HashiCorp Certified: Vault Operations Professional 2022
Create a working Vault server configuration given a scenario
Demo Auto Unseal Vault
In this guide, you’ll learn how to start a Vault server locally, initialize it with Raft storage, configure AWS KMS for auto-unseal, migrate from Shamir sealing to AWS KMS, and validate the auto-unseal workflow. This is ideal for test environments and hands-on practice toward certification.
Prerequisites
- Vault v1.10.0-ent or later
- AWS CLI v2 configured with sufficient IAM permissions
- A customer-managed AWS KMS key in the desired region
- Basic knowledge of Vault CLI and AWS IAM
Table of Contents
- Initial Vault Configuration
- Start Vault Server
- Initialize & Unseal Vault
- Enable KV Secrets Engine
- Configure AWS KMS Auto-Unseal
- Grant AWS IAM Permissions
- Set AWS Credentials
- Restart & Migrate Seal
- Validate Auto-Unseal
1. Initial Vault Configuration
Create a vault.hcl with Raft storage and default Shamir sealing (no seal stanza yet):
storage "raft" {
path = "/Users/bk/vault/data"
node_id = "btk-macbook-pro"
}
listener "tcp" {
address = "0.0.0.0:8200"
cluster_address = "0.0.0.0:8201"
tls_disable = true
}
api_addr = "http://btk-macbook-pro:8200"
cluster_addr = "http://btk-macbook-pro:8201"
cluster_name = "btk-macbook-pro"
ui = true
log_level = "INFO"
license_path = "/Users/bk/vault/vault.hclic"
2. Start Vault Server
Launch Vault with the above configuration:
vault server -config=vault.hcl
Look for:
Version: Vault v1.10.0-ent
Storage: raft (HA available)
Api Address: http://btk-macbook-pro:8200
Cluster Address: https://btk-macbook-pro:8201
==> Vault server started! Log data will stream in below:
In a new shell, set:
export VAULT_ADDR="http://127.0.0.1:8200"
3. Initialize & Unseal Vault
Check status:
vault statusExpected output:
Seal Type shamir Initialized false Sealed true Storage Type raft HA Enabled trueInitialize Vault with 1 key share and threshold:
vault operator init -key-shares=1 -key-threshold=1Save the Unseal Key and Initial Root Token.
Unseal Vault:
vault operator unseal <your-unseal-key>Login:
vault login <your-root-token>Verify unseal:
vault status
4. Enable KV Secrets Engine
Enable the KV (Key/Value) secrets engine and add a sample secret:
vault secrets enable kv
vault kv put kv/hcvop certification=fun
5. Configure AWS KMS Auto-Unseal
Edit vault.hcl to include the seal stanza for AWS KMS:
seal "awskms" {
region = "us-east-1"
kms_key_id = "arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:003674902126:key/8bc6b2ab-840a-4eef-8f2d-5616a3e67900"
}
storage "raft" {
path = "/Users/bk/vault/data"
node_id = "btk-macbook-pro"
}
listener "tcp" {
address = "0.0.0.0:8200"
cluster_address = "0.0.0.0:8201"
tls_disable = true
}
api_addr = "http://btk-macbook-pro:8200"
cluster_addr = "http://btk-macbook-pro:8201"
cluster_name = "btk-macbook-pro"
ui = true
log_level = "INFO"
license_path = "/Users/bk/vault/vault.hclic"
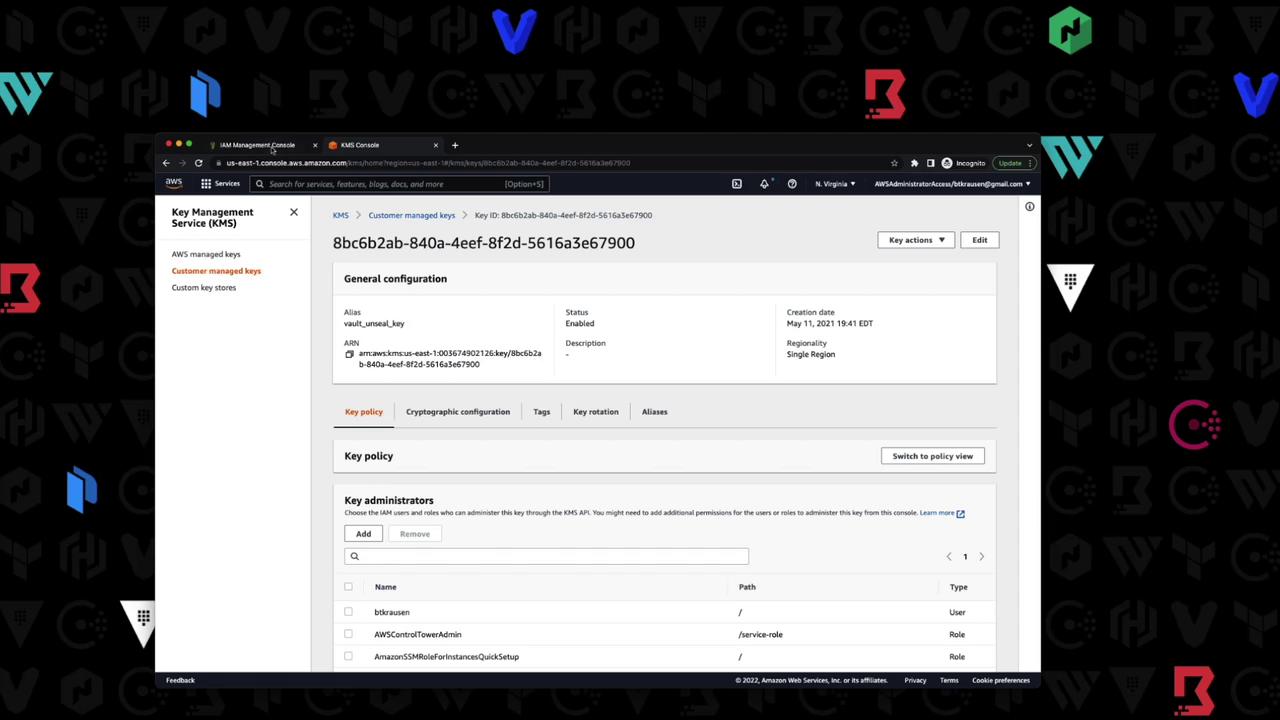
5.1 Retrieve KMS Key ARN
In the AWS KMS console, copy your customer-managed key ARN:
6. Grant AWS IAM Permissions
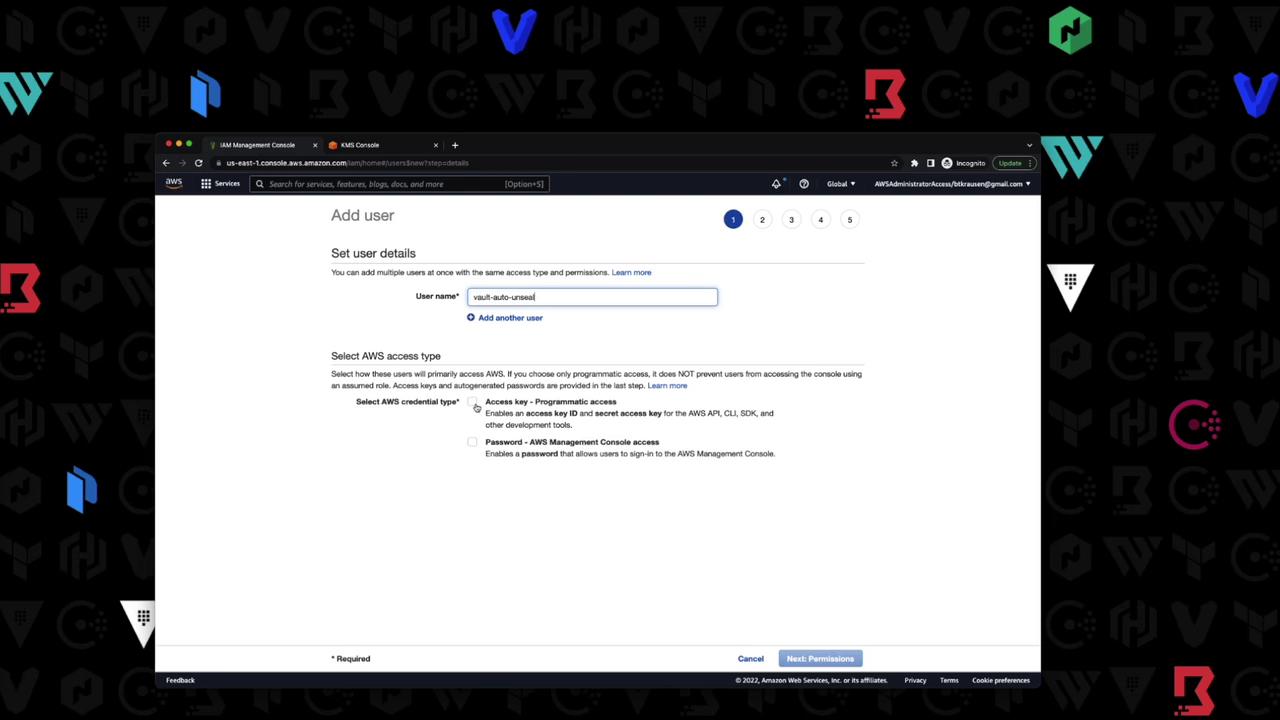
Create an IAM user with programmatic access and attach a policy allowing Vault to use the KMS key.
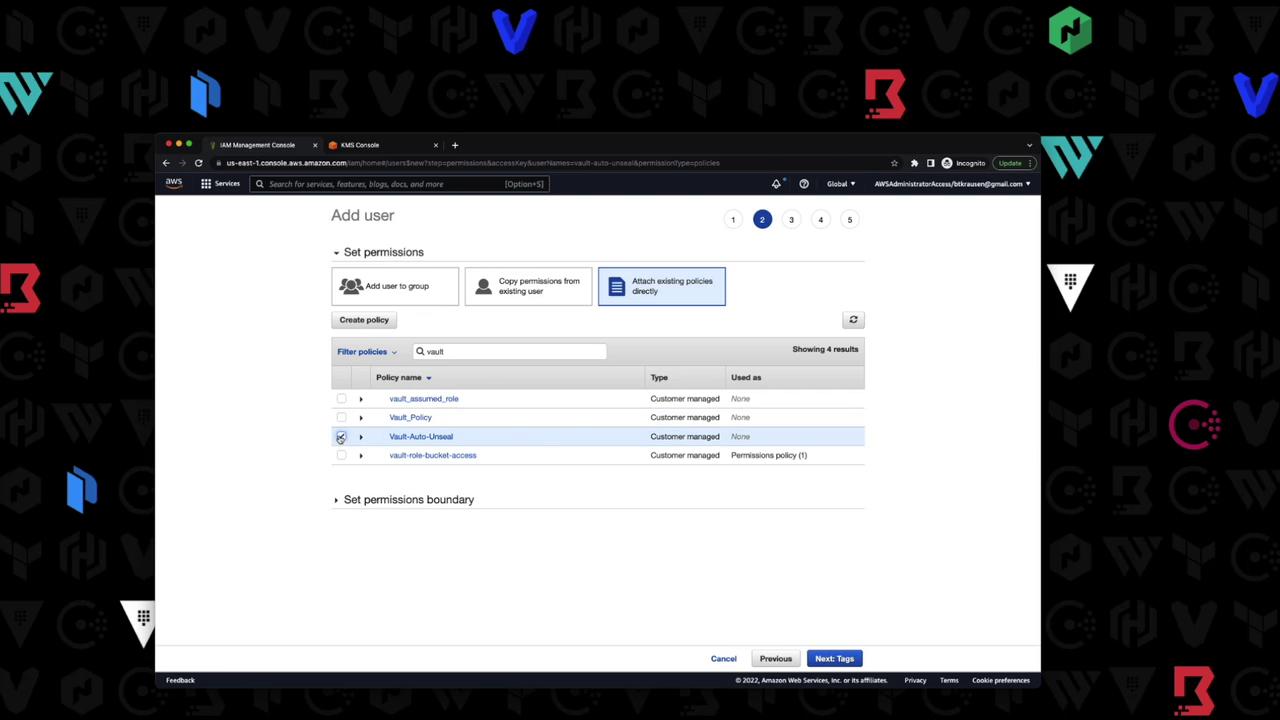
Example IAM policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"kms:Encrypt",
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:DescribeKey"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:003574902126:key/88cbe20f-848a-4eef-87d4-561636729908"
}
]
}
| IAM Action | Description |
|---|---|
| kms:Encrypt | Allows encryption operations |
| kms:Decrypt | Allows decryption operations |
| kms:DescribeKey | Allows viewing key metadata |
7. Set AWS Credentials
In your shell, export the IAM user credentials and region:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="AKIAQBWYKRZAXUEDIHZ"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="srKLi5zFuJRj8E23mRoY5w5FgLzts23cb52K"
export AWS_REGION="us-east-1"
Warning
Perform seal migration only in a non-production environment first. Ensure you have backups of your unseal keys before proceeding.
8. Restart & Migrate Seal
Stop the Vault process (
Ctrl+C).Restart with the updated
vault.hcl:vault server -config=vault.hclYou’ll see:
[WARN] core: entering seal migration mode; Vault will not automatically unseal even if using an autoseal: from_barrier_type=shamirMigrate the seal:
vault operator unseal -migrate <your-unseal-key>Successful output:
[INFO] core: migrating from shamir to auto-unseal: to=awskms [INFO] core: seal migration complete
9. Validate Auto-Unseal
Stop and start Vault again:
vault server -config=vault.hclLook for:
[INFO] core: vault is unsealed [INFO] core: unsealed with stored keyConfirm seal type:
vault statusThe
Seal Typeshould beawskmsandSealedshould befalse.
You have now configured Vault with AWS KMS auto-unseal, migrated from Shamir, and verified the process. For more details, see:
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab