1. Workspace Isolation
Terraform Cloud workspaces each manage their own state, ensuring changes in one environment don’t affect another. In our example, HashiCat and Clumsy Bird are deployed in separate workspaces.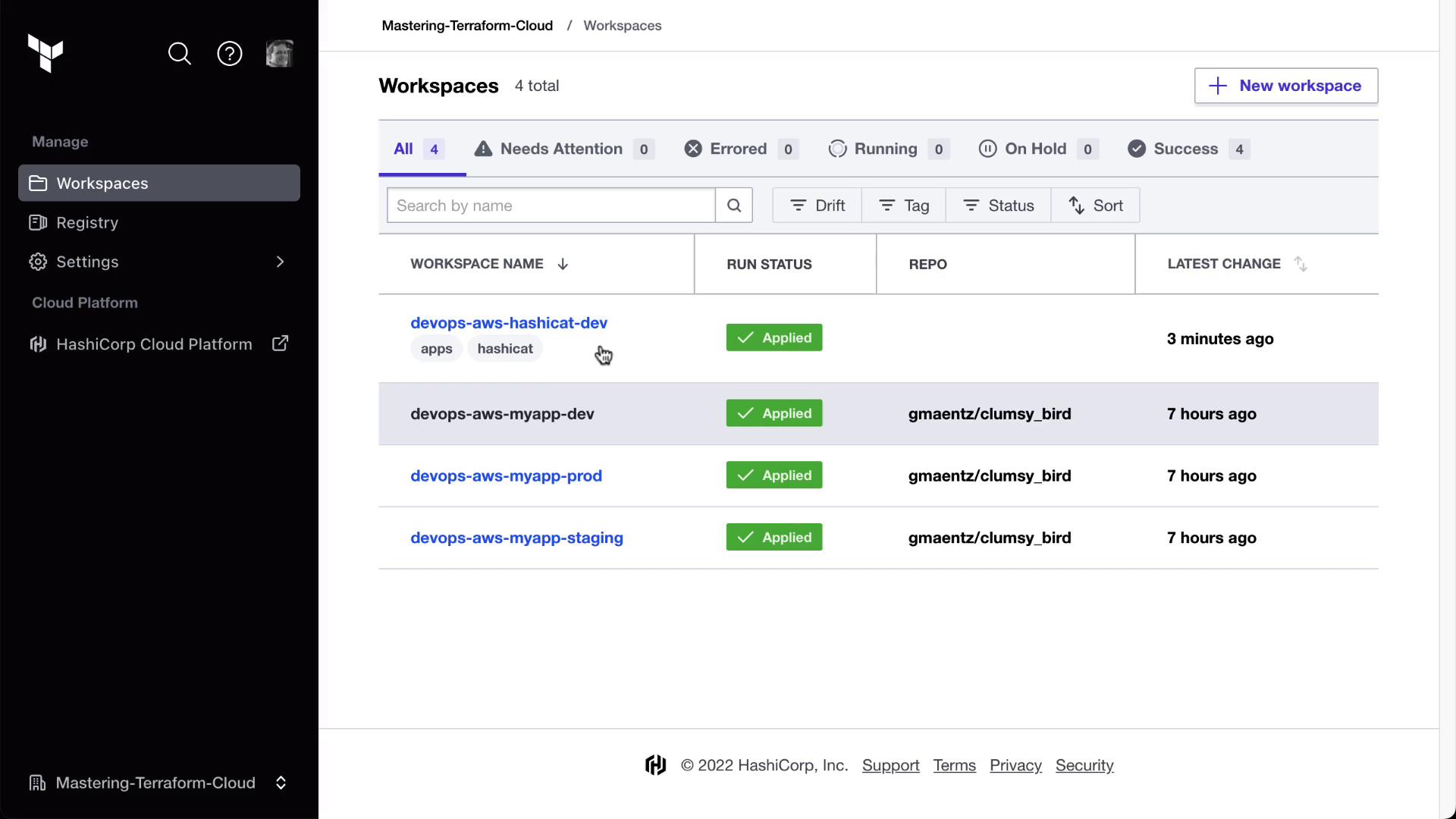
1.1 Sharing Outputs with tfe_outputs
To consume outputs from one workspace in another, use the tfe_outputs data source. Below is an example of pulling the Clumsy Bird URL into the HashiCat workspace.
backend.tf:
2. Authenticate and Setup
First, log in to Terraform Cloud from your CLI:
3. Enabling Remote State Sharing
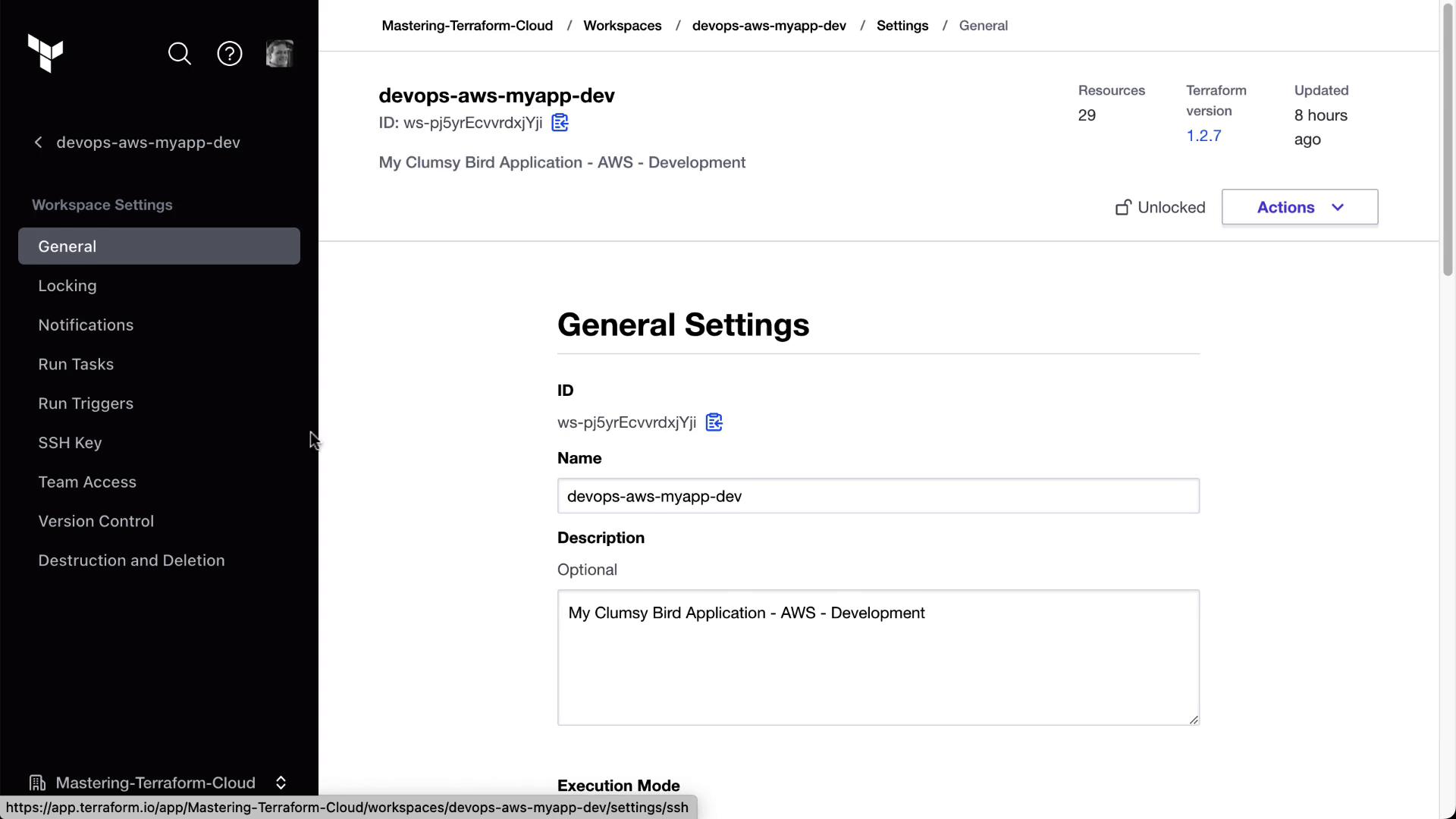
Allow downstream workspaces to read the state of an upstream workspace by enabling Remote State Sharing:- Navigate to the devops-aws-myapp-dev (Clumsy Bird) workspace.
- Go to Settings → General.
- Toggle Remote State Sharing on.
- Specify which workspaces (e.g., HashiCat) can access the state.
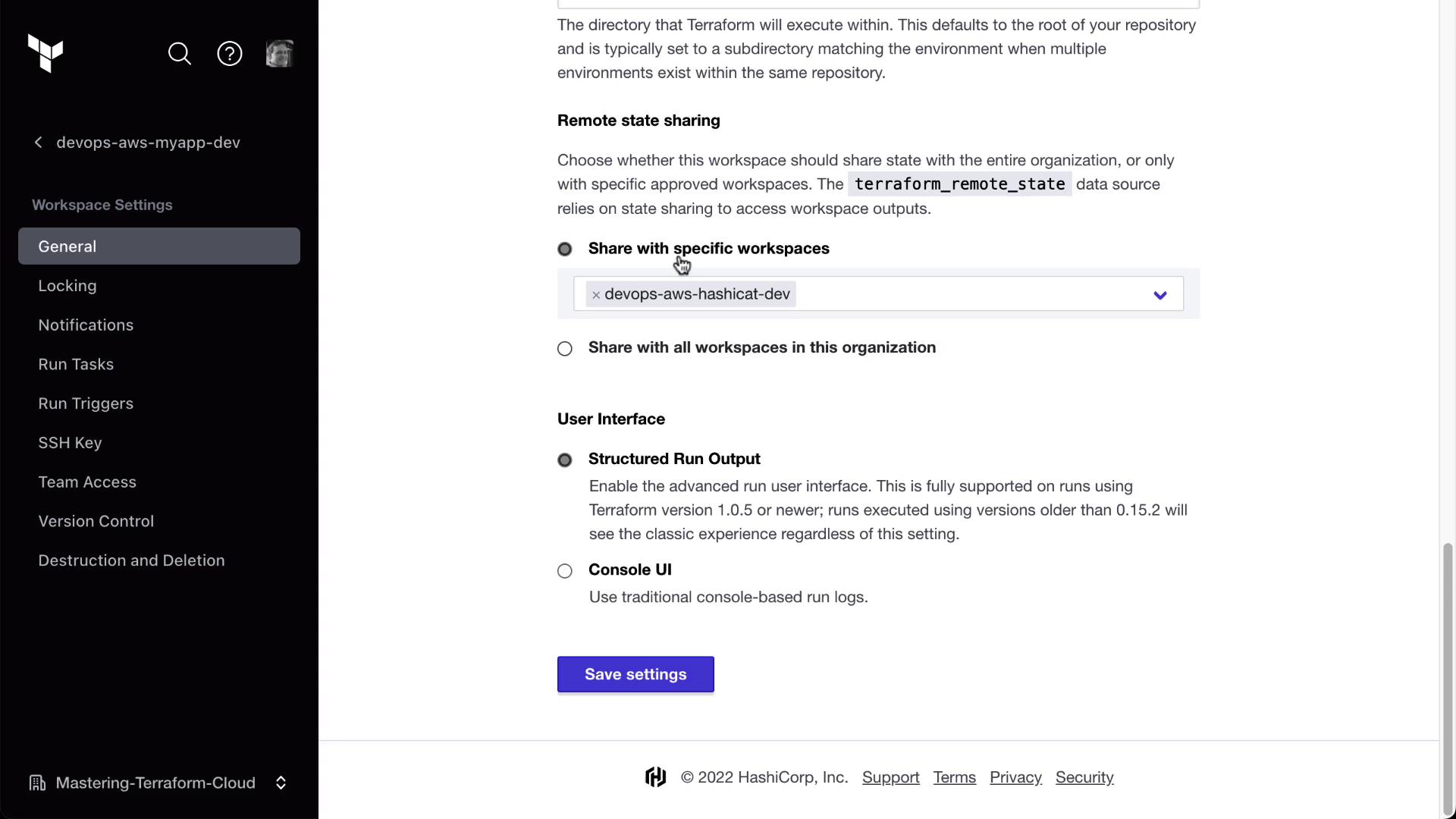
Only workspaces with Remote State Sharing enabled can be referenced by
tfe_outputs. Ensure you have the right permissions before sharing state.4. Configuring Run Triggers
Run triggers automatically queue a run in a downstream workspace after a successful apply in an upstream workspace.- In the HashiCat workspace, go to Settings → Run Triggers.
- Click Add Trigger, then select the devops-aws-myapp-dev workspace.
| Upstream Workspace | Downstream Workspace | Trigger Type |
|---|---|---|
| devops-aws-myapp-dev | HashiCat | On successful apply |
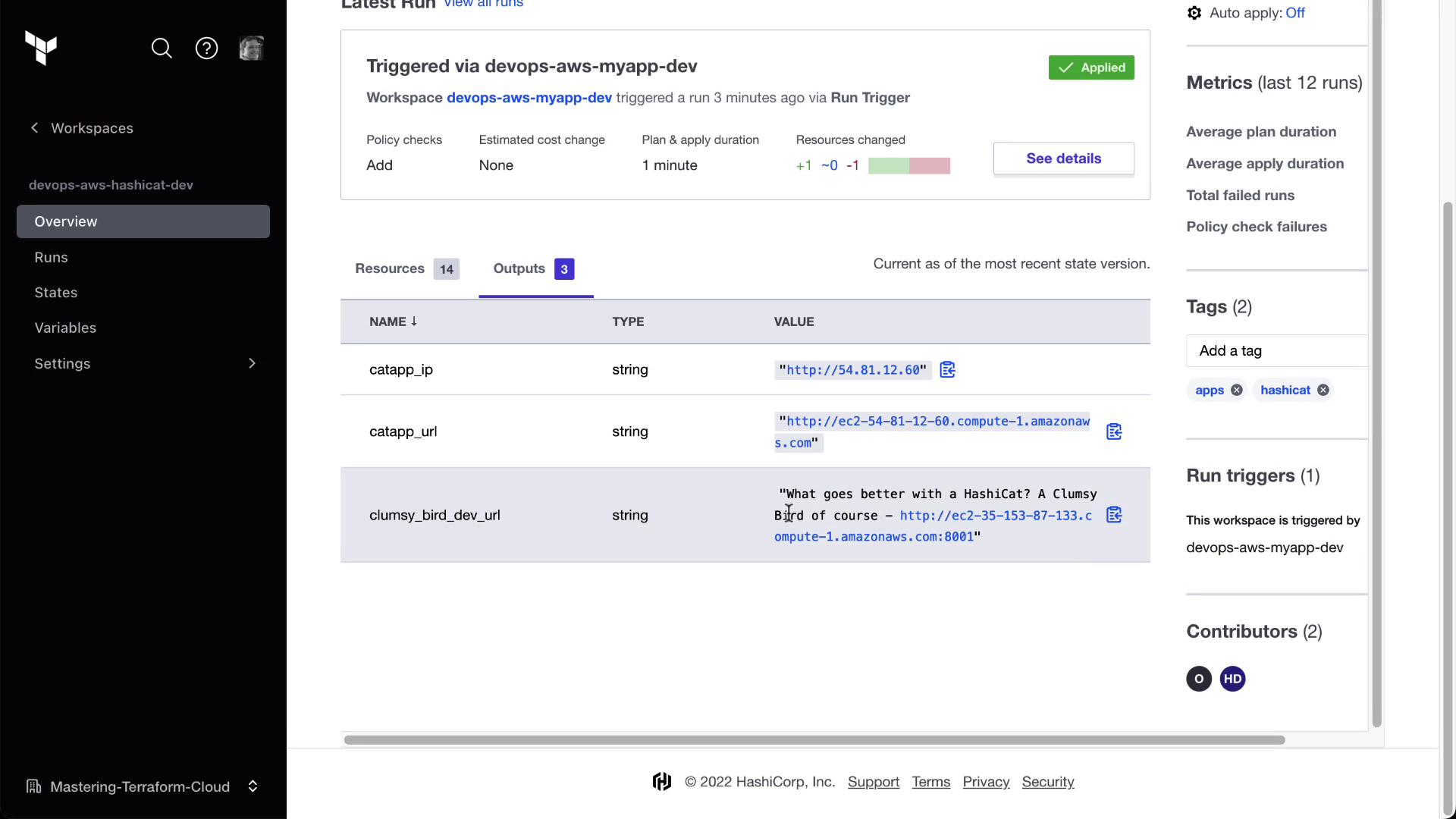
5. Demonstrating a Triggered Run
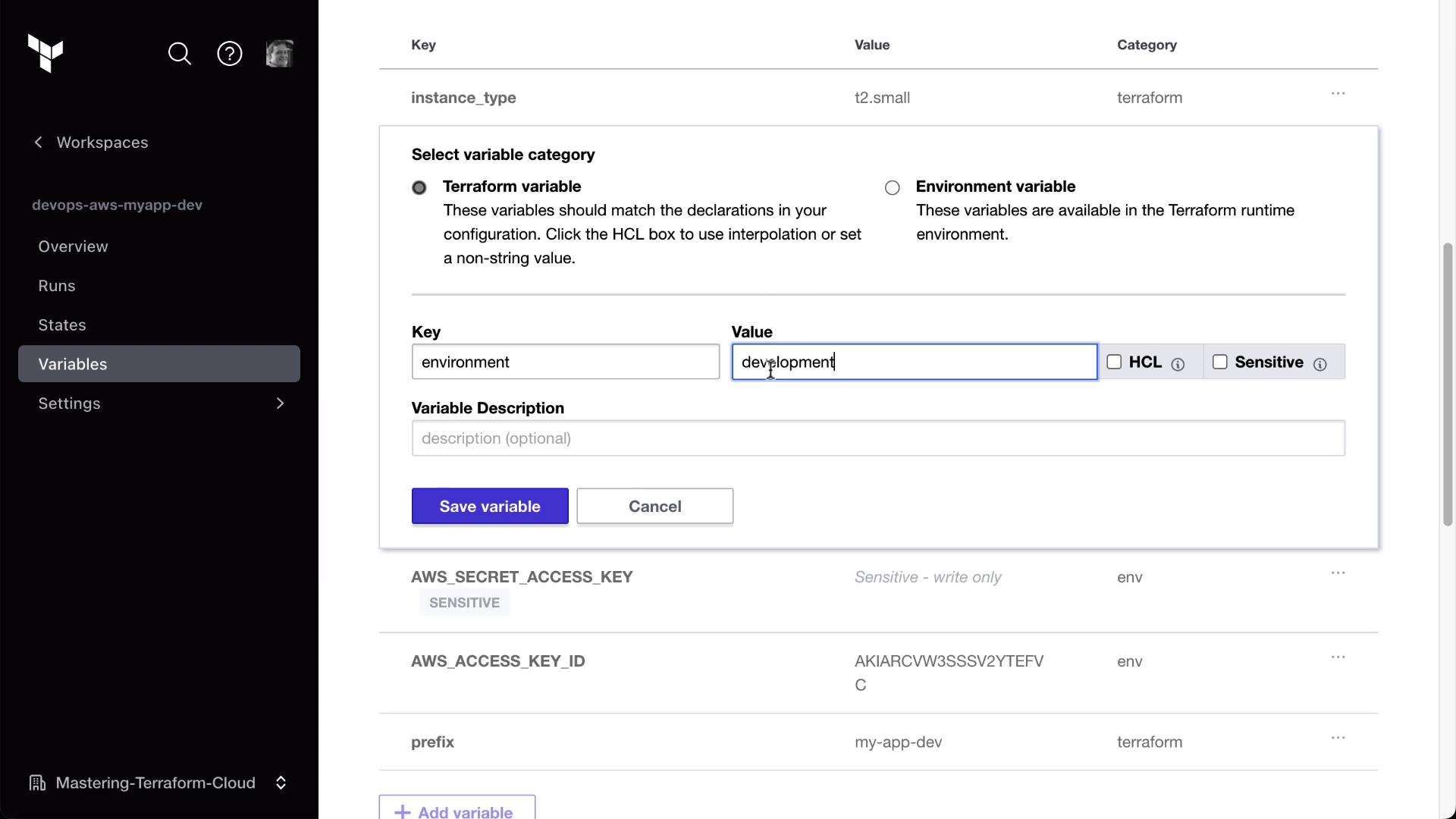
Follow these steps to see run triggers in action:- Update a Variable in Clumsy Bird
Modify any environment variable (e.g.,environment = "development-hashiCat2").
-
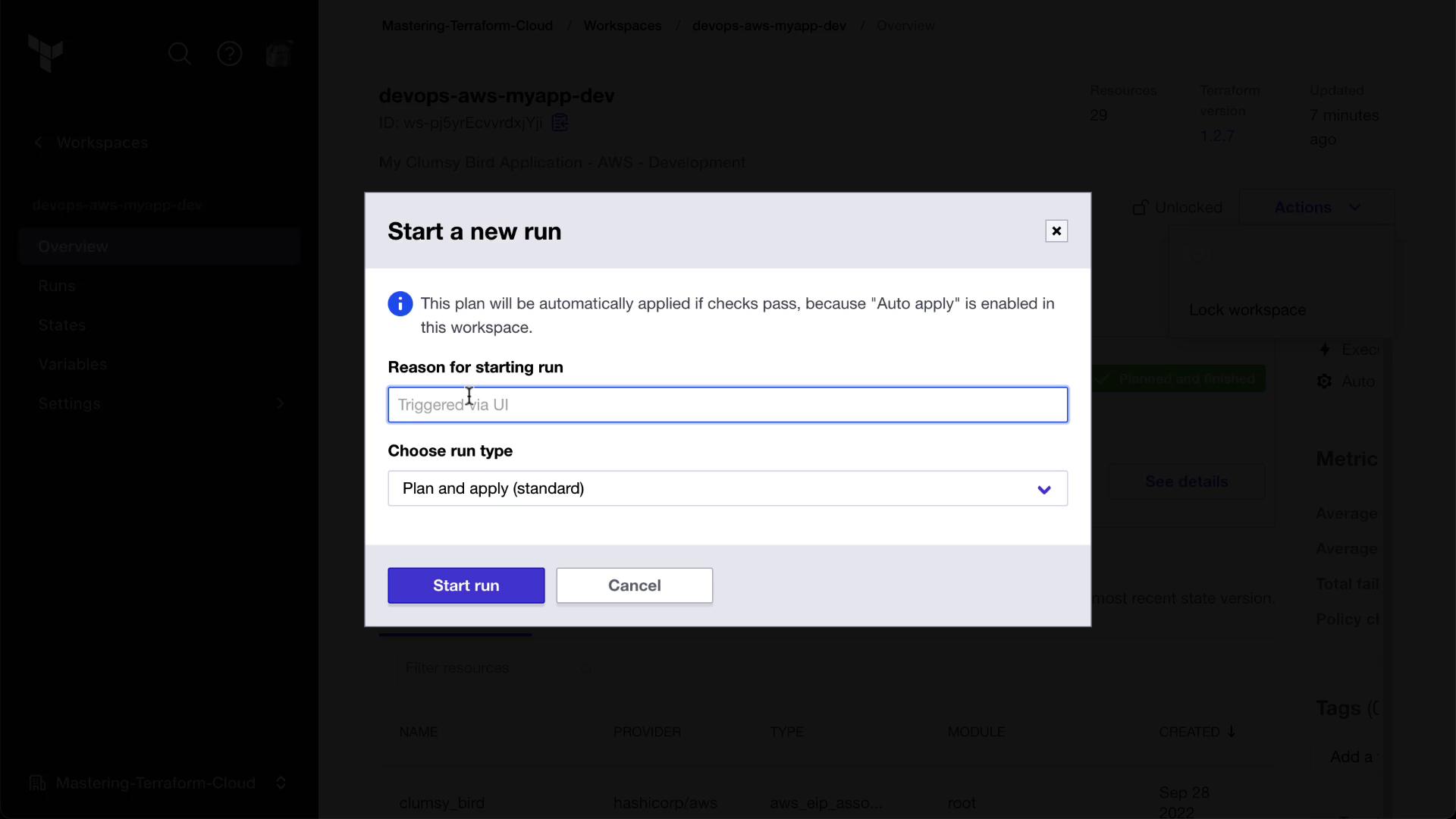
Start a New Run Manually
Trigger the change in Clumsy Bird.
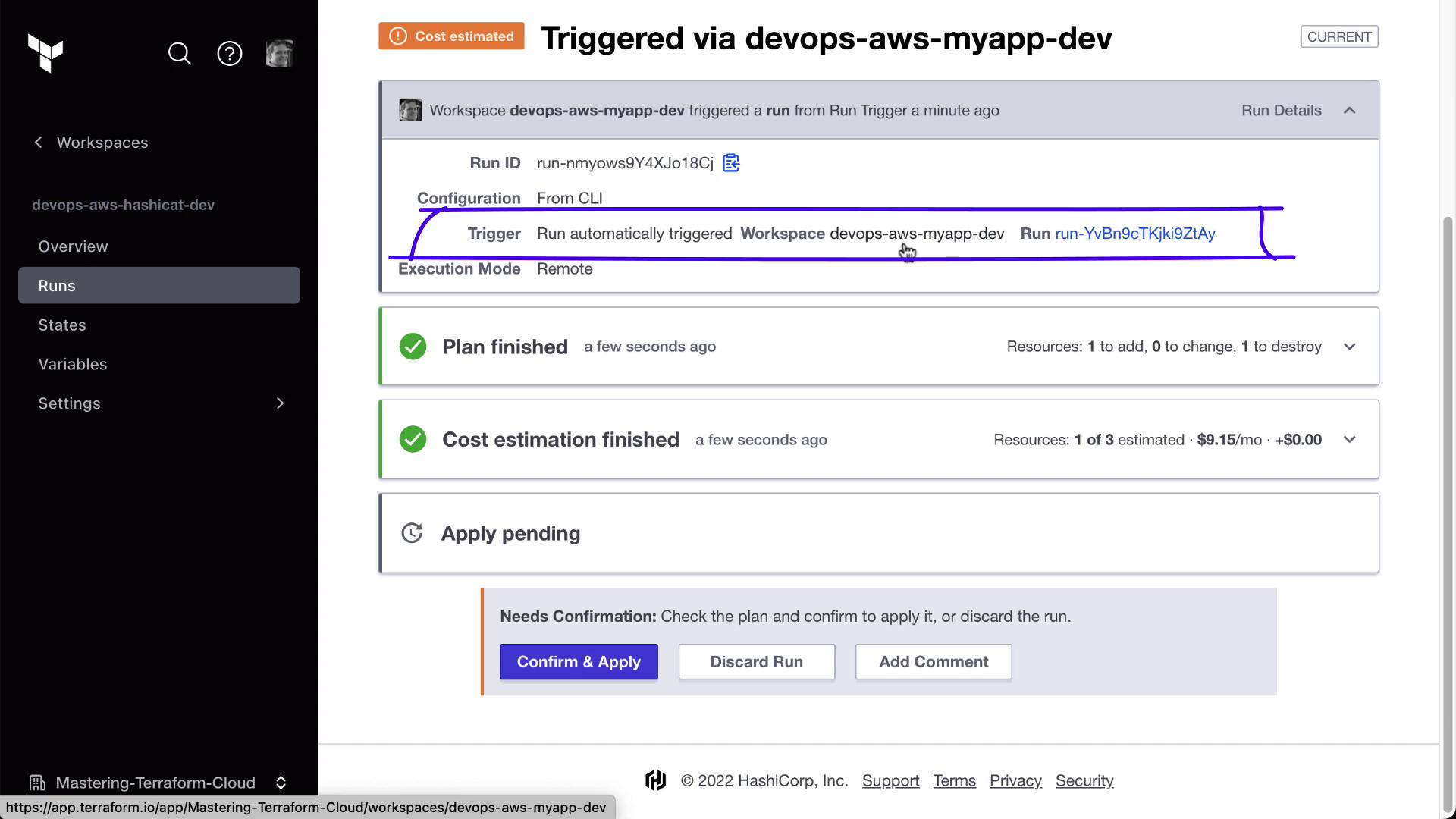
- Observe the Triggered Plan in HashiCat
After Clumsy Bird applies, HashiCat will queue a run automatically. Check the Runs tab for a trigger entry.
- Approve and Review Outputs
Approve the plan in HashiCat. You’ll now see the Clumsy Bird URL retrieved from the other workspace.
By isolating state and chaining workspaces with run triggers, you can build modular, resilient infrastructure pipelines in Terraform Cloud.