Table of Contents
- Prerequisites
- Creating an Agent Pool and Token
- Installing and Running an Agent on Linux
- Running an Agent in Docker
- Agent Auto-Update Behavior
- Configuring a Workspace for Agent Execution
- Running Terraform via the Agent
- Scaling with Multiple Agents
- Managing Pools and Tokens
- References
Prerequisites
- A Terraform Cloud organization on the Business tier
- Permissions to manage Settings → Agents
- Outbound TCP/443 connectivity to
app.terraform.io
Agents use a pull-based model and require only outbound TCP/443 access to Terraform Cloud.
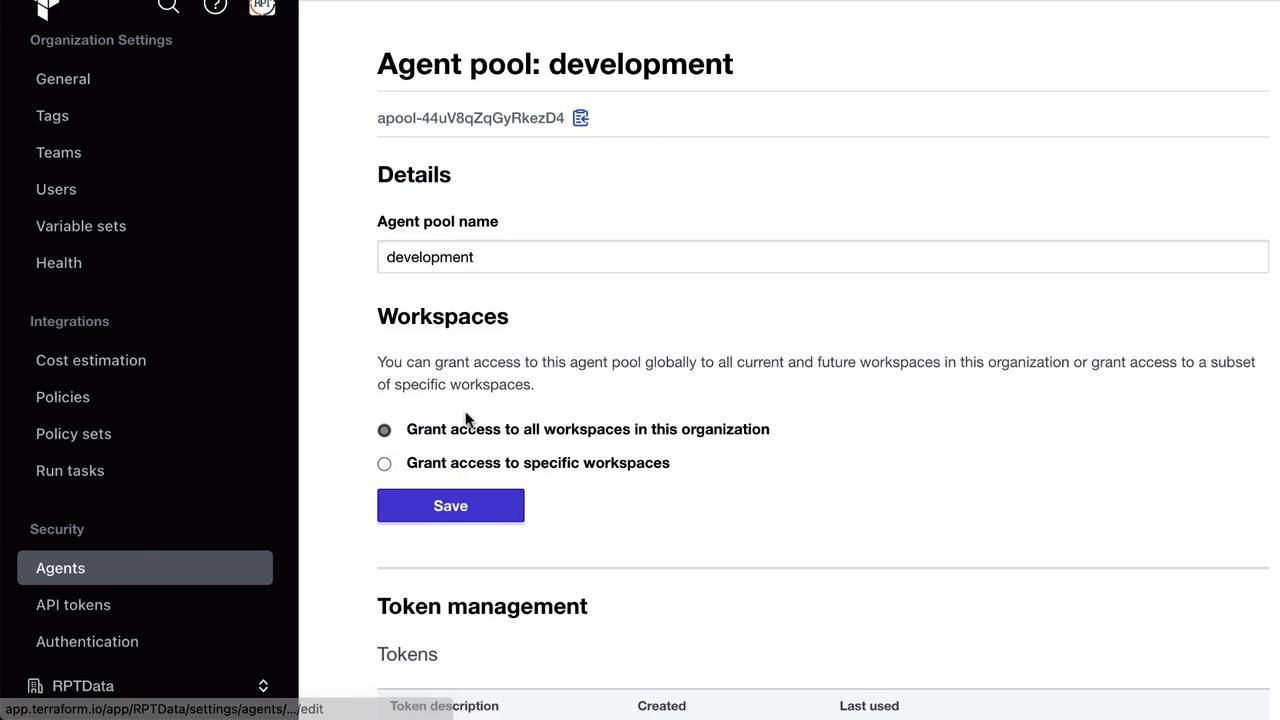
Creating an Agent Pool and Token
An Agent Pool is a logical group of self-hosted agents. You scope pools to environments (e.g.,development, production) and assign tokens for authentication.
| Component | Description | Example Command |
|---|---|---|
| Agent Pool | Logical grouping of agents | Manage under Settings → Agents |
| API Token | Scoped to one pool; used by each registered agent | Created via the Create token button |
| Agent Name | Unique identifier for each host/container | east-dc-1, us-west-2 |
- Navigate to Settings → Agents in your Terraform Cloud organization.
- Click New Agent Pool, name it (e.g., development), and save.
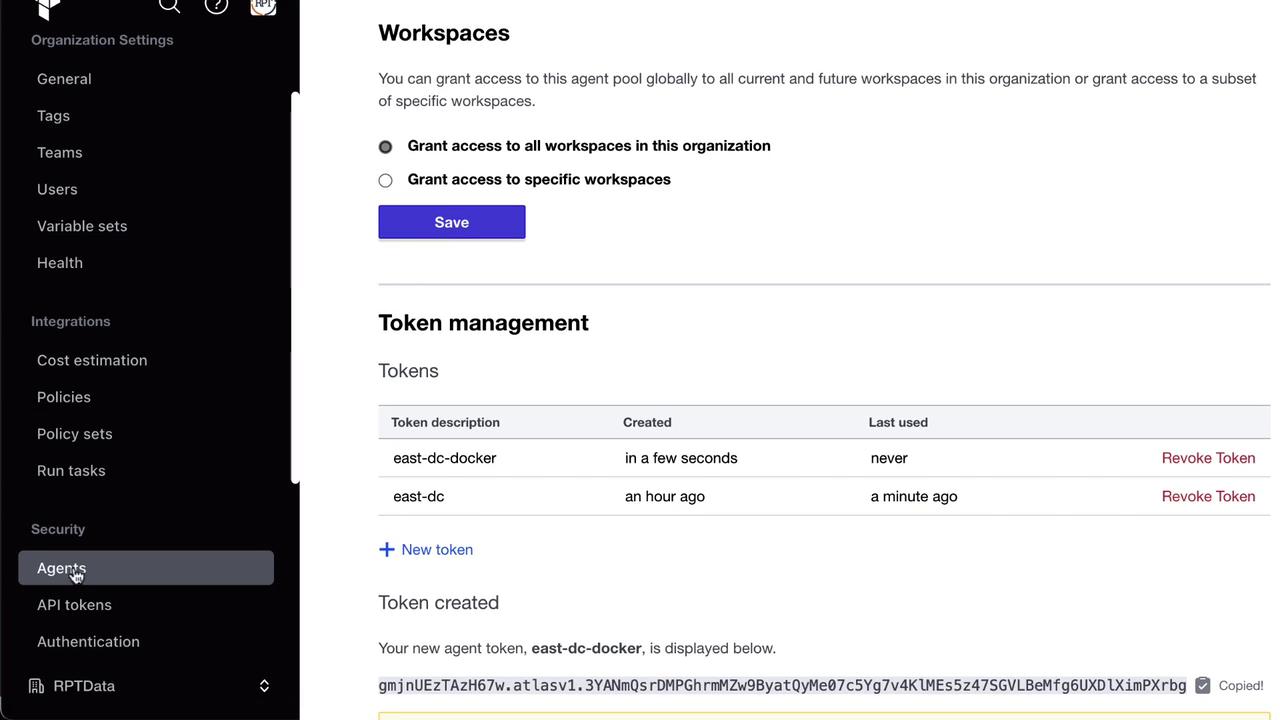
- In the pool’s page, click Create token, scope it to your data center or environment (e.g.,
EastDC), and copy the value.
Keep your agent tokens confidential. Rotate or revoke tokens regularly to maintain security.
Installing and Running an Agent on Linux
Download and unzip the latest agent binary on any Linux host: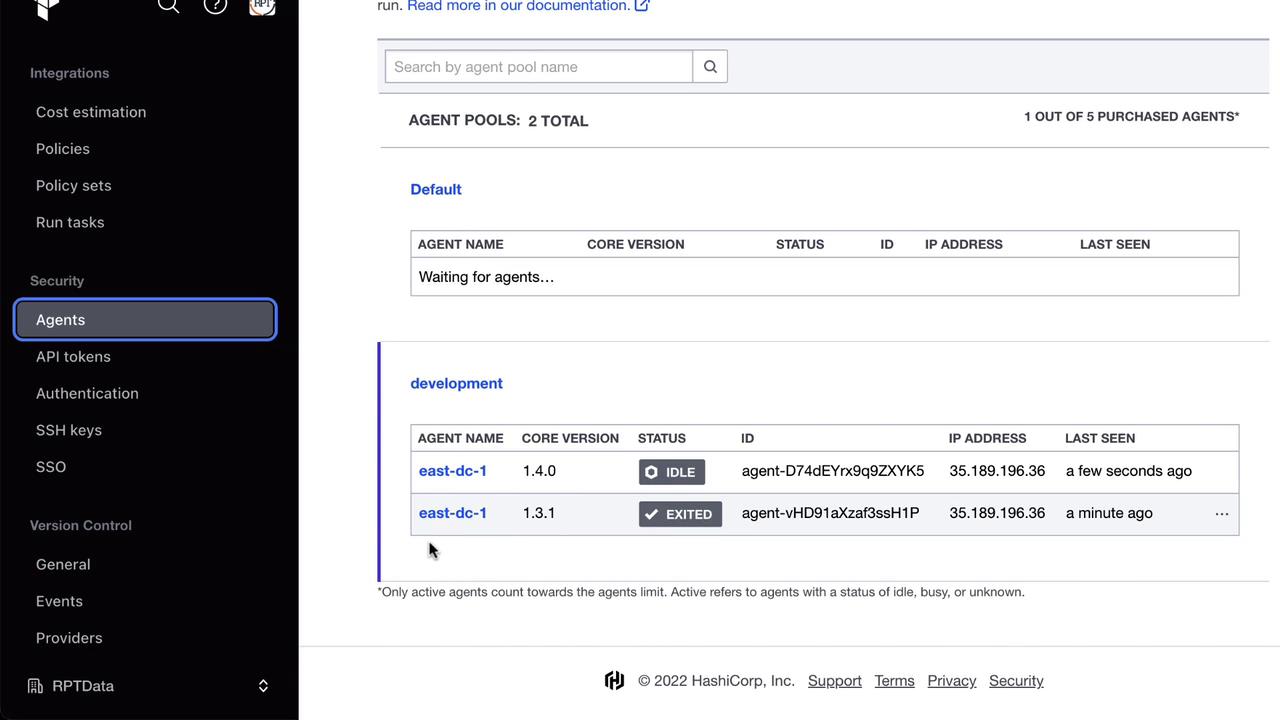
Running an Agent in Docker
Alternatively, launch an agent as a Docker container:latest image, auto-updates its core if enabled, and registers to your specified pool.
Agent Auto-Update Behavior
Agents check for newer core versions by default. Sample logs:Configuring a Workspace for Agent Execution
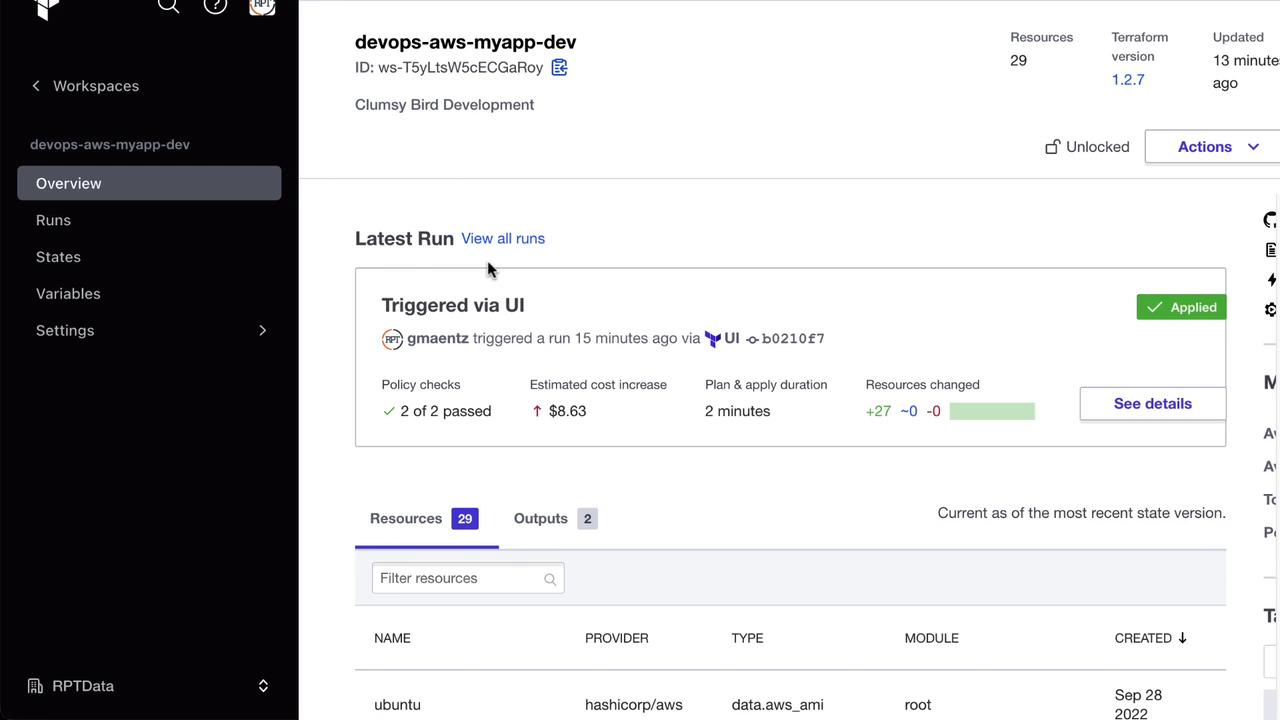
- Go to Workspaces → [Your Workspace] in Terraform Cloud.
- Under Settings → Execution Mode, select Agent.
- Choose your development pool and save.


Running Terraform via the Agent
Trigger a run in the workspace. The agent logs will indicate progress: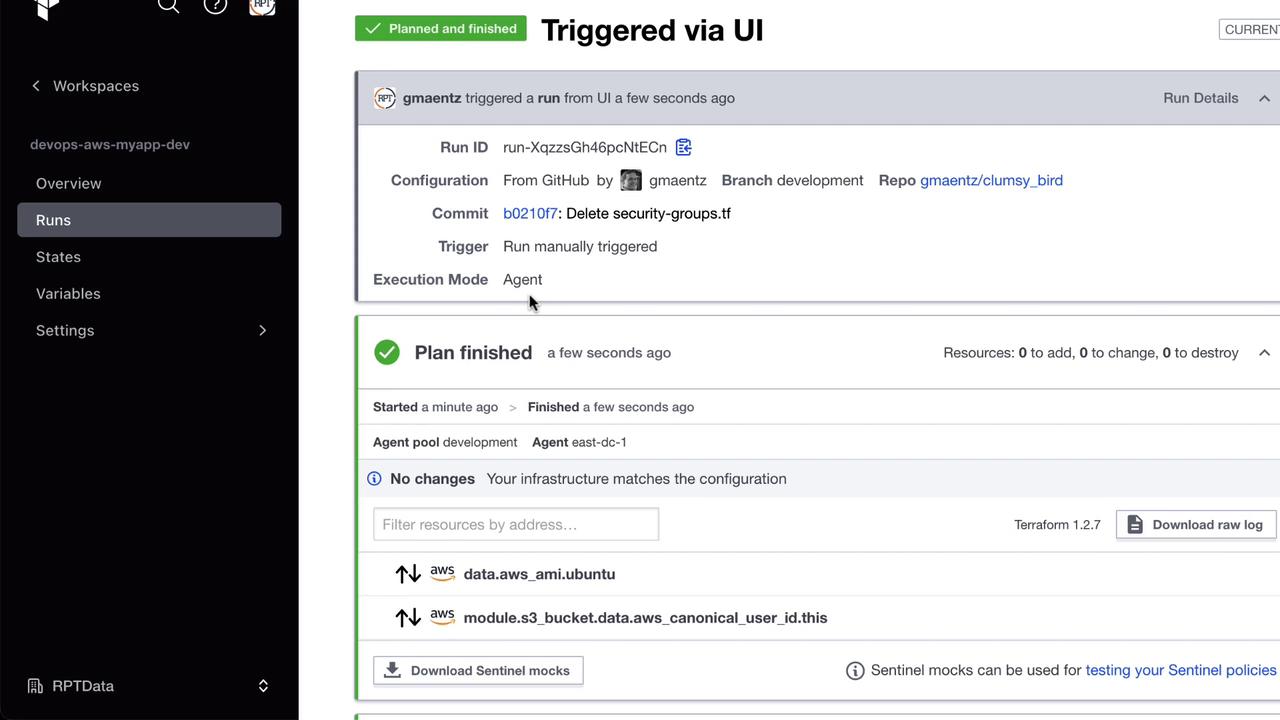
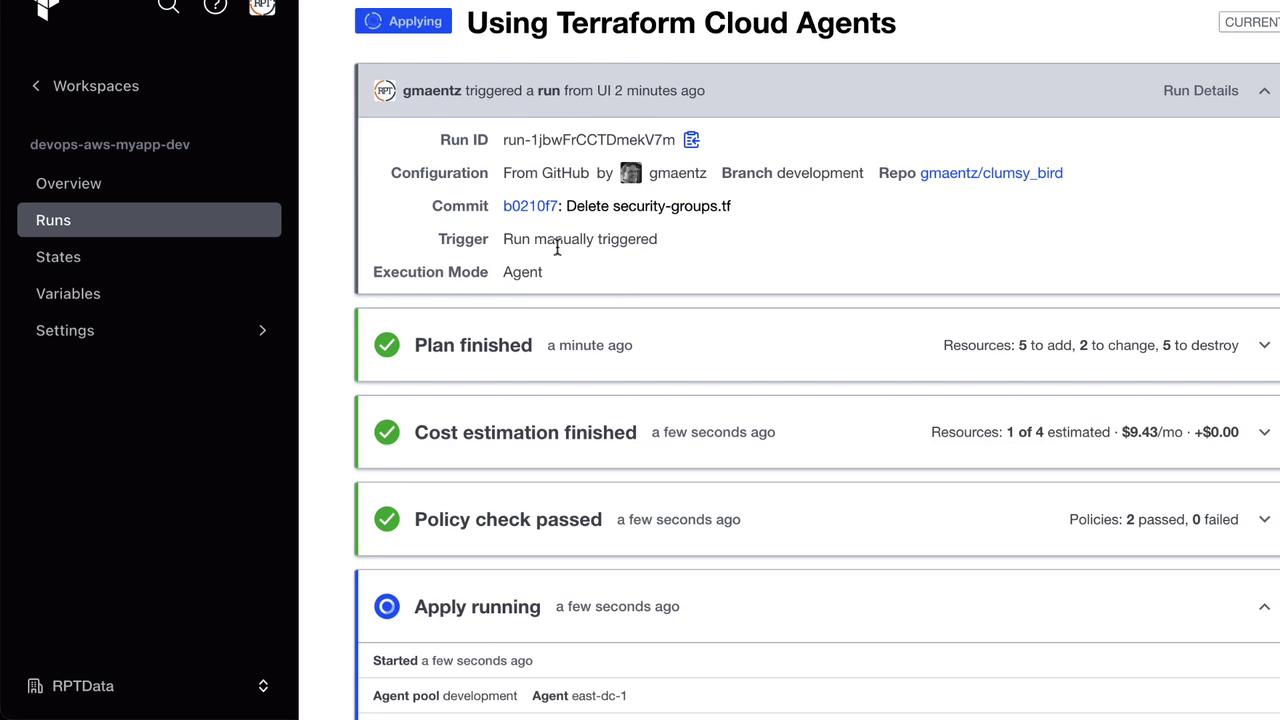
apply as well:
Scaling with Multiple Agents
To increase throughput, register additional agents to the same pool. Your Terraform Cloud license determines the maximum concurrent agents.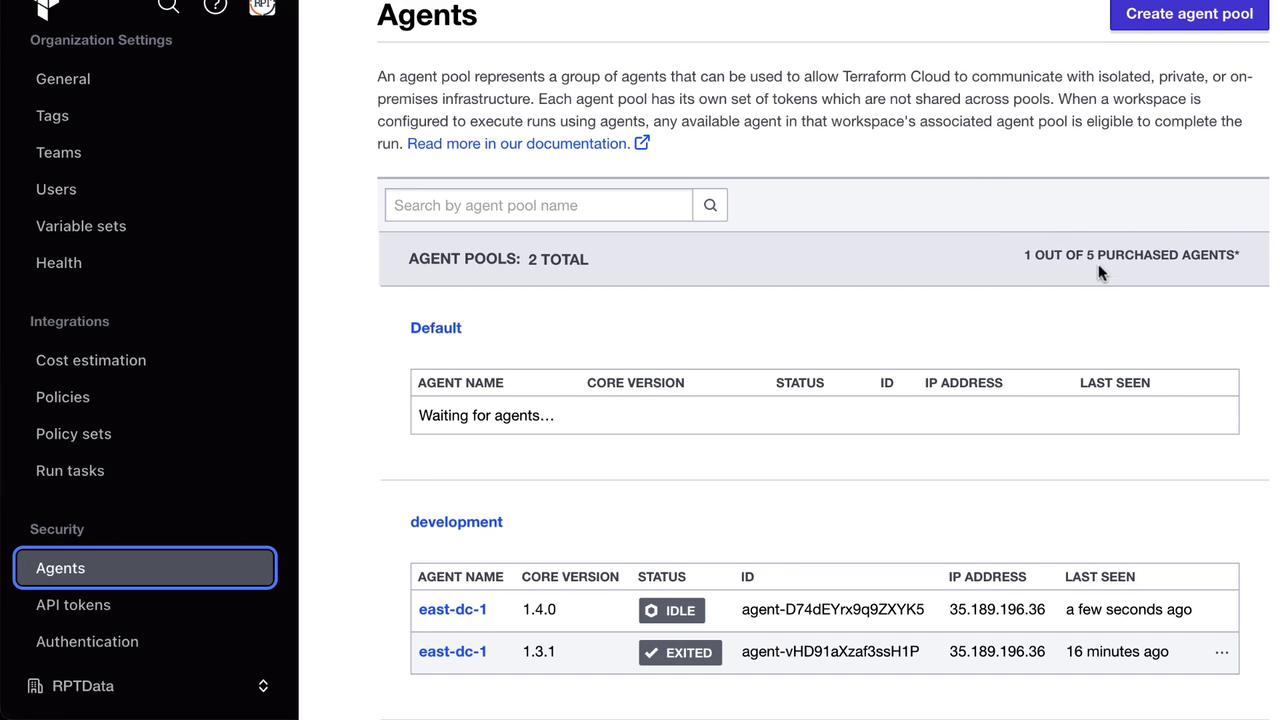
Managing Pools and Tokens
- Create multiple tokens per pool or assign one per agent.
- Rotate or revoke tokens under Settings → Agents → [Your Pool] → Tokens.
- Delete agents or pools when no longer in use—ensure they aren’t linked to active workspaces.