What Is a Root Token?
A root token is Vault’s superuser credential. It’s bound to the built-inroot policy—which cannot be modified or deleted—and grants unrestricted access across your Vault cluster.

| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| No TTL | Never expires; valid indefinitely |
| Usage scope | Only for initial setup or critical emergencies |
| Immediate revocation needed | Revoke the root token as soon as tasks are complete |
| Immutable | Cannot be altered or deleted |
Initial Root Token and Revocation
Immediately after initializing Vault, your only authentication method is the initial root token. Once you enable and configure other auth backends (e.g., LDAP, AppRole, Kubernetes) and create policies, revoke this token to minimize risk:The token prefix (
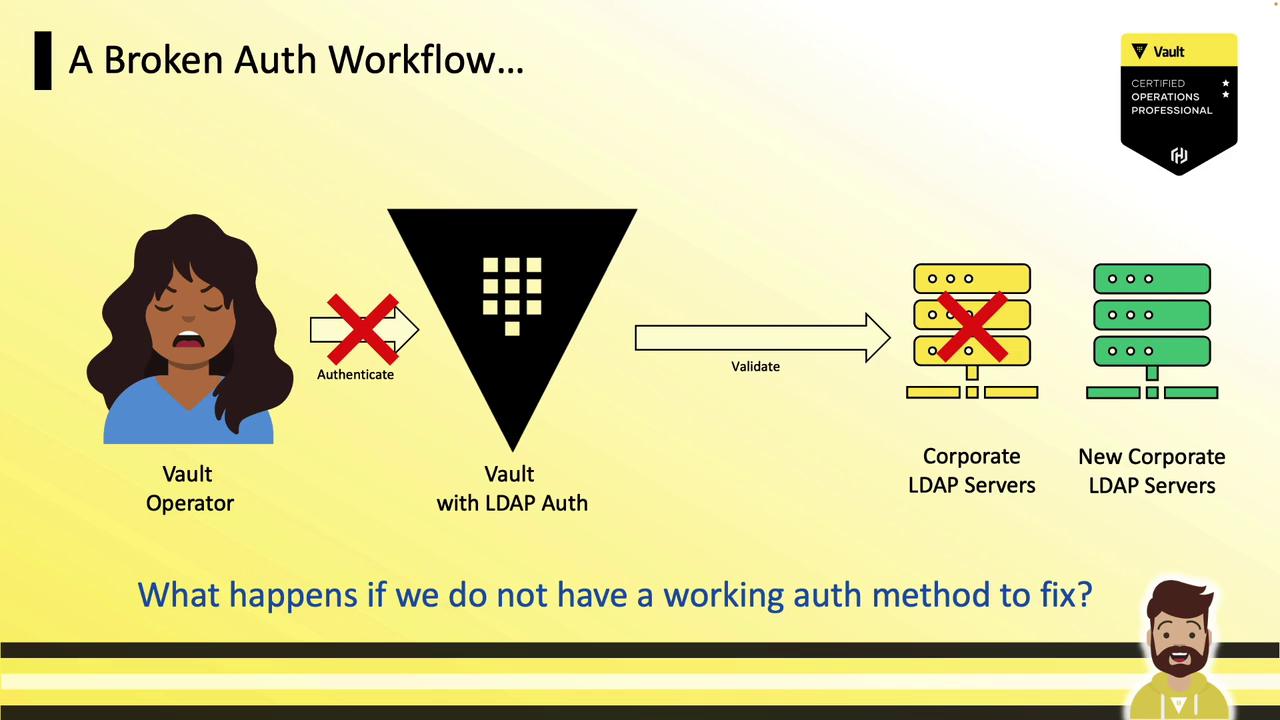
s. or hvs.) varies by Vault version.Emergency Scenario: Broken Authentication
Imagine Vault uses corporate LDAP for operator logins:- Operator logs in via LDAP
- Vault validates credentials against the LDAP server
- A network change or firewall misconfiguration breaks LDAP connectivity
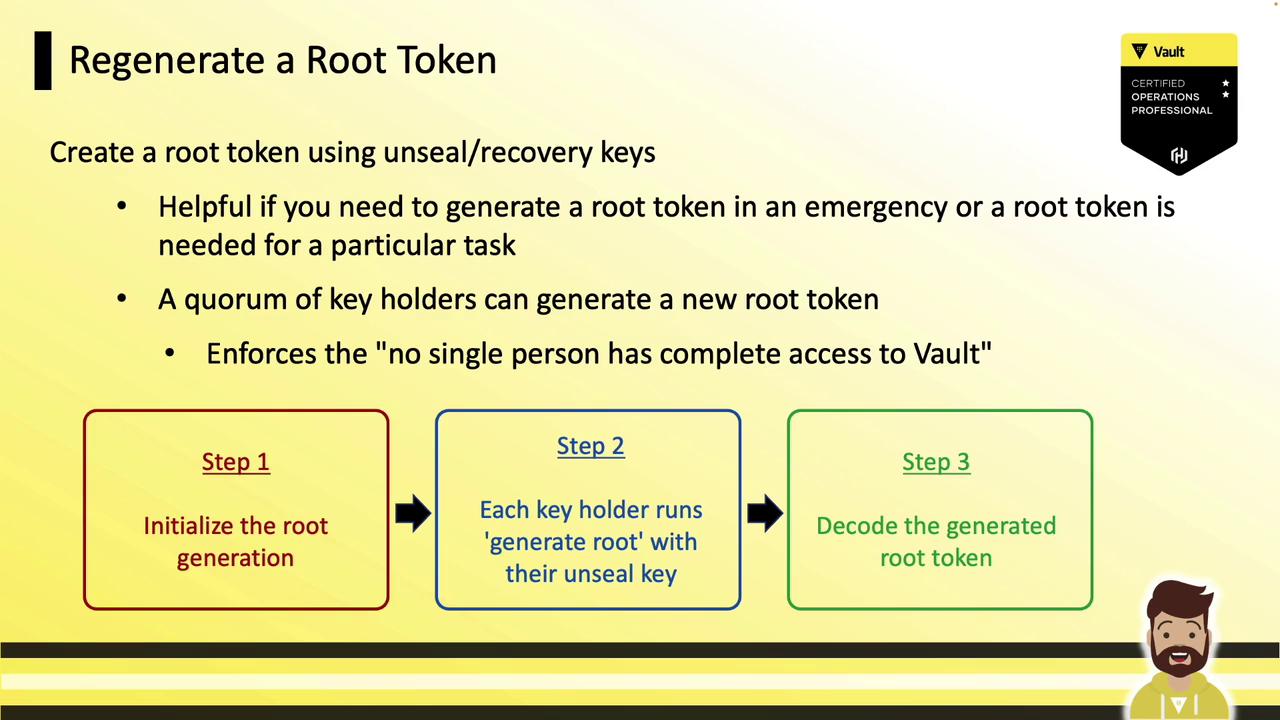
Regenerating a Root Token
Root token regeneration follows the same quorum-based approach as Vault unsealing. You’ll:- Initialize the generation process.
- Have each key holder submit their unseal key.
- Decode the new root token with the one-time password (OTP).
Command Options
Below are the primary flags forvault operator generate-root:
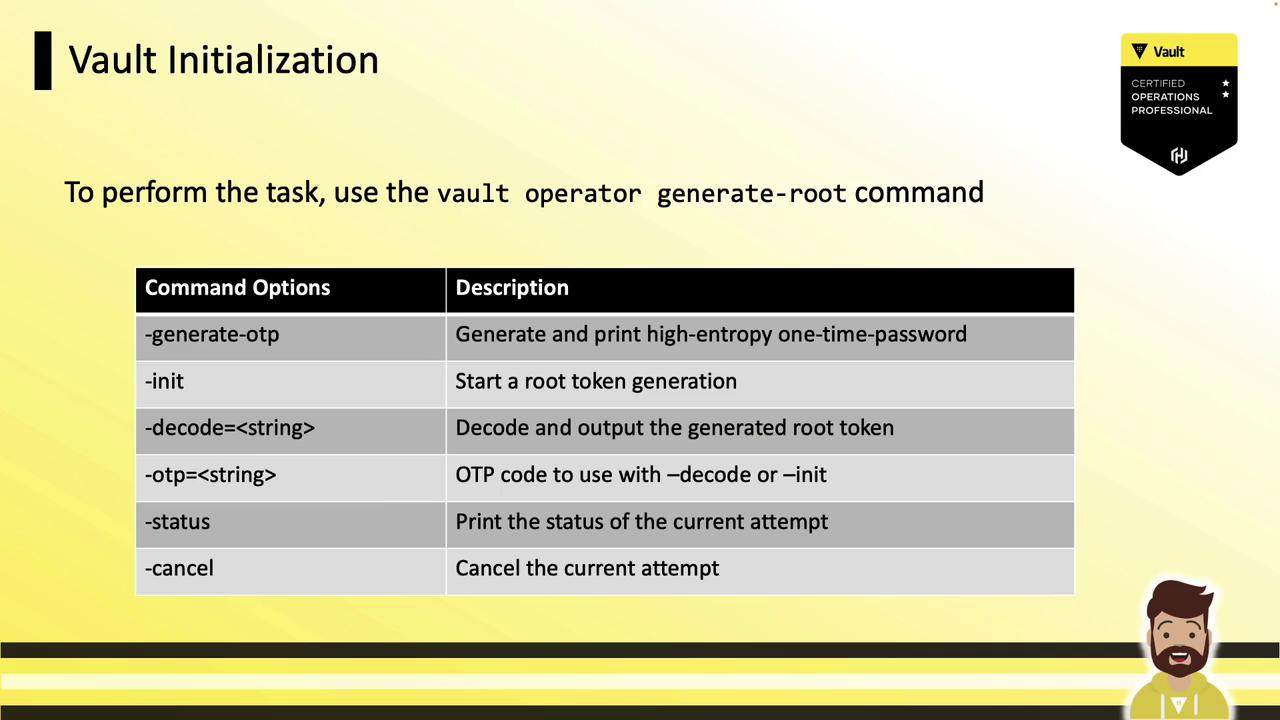
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
-init | Start root generation; outputs a nonce and OTP. |
-status | View progress (Progress X/Y). |
-cancel | Abort the generation operation. |
-otp | Supply the one-time password when decoding the token. |
-decode | Provide the encoded token string for decoding. |
Step 1: Initialize Root Generation
Kick off the process to obtain a Nonce and OTP:- Nonce: Share with key holders.
- OTP: Confidential; do not expose.
- Progress: Tracks submissions (e.g., 0/3 keys submitted).
Guard the OTP carefully. Anyone with the OTP and the final encoded token can reconstruct the root token.
Step 2: Key Holders Submit Unseal Keys
Each key holder runs the command (no flags):Step 3: Decode the Root Token
Use the OTP and the encoded token to reveal the new root token:Best Practices
- Always revoke root tokens immediately after use.
- Limit the number of key holders and enforce MFA for key storage.
- Rotate recovery keys and OTP lifetimes regularly.