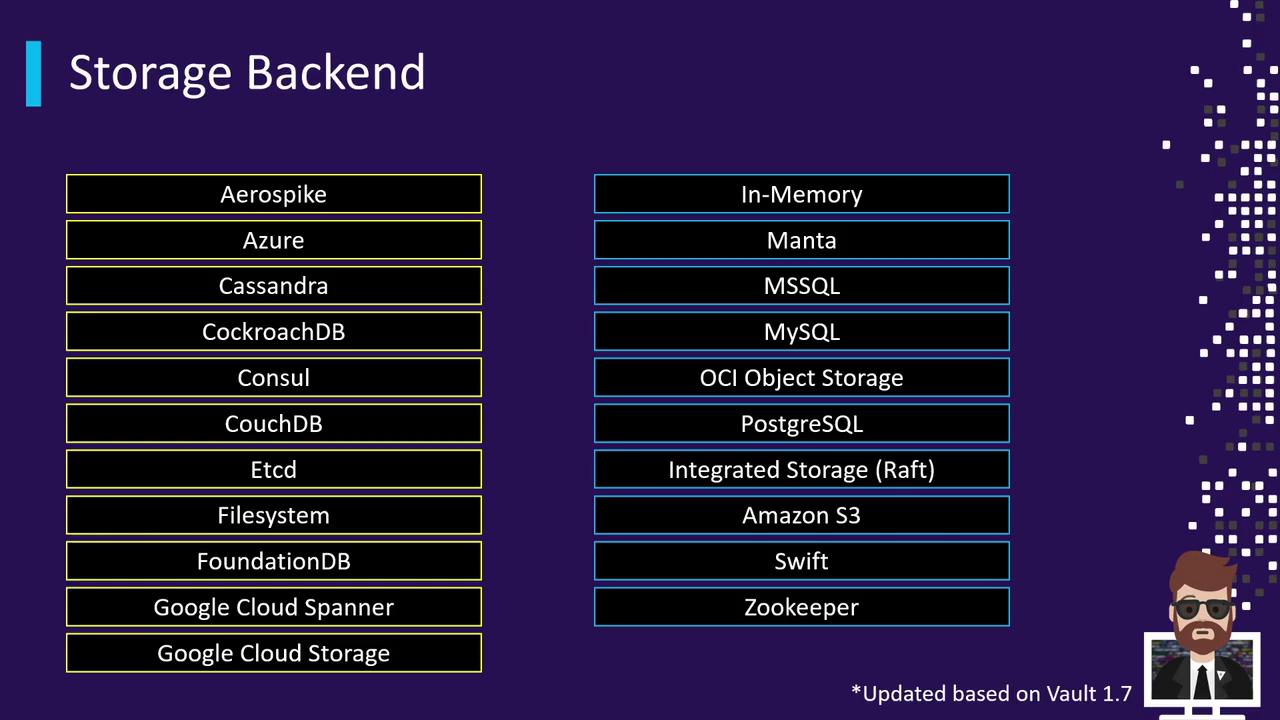
Supported Storage Backends
Vault 1.7 provides a broad selection of backends for any environment:| Backend | Edition | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Consul | Open Source & Ent. | HA clusters with mature ecosystem |
| Integrated Storage (Raft) | Open Source & Ent. | Built-in HA, auto-join, backups |
| S3 | Open Source | Simple scalable object storage |
| DynamoDB | Open Source | Key/value store with single-region HA |
| Azure Blob Storage | Open Source | Blob-based storage on Microsoft Azure |
| Google Cloud Storage | Open Source | Object storage on GCP |
| etcd, MySQL, PostgreSQL | Community | Custom database deployments |
| In-Memory (dev mode) | Open Source | Testing and non-production |
Storage Backend Architecture
A Vault cluster consists of one active node and one or more standbys, all sharing a single storage backend. Every node reads from and writes to the same data store. If you deploy multiple clusters for geographic redundancy, each cluster uses its own backend. Enterprise-level replication is handled between Vault nodes via the Vault API—not directly between storage backends.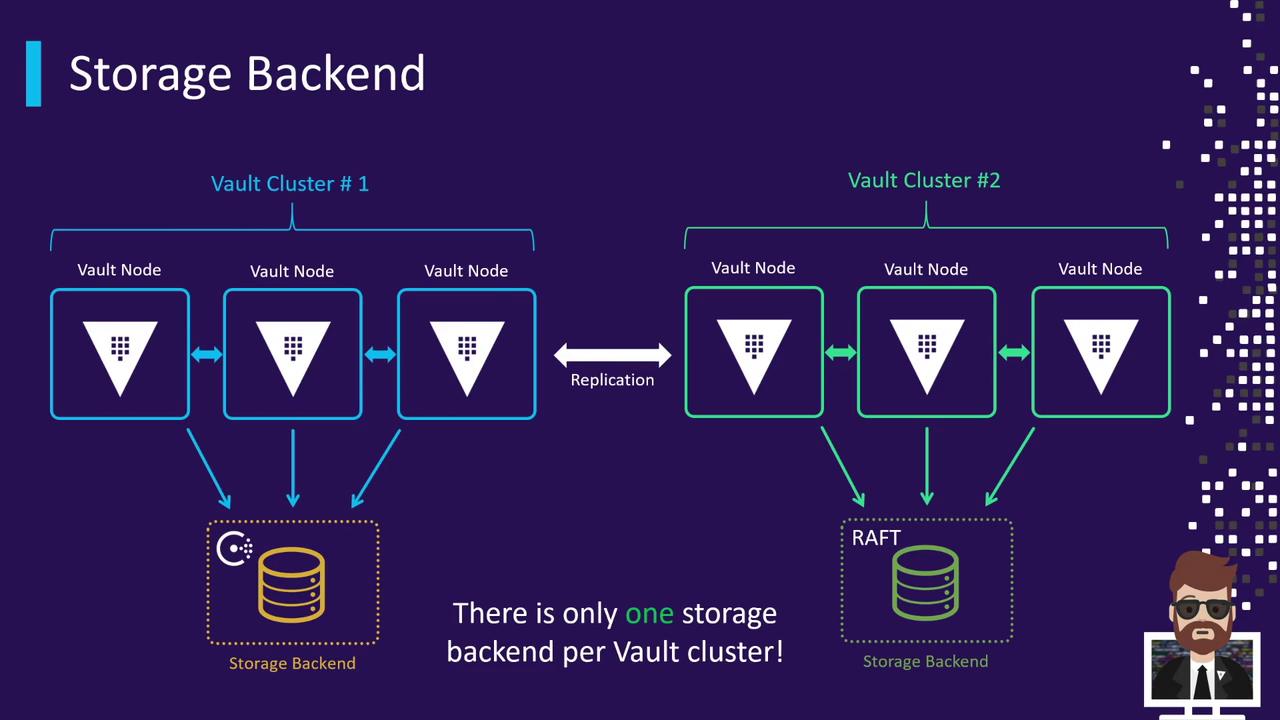
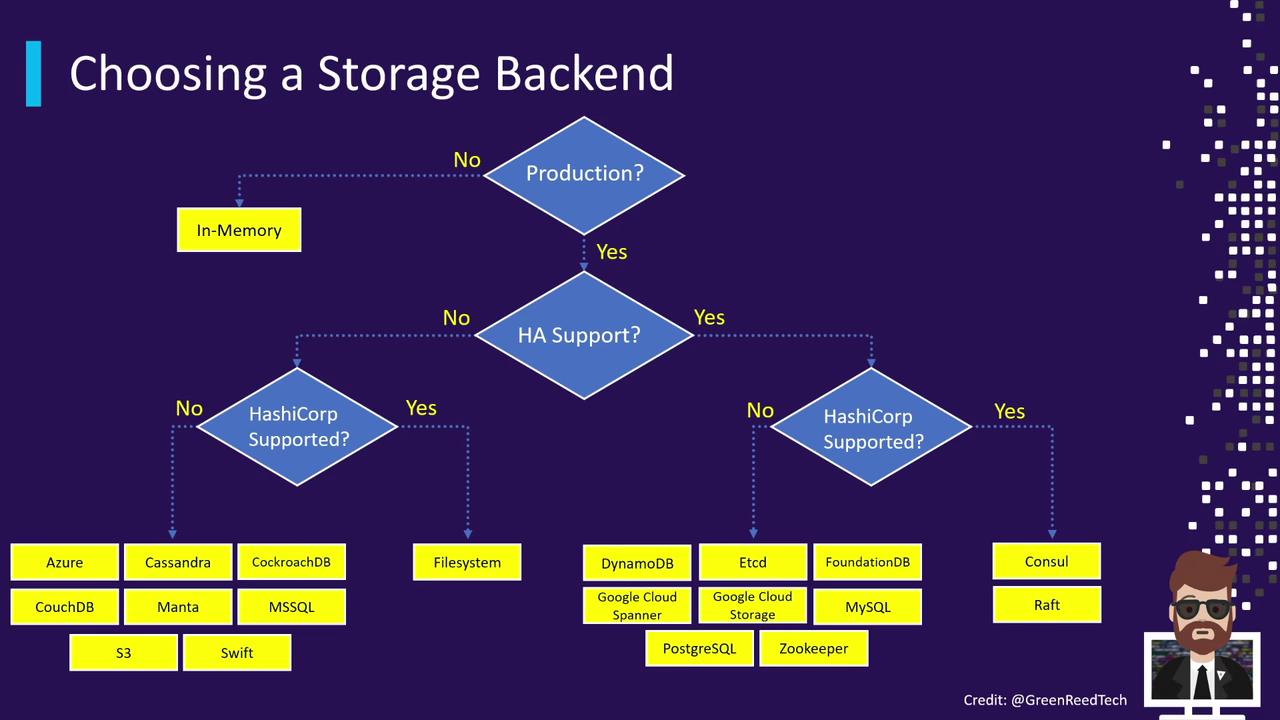
Choosing a Storage Backend
When evaluating storage backends, consider:- Production vs. non-production environments
- HA requirements (single-node vs. multi-node)
- Whether Enterprise support and features are needed
Use this decision flow to match your requirements with the right backend. For simple testing or CI, in-memory dev mode may suffice. For critical production data, choose a robust HA backend like Consul or Raft.
Configuring Your Storage Backend
Define your storage backend inside thestorage stanza of your Vault HCL configuration file.
Example: Consul
- address: Host and port of the Consul agent
- path: Prefix within Consul’s key/value store
- token: ACL token granting Vault access
Example: Integrated Storage (Raft)
- path: Filesystem path for replicated data
- node_id: Identifier used by Raft to address each node
- retry_join.auto_join: Uses AWS EC2 tags to discover and join peers automatically
Do not commit configuration files containing plain-text tokens or credentials to version control. Use environment variables or a secure secrets manager to inject sensitive data.