HashiCorp Certified: Vault Operations Professional 2022
Scale Vault for Performance
Using Batch Tokens
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to work with batch tokens in Vault—lightweight, non-persistent tokens designed for high-throughput operations and seamless replication.
What Are Batch Tokens?
Batch tokens are encrypted binary large objects (BLOBs) that Vault issues directly to clients without persisting them to storage. They excel in scenarios requiring:
- High-volume cryptographic operations (e.g., Transit encrypt/decrypt)
- Frequent KV reads and writes
- Replication to performance and DR clusters

Note
Batch tokens are never written to the storage backend. This makes them faster to create and cheaper to replicate across performance clusters.
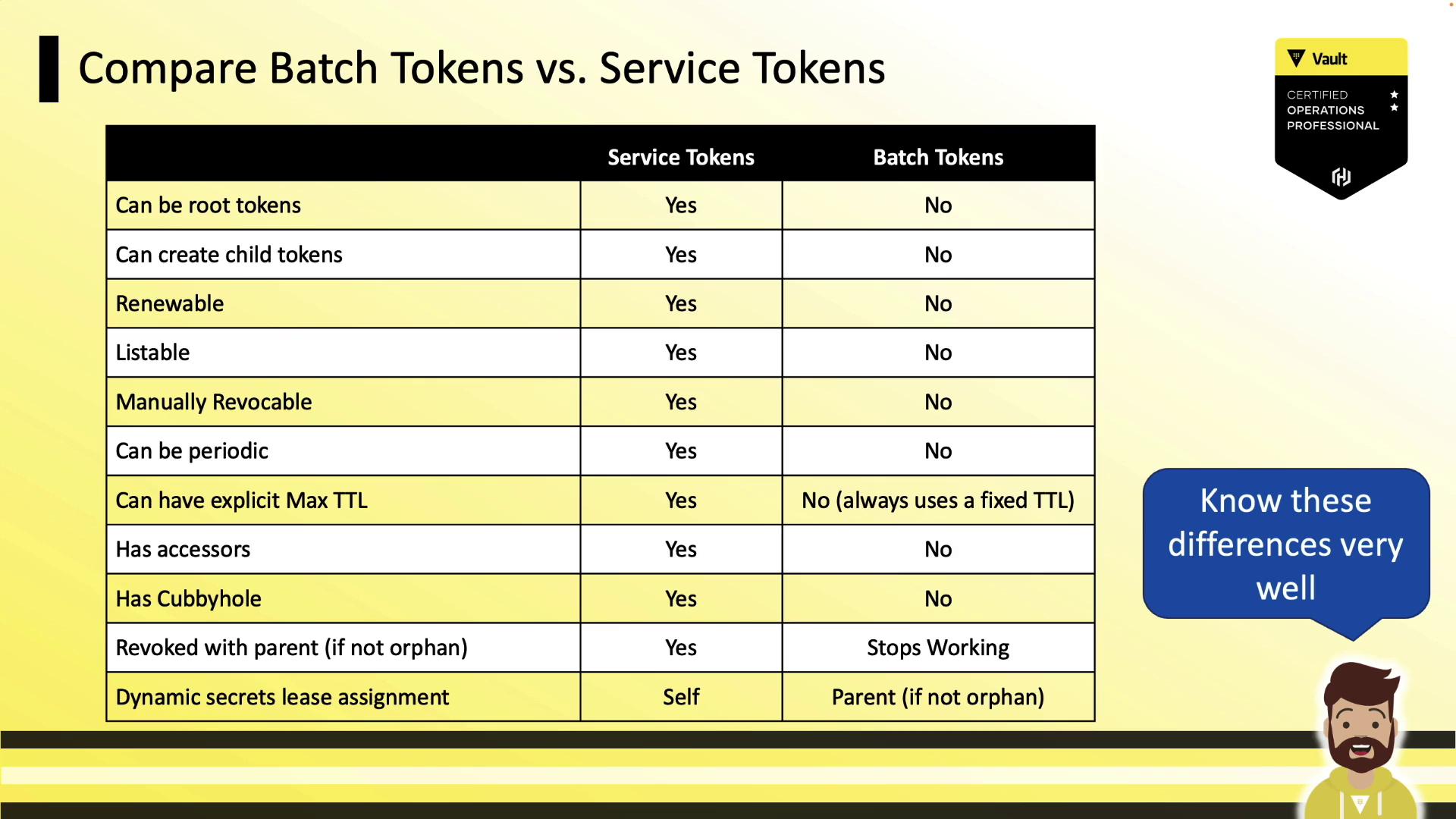
Service Tokens vs. Batch Tokens
Batch tokens trade off some features for speed and replication agility. Key differences include:
- Renewability & Revocation: Batch tokens are not renewable, listable, or manually revocable.
- Accessors & Cubbyholes: They lack token accessors and cubbyholes.
- Child Tokens: You cannot create child tokens from batch tokens.
- TTL Configuration: No periodic issuance or explicit max TTL.
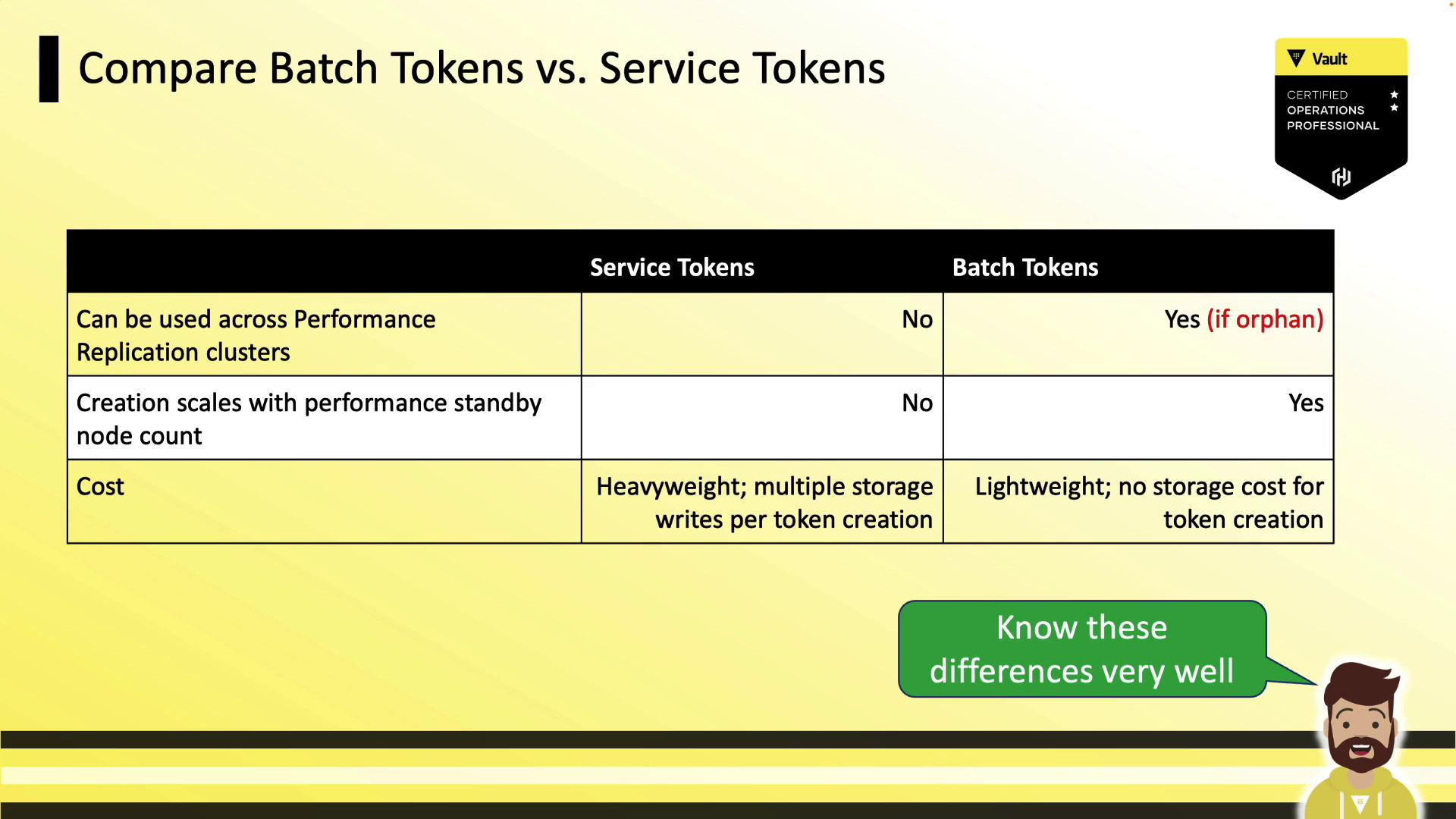
- Replication: Orphan batch tokens replicate to performance and DR clusters; non-orphans do not.
Identifying Token Types
Starting with Vault 1.10, tokens are prefixed to indicate their type:
| Prefix | Token Type |
|---|---|
| hvs. | Service Token |
| hvb. | Batch Token |
| hvr. | Recovery Token |
Batch tokens tend to be longer (≈128 bytes) than service tokens (≈96 bytes). Always plan for tokens up to 255 bytes in length.


# Service Token (96 bytes)
hvs.CAESIA4CZQisJNn9eq3g5TS5xP0-DPkFDsshli_jb5UH28AuGiAKHGh2cy5wZjPU1NsVlpWaTQxSFUyczFuQk9DOFgQHQ
# Batch Token (128 bytes)
hvb.AAAAAQKskxnAqTz0Ah3qu5Hc4Q3lYdqCocdDZjLXhyLAjuhhBJktOCrBaJVbKwE6AVsxD6WAFvlZ2UHs2MUb1gcpqYvro-kfVv10x7tKZ9GqUObUwKnn5341sU
Batch Token Replication
Vault supports two replication modes for batch tokens:
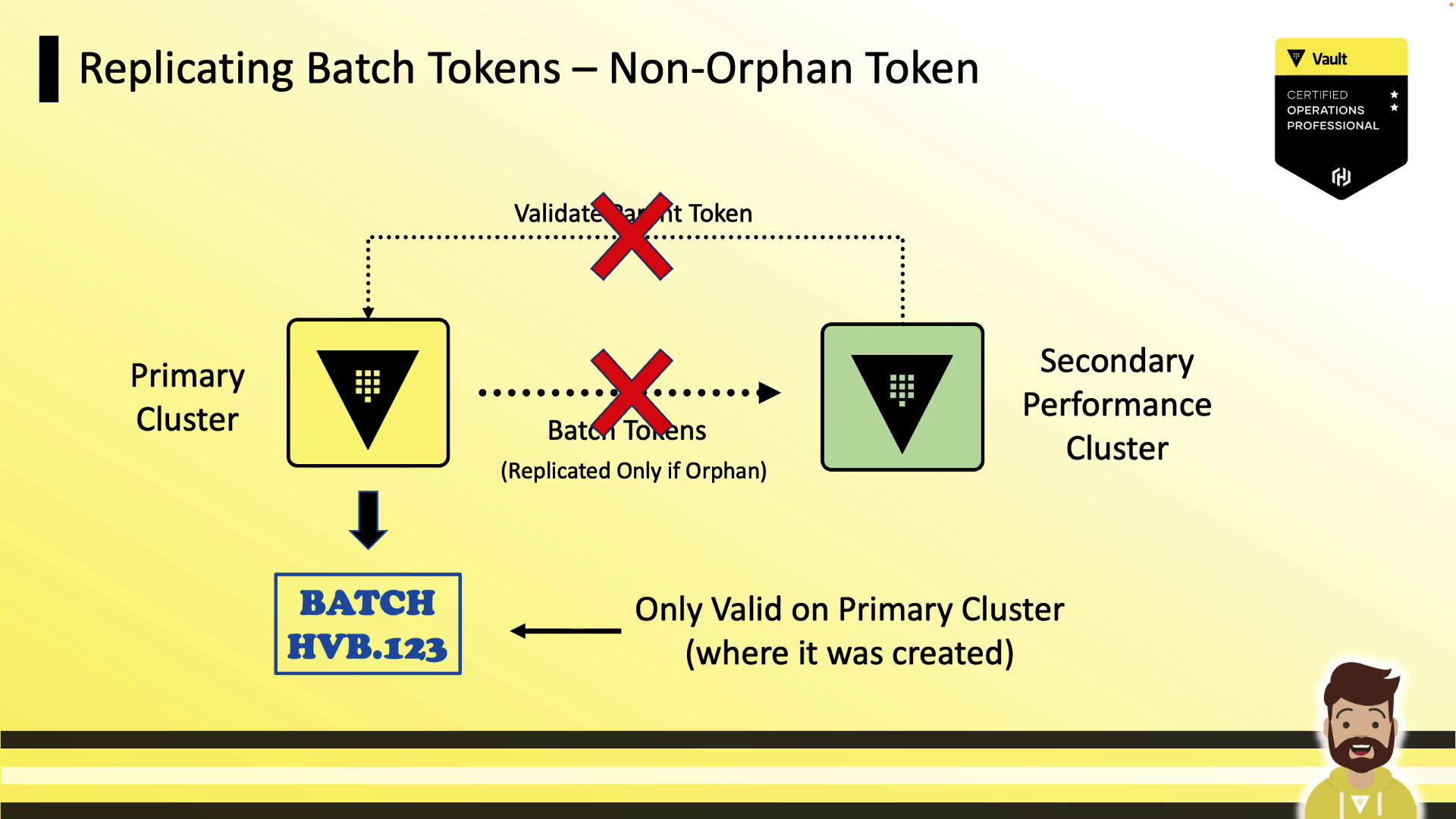
Non-Orphan Tokens
Batch tokens created with a parent token remain bound to the original cluster. Performance secondaries cannot validate the parent, so these tokens do not replicate.
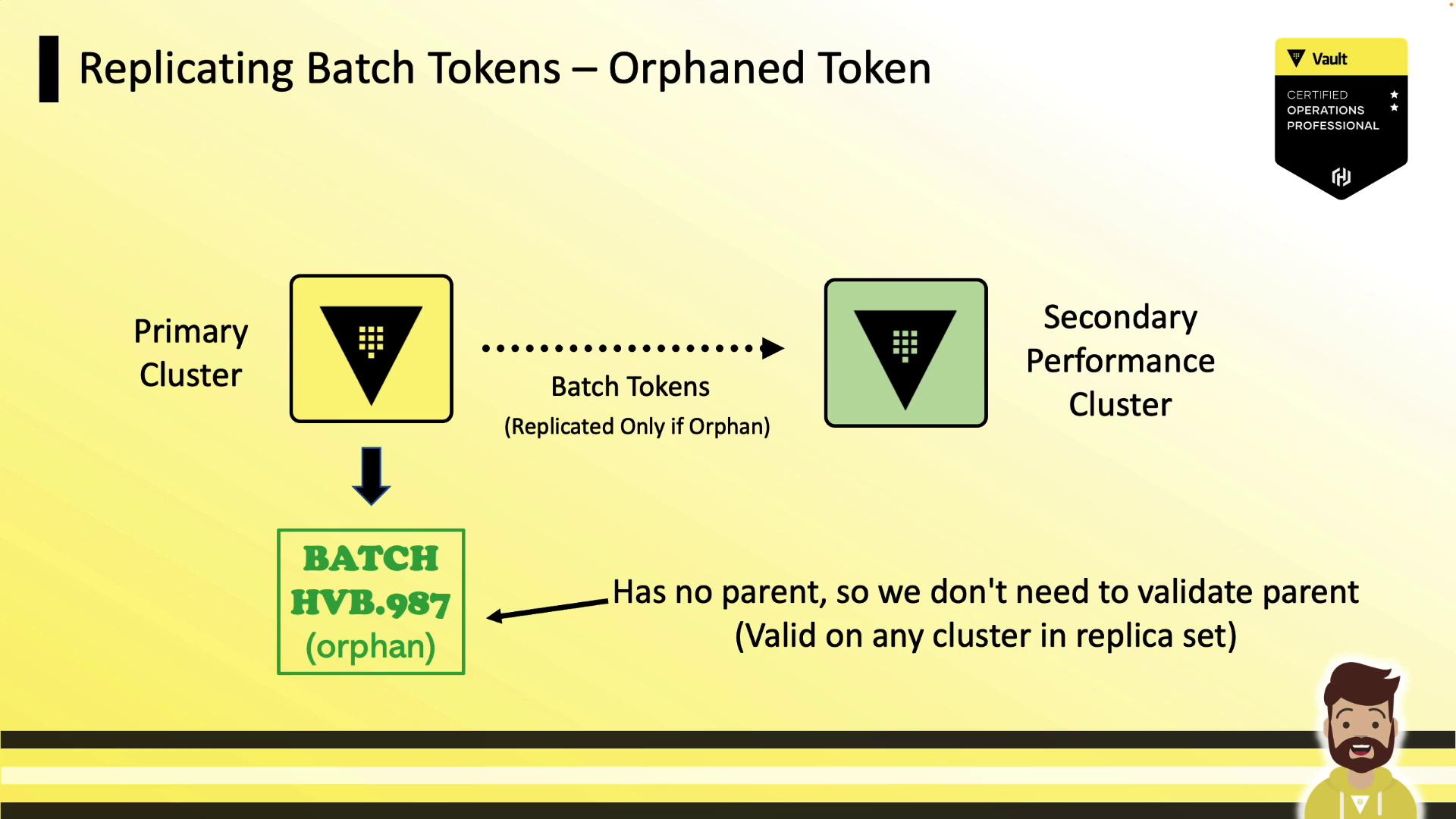
Orphan Tokens
Orphan batch tokens have no parent and are automatically replicated to all performance and DR clusters. Use these when you need a single token valid across multiple clusters.
Creating Batch Tokens
Direct Token Creation
Use the vault token create command:
vault token create -type=batch -orphan=true -policy=hcvop
Example output:
Key Value
--- -----
Token hvb.AAAAAQKsxnAqTz0Ah3qu5Hc4Q31YdqCocdDZjLXhyLAjuhhBJktOCrBaIJVbKwE6AVsxD6WAFvlI2ZUHs2MUb1gcpqYvro-kfVv
token_accessor n/a
token_duration 768h
token_renewable false
token_policies ["default" "hcvop"]
Note
The -orphan=true flag ensures this token replicates across performance and DR clusters.
Via AppRole
Configure an AppRole to issue batch tokens:
vault write auth/approle/role/hcvop \
policies=devops \
token_type="batch" \
token_ttl="60s"
DR Operations Batch Token
A DR operations batch token lets you promote a DR secondary without needing unseal or recovery keys. Grant it the following permissions:

path "sys/replication/dr/secondary/promote" {
capabilities = ["update"]
}
path "sys/replication/dr/secondary/update-primary" {
capabilities = ["update"]
}
path "sys/storage/raft/autopilot/state" {
capabilities = ["update", "read"]
}
- Create an orphan batch token with the
dr-opspolicy:vault token create -type=batch -orphan=true -policy=dr-ops - Use it to promote the DR secondary:
vault write sys/replication/dr/secondary/promote
Summary
- Batch tokens are lightweight, non-persistent tokens for high-throughput workloads.
- Only orphan batch tokens replicate to performance and DR clusters.
- Token prefixes (
hvs.,hvb.,hvr.) and lengths help identify types. - Create batch tokens directly or via auth methods like AppRole.
- Use DR operations batch tokens to streamline disaster recovery promotions.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content