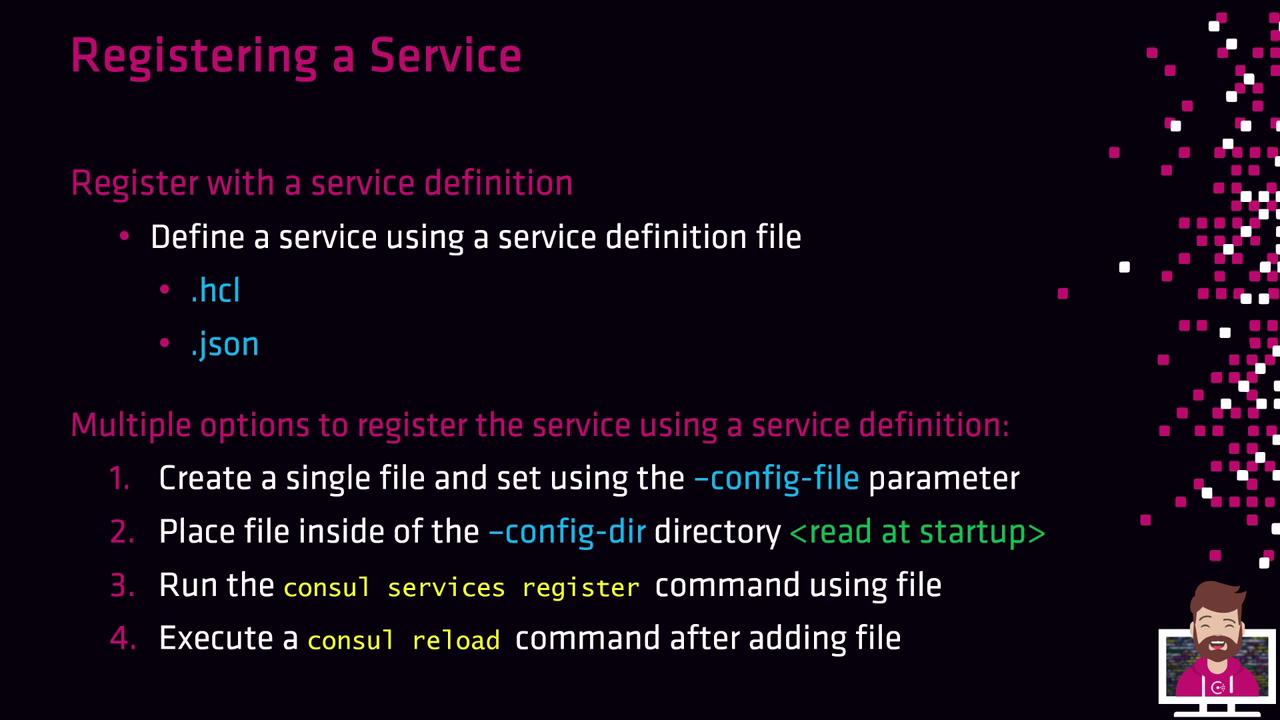
2. Register via a Service Definition File
Service definitions can be authored in HCL or JSON. The Consul agent loads these files at startup or when reloaded:
Single config file
Launch the agent with-config-file=/path/to/config.hclto include both agent and service settings.Config directory
Place one or more.hclor.jsonfiles into/etc/consul.d/. The agent reads all definitions at startup.CLI registration
consul services register /path/to/service.hclAgent reload
consul reload
Example: Registering Multiple Service Instances
In a high-availability setup, you might run identical web applications on three client nodes, each registering as retail-web. Each client uses the same service name and port but can differ in tags or health checks. For instance, on each node:
consul services register /etc/consul.d/retail-web.hcl
After registration, Consul’s catalog lists all three instances. DNS queries such as:
dig @127.0.0.1 -p 8600 retail-web.service.consul
or HTTP API calls return the healthy endpoints, enabling load balancing and failover across your infrastructure.
Further Reading
Watch Video
Watch video content