- Granting Vault access to the backend platform.
- Defining Vault roles that map to the platform’s permission sets.
Step 1: Grant Vault Access to the Backend Platform
Vault must authenticate to the external system to provision credentials. Depending on your deployment, you can use API keys, instance metadata, environment variables, or service principals.AWS Example
Vault’s AWS Secrets Engine supports multiple authentication methods:- IAM access key & secret key
- EC2/EKS instance roles (when Vault runs in AWS)
- Environment variables
aws/config/root:
Store your AWS root credentials securely (e.g., in HashiCorp Vault Enterprise) and restrict their scope.
Database Example
Vault’s Database Secrets Engine supports popular databases via plugins (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, etc.). To configure a connection: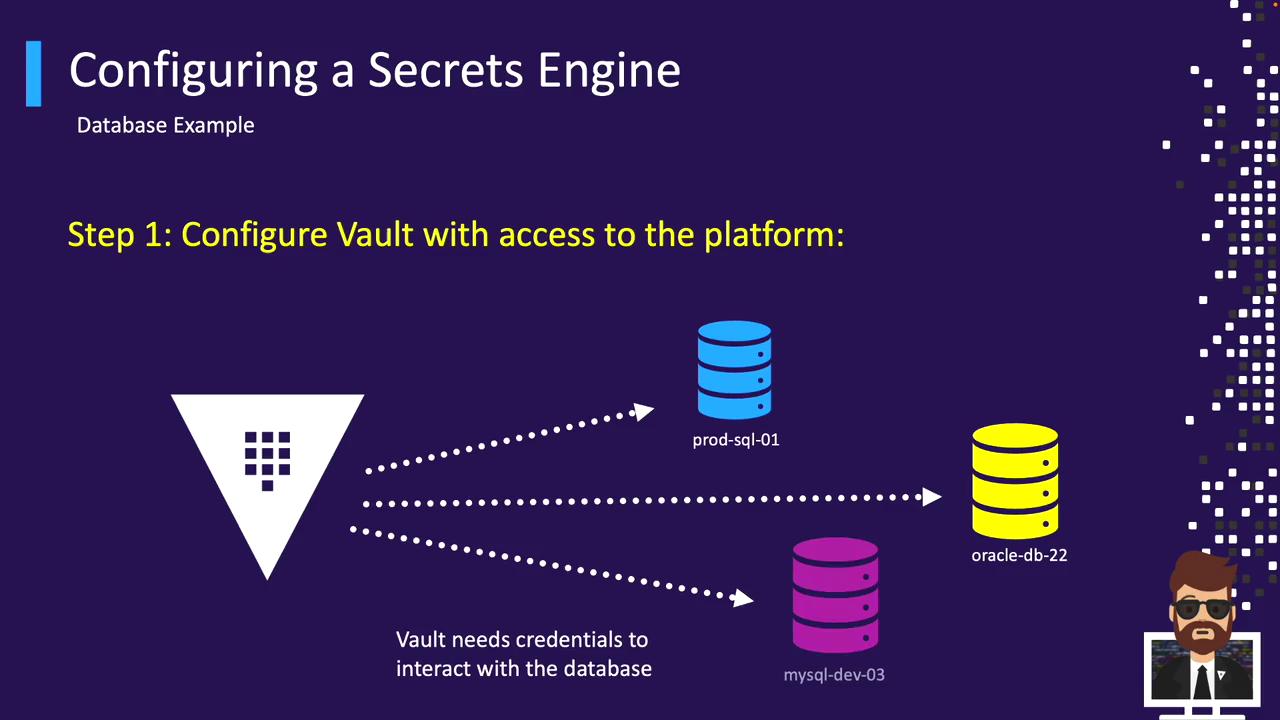
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| plugin_name | Database plugin (e.g., mysql-aurora-database-plugin) |
| connection_url | Connection string with {{username}} & {{password}} vars |
| allowed_roles | Comma-separated list of Vault roles permitted to use this DB |
| username/password | Admin credentials for provisioning users |
Step 2: Define Vault Roles to Map to Backend Permissions
Roles tell Vault which permissions to request or create when issuing credentials.AWS Roles
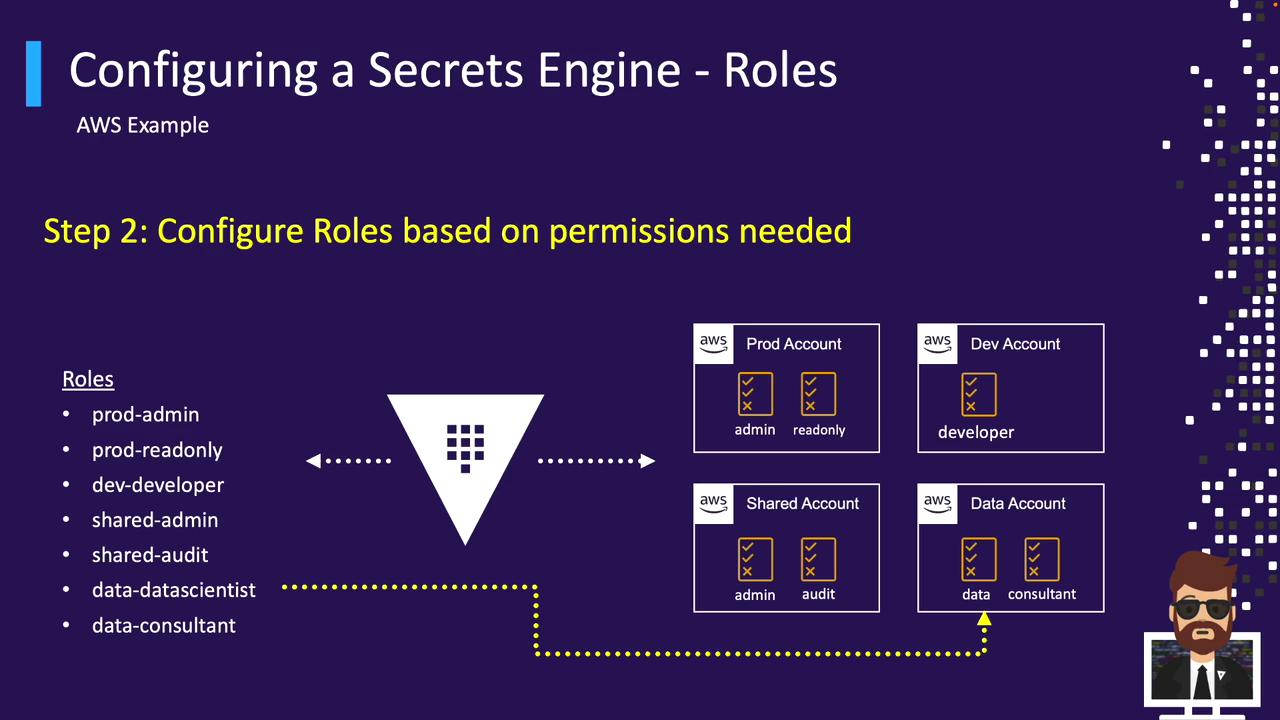
Create a Vault role for each AWS permission set or account: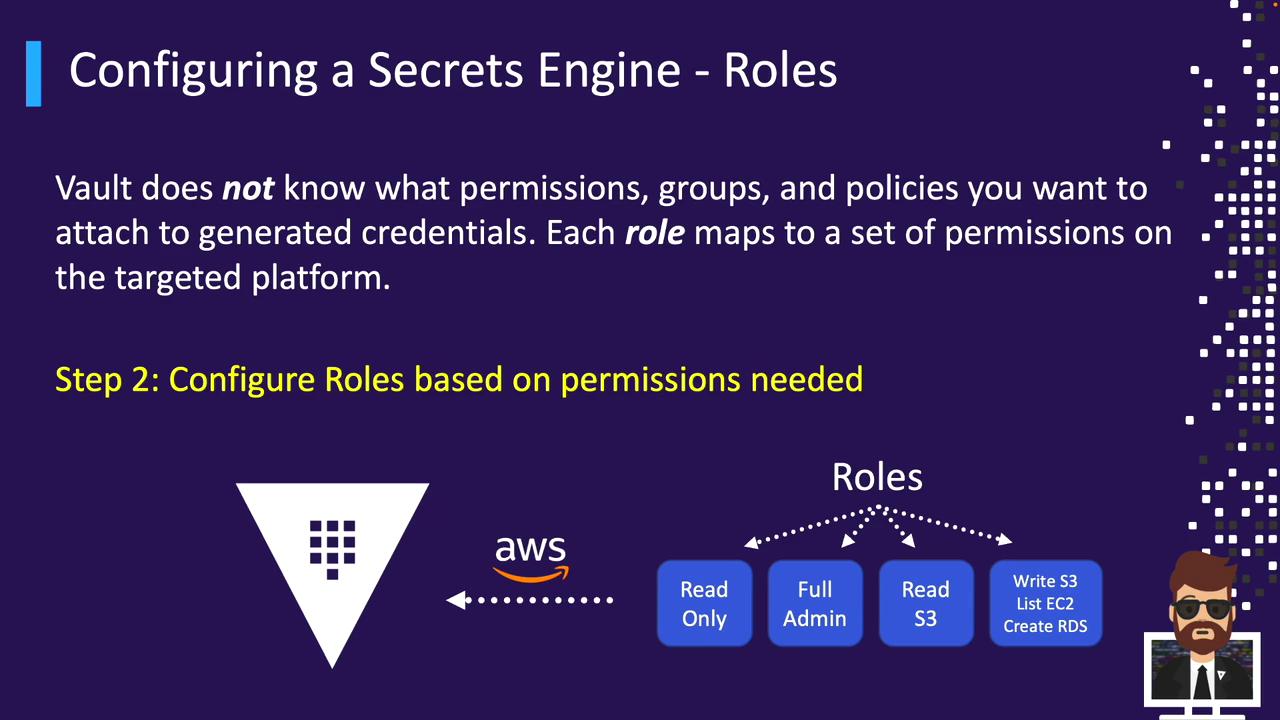
| Vault Role | AWS Permissions |
|---|---|
| prod-admin | Full IAM Administrator in the production account |
| prod-read-only | Read-only Auditor in the production account |
| dev-developer | Developer Permissions in the development account |
| shared-admin | Cross-account Admin |
| data-scientist | Data Scientist access in the analytics account |
Database Roles
Similarly, define SQL-based roles for each database connection: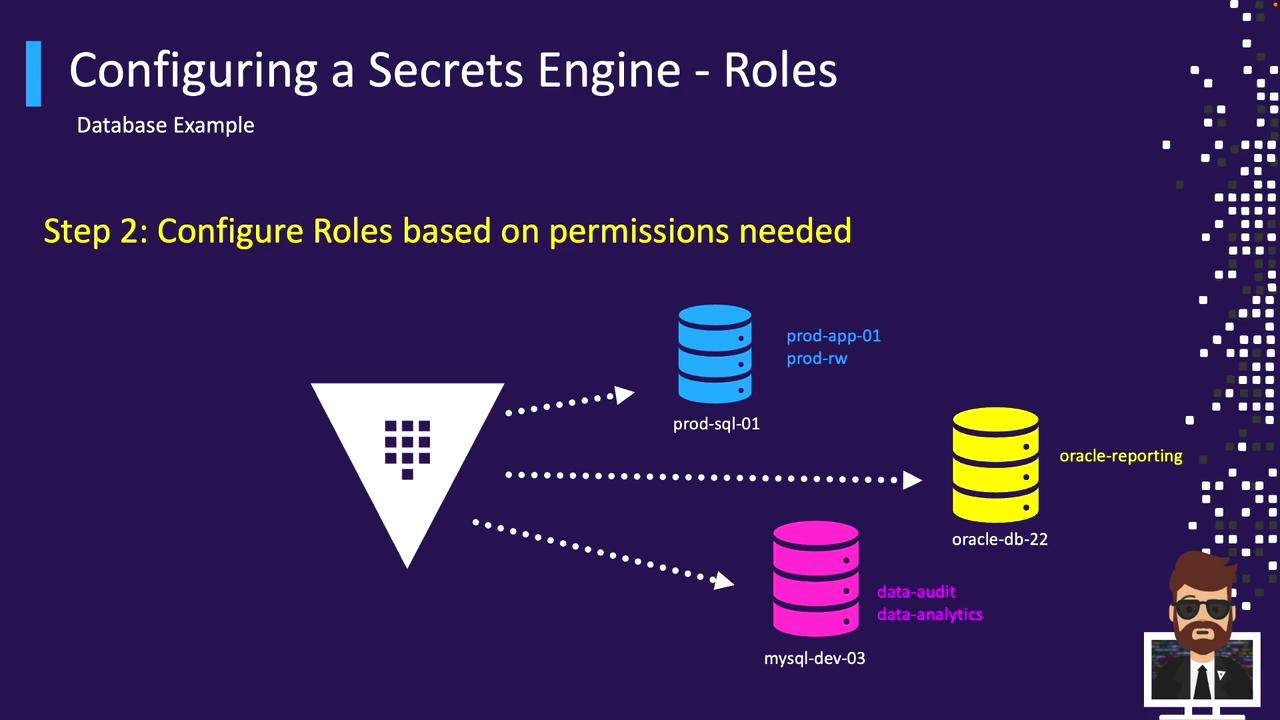
Generating Dynamic Credentials
After configuring the engine and roles, clients authenticate to Vault and request temporary credentials.AWS Credential Retrieval
Database Credential Retrieval
Summary
Vault’s dynamic Secrets Engines streamline credential management by centralizing access, automating rotation, and enforcing least privilege.
- Configure Vault’s engine with backend access.
- Define roles that encapsulate specific permission sets.
- Authenticate to Vault and request credentials; Vault leases and renews them automatically.