- The UI provides a user-friendly dashboard for visual secret management.
- The CLI is a thin wrapper over the HTTP API, supporting almost every Vault operation.
- The HTTP API is the underlying mechanism for both the UI and CLI, so every action—even in the UI—translates to an API request.
Enabling the UI requires Vault to be served over TLS in production environments to prevent credentials leakage.
Keep your tokens secure. Avoid committing them to source control or sharing them in logs.
- Retrieve or store secrets (
vault kv get,vault kv put) - Generate dynamic credentials (e.g., database or AWS tokens)
- Encrypt/decrypt data with Transit secrets engine
- Manage leases and token renewals
Vault Interfaces and Their Users
Different personas leverage Vault’s interfaces to manage secrets at varying levels of automation and scale.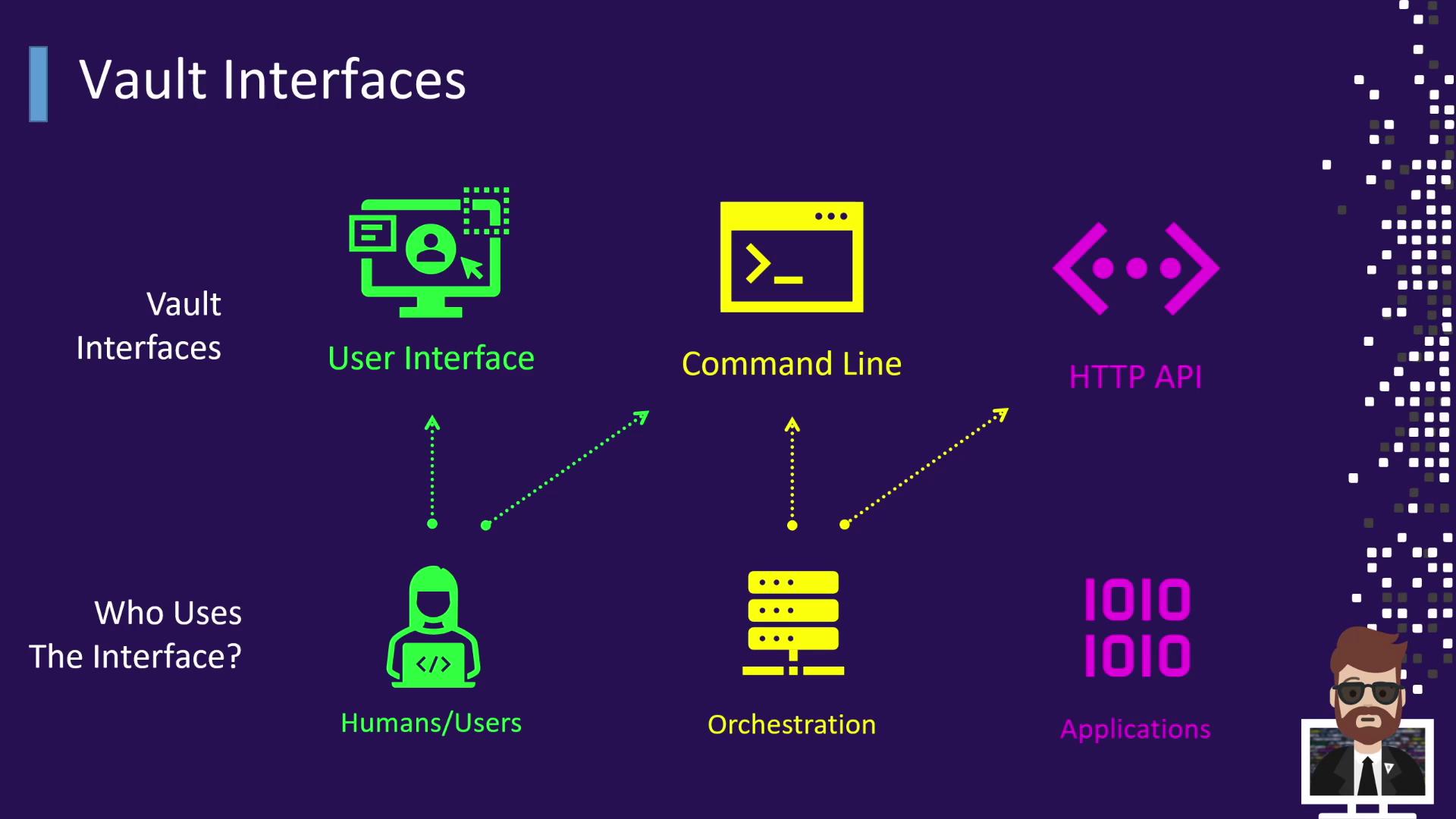
| Interface | Typical User | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| UI | Human operators | Browsing secrets, viewing leases, managing policies |
| CLI | DevOps engineers & CI/CD | vault kv get secret/data/app |
| HTTP API | Applications & orchestration | `curl —header “X-Vault-Token: $VAULT_TOKEN” \ |
| https://vault.example.com/v1/secret/data/app` |
-
Humans
Operators often prefer the UI for its graphical overview but can also use the CLI by settingVAULT_ADDR: -
Orchestration Tools
CI/CD platforms like Jenkins, CircleCI, Chef, and Puppet integrate via CLI commands or directly call the HTTP API to automate secret retrieval and renewal. -
Applications
Most applications interact programmatically through the HTTP API. They authenticate, receive a token, and request secrets or dynamic credentials. They must handle token TTL, lease durations, and renewal processes.
Learning Objectives
In subsequent sections, aligned with the Vault Associate Exam objectives, we will explore each interface in depth:
- Objective 6: Utilize the Vault CLI
- Objective 7: Utilize the Vault UI
- Objective 8: Be aware of the Vault HTTP API