HashiCorp Certified: Vault Associate Certification
Compare Authentication Methods
Choosing an Auth Method
In this lesson, we’ll walk through how to select the optimal Vault authentication method for your environment. Vault supports various Auth Methods—each with unique benefits. By aligning your security requirements with Vault’s capabilities, you can ensure seamless, secure access.
Platform Versus Flexibility
You don’t have to be locked into your hosting platform’s native Auth Method. Whether you’re on Azure, AWS, or Kubernetes, you can choose any Vault Auth Method that meets your needs.
- Azure VMs can use the Azure auth method—or AppRole, Userpass, TLS, or OIDC.
- AWS workloads can authenticate via AWS—yet AppRole or Kubernetes Auth also work.
- Kubernetes pods often use Kubernetes Auth but are free to switch if integration or policy demands differ.
Note
Platform-native methods simplify integration and audit trails, but you can mix and match methods to satisfy complex requirements.
Narrowing Down by Integration Characteristics
Identify keywords in your use case—such as “frequently rotated” or “existing user credentials”—to eliminate unsuitable Auth Methods quickly.
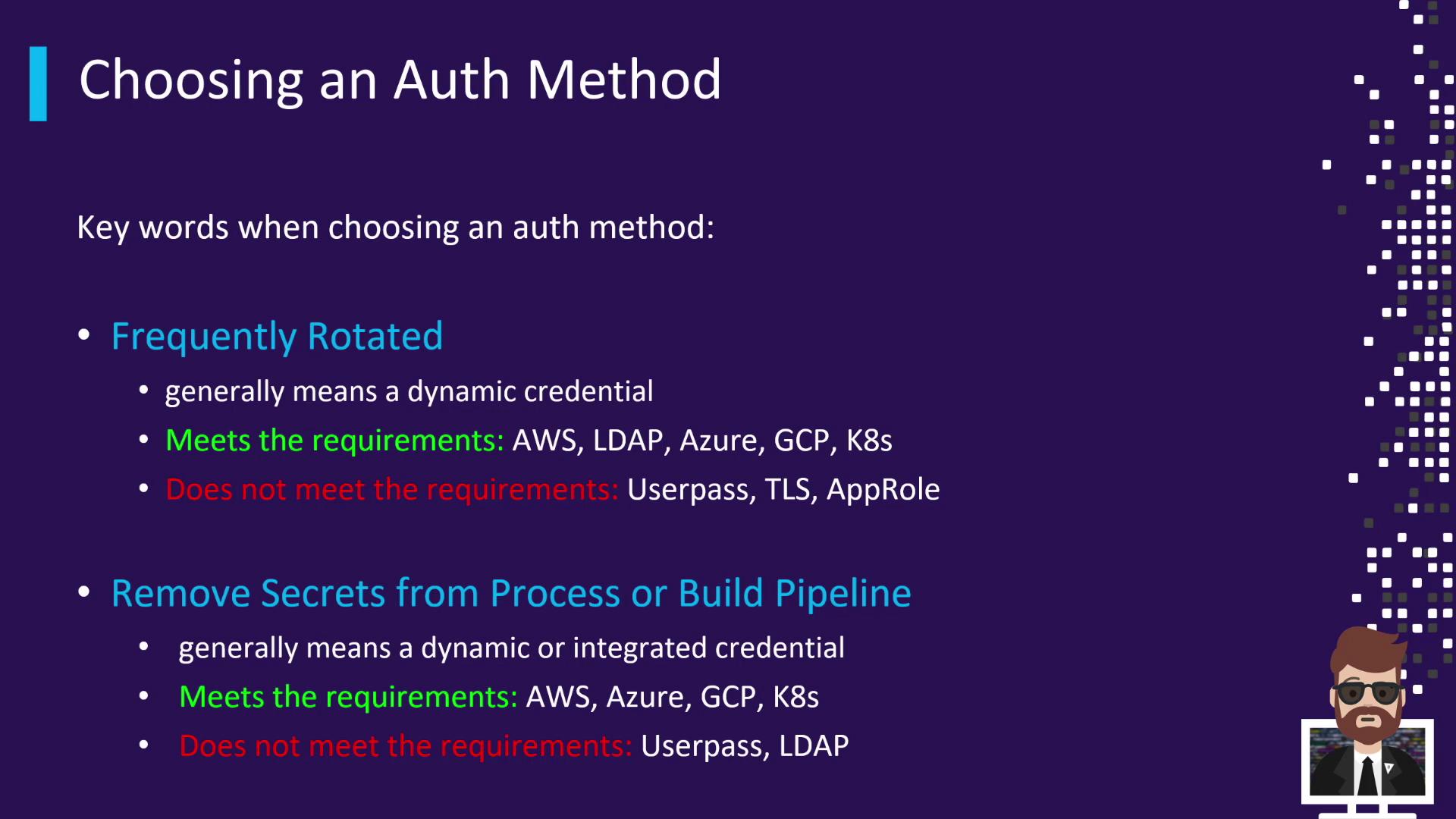
1. Frequently Rotated
Dynamic credentials are essential when secrets must rotate often. Avoid baking static tokens into your images or CI/CD pipelines.
- Meets requirement (dynamic):
• AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes Auth Methods
• LDAP (with regular rotation) - Does not meet requirement (static):
• Userpass
• TLS Certificates
• AppRole
Warning
Avoid embedding Userpass, TLS certificates, or AppRole secrets directly in images or pipelines—they are static and not automatically rotated.
2. Removing Secrets from a Process or Pipeline
When build or deployment workflows must avoid hardcoded secrets, choose platform-integrated or auto-generated methods.
- Best choices: AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes Auth Methods
- To avoid: Userpass, TLS, AppRole
3. Using Existing User Credentials
Leverage your identity provider if you prefer human-centric logins without managing extra secrets.
- Meets requirement (human-centric):
• OIDC
• LDAP
• Okta
• GitHub - Does not meet requirement (requires separate credentials):
• Userpass
• AWS, Azure, GCP Auth Methods

Summary Table
| Scenario | Recommended Auth Methods | To Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Frequently rotated | AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, LDAP (rotated) | Userpass, TLS, AppRole |
| Removing secrets from pipelines | AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes | Userpass, TLS, AppRole |
| Existing user credentials (human) | OIDC, LDAP, Okta, GitHub | Userpass, AWS, Azure, GCP |
By matching keywords—dynamic vs. static, integrated vs. standalone, identity provider vs. new credentials—you’ll converge on the Vault Auth Method that best fits your use case.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content