HashiCorp : Terraform Cloud
Introduction to Terraform Cloud
Demo Terraform Cloud
This guide provides a quick walkthrough of Terraform Cloud’s core features, including organization setup, workspace management, VCS integration, and the Private Module Registry. By the end, you’ll understand how to log in, configure settings, and use Terraform Cloud for collaboration and automation.
1. Logging In & Selecting an Organization
- Navigate to the Terraform Cloud login page and sign in with your credentials.
- From the dashboard, select the desired organization (e.g., Enterprise Cloud).
- You’ll now see a list of workspaces, each showing its run status, linked repository, and the timestamp of the latest change.

2. Plan & Billing Overview
Under Organization Settings > Plan & Billing, you can review and upgrade your subscription.
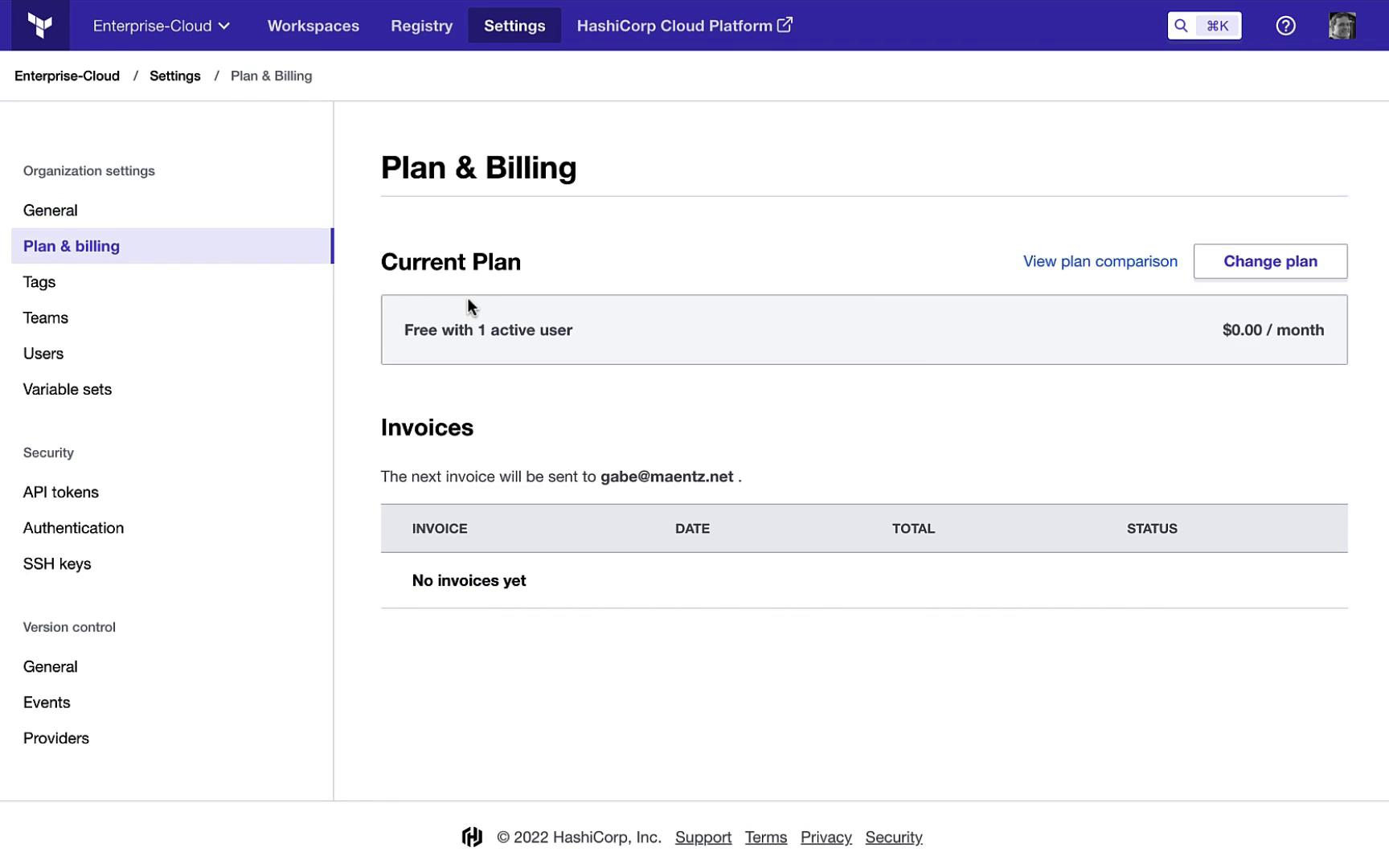
| Plan | Users | Workspaces | Remote State | VCS Integration | Private Module Registry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | Up to 5 | Unlimited | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Team | Up to 10 | Unlimited | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Team & Governance | Unlimited | Unlimited | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
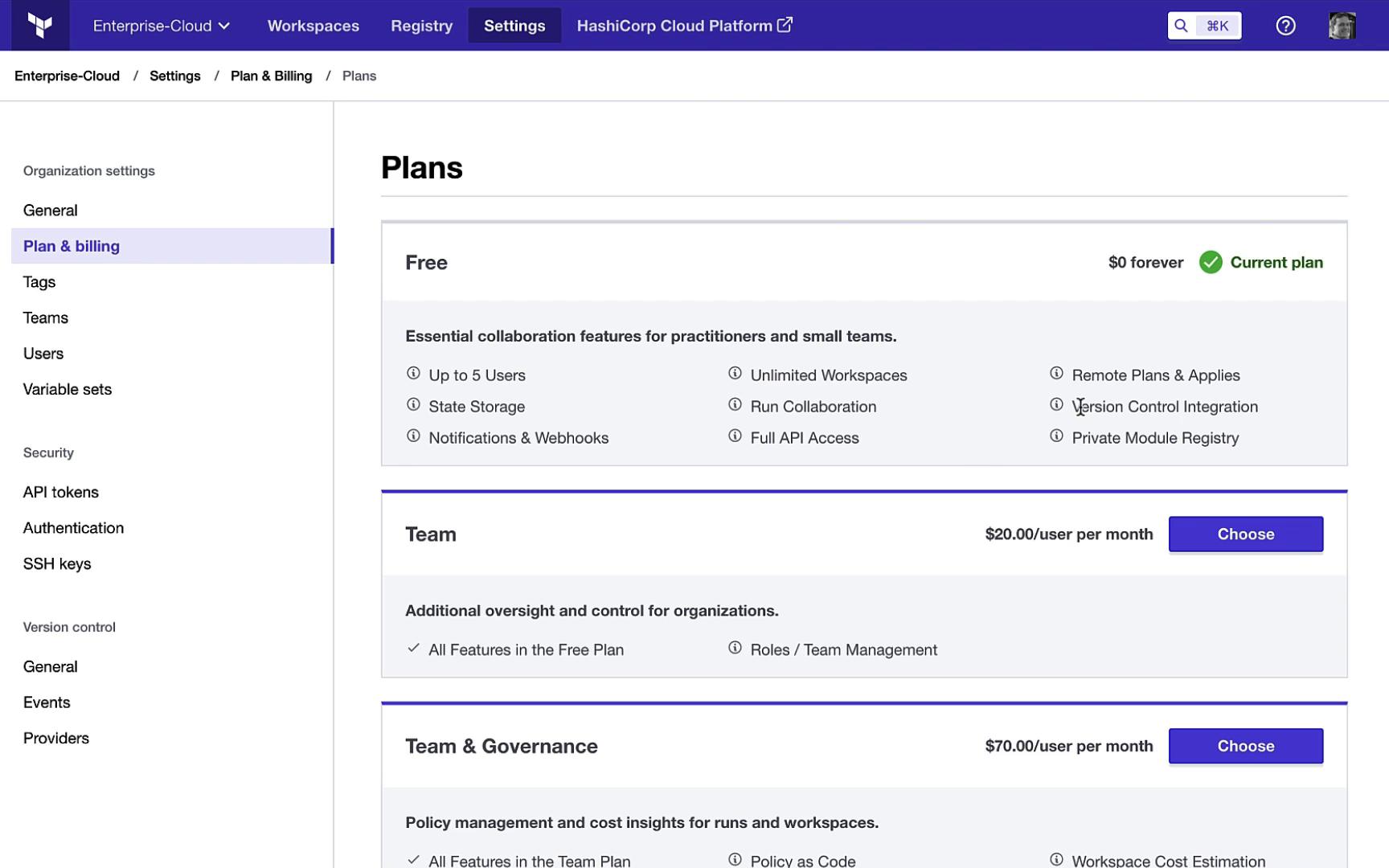
3. Workspace Dashboard
Overview of Runs & Resources
Select a workspace (e.g., devops-aws-myapp-dev) to see details of recent runs, resource changes, and performance metrics.

A chronological log of all plan and apply events shows branch names, trigger methods, and statuses at a glance.
Terraform Cloud securely stores and versions your state file. Here’s an example of a raw state export:
{
"version": 4,
"terraform_version": "1.0.7",
"serial": 8,
"lineage": "06f59866-a545-55ba-439a-41e55ed551ba",
"outputs": {
"clumsy-bird-ip": {
"value": "http://52.71.182.141",
"type": "string"
},
"clumsy-bird-url": {
"value": "http://ec2-52-71-182-141.compute-1.amazonaws.com",
"type": "string"
}
}
}
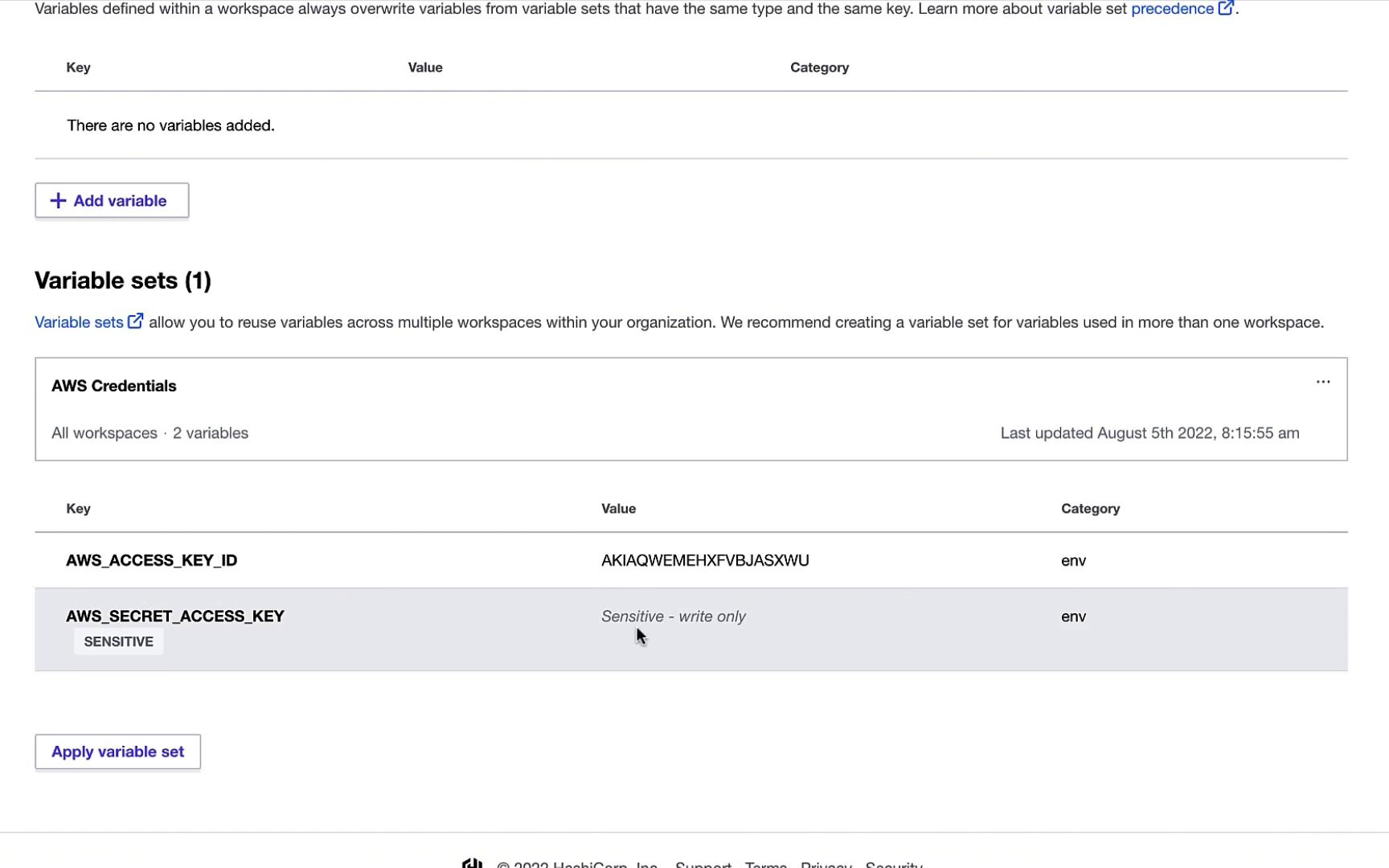
4. Managing Variables & Secrets
At the workspace level, define Terraform variables and reference organization-level variable sets for sensitive data (e.g., AWS credentials). This ensures secrets never appear in your configuration files.
Note
Use organization-level variable sets to centralize credential management and avoid committing secrets to VCS.
5. Execution Modes: Manual & Remote
You can lock a workspace during maintenance to prevent changes. Unlock it to run Plan & Apply or Plan Only directly in Terraform Cloud’s UI.
6. Configuring Workspace Settings
Under General Settings, adjust the workspace ID, name, description, execution mode (remote or local), apply method (auto or manual), and Terraform version.

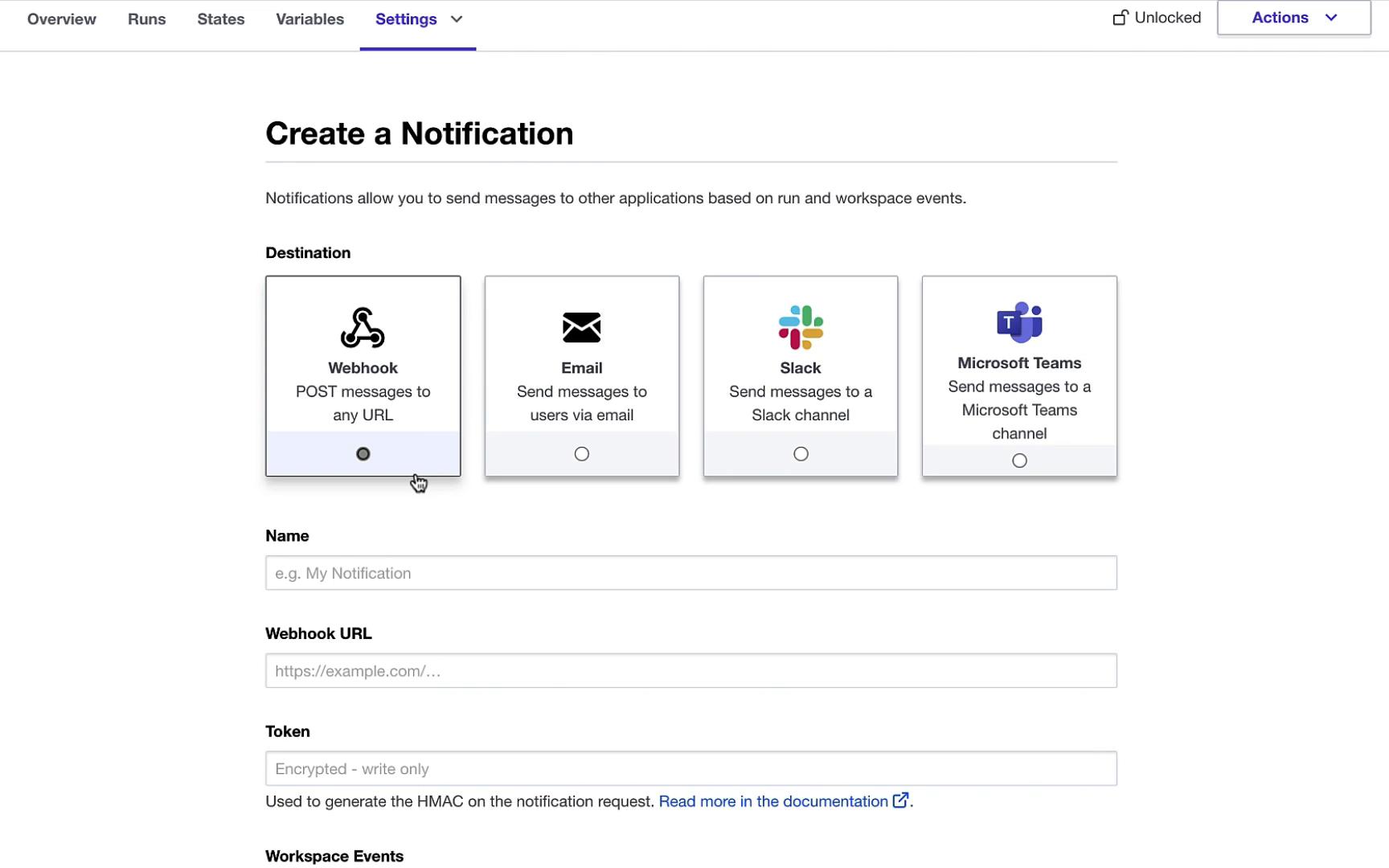
7. Setting Up Notifications
Create alerts for run events—such as plan completion or apply failures—via Webhook, Email, Slack, Microsoft Teams, or custom channels.
8. Version Control Integration
Connect workspaces to GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, or Azure DevOps. Commits, pull requests, and merges can automatically trigger plans (and applies, if enabled).

9. Workflow Options
Terraform Cloud supports multiple workflows:
| Workflow | Trigger Method |
|---|---|
| VCS-driven | Commits, PR merges |
| CLI-driven | terraform login + terraform push |
| API-driven | Direct API calls for runs and applies |

10. Reviewing GitHub-Triggered Runs
Click on a Git commit in Terraform Cloud to see what changed. For example, an HCL module definition might look like this:
module "security-group-http" {
source = "app.terraform.io/Enterprise-Cloud/security-group/aws//modules/http-80"
version = "4.8.0"
name = "http-traffic-${var.environment}"
description = "Security group for ${var.environment} with HTTP ports open within VPC"
}
Back in the workspace, you’ll find run metrics, tags, and access controls for contributors.

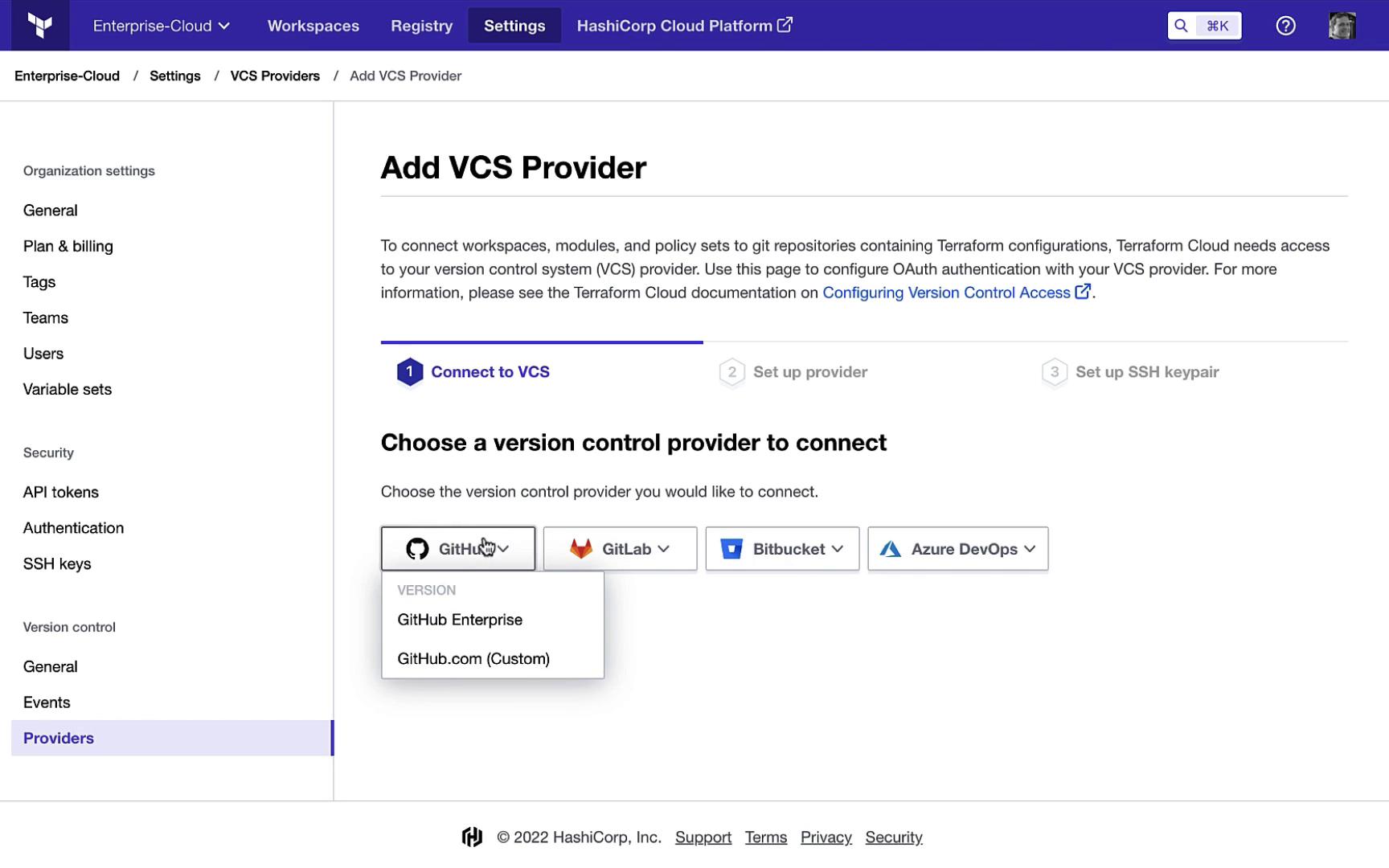
11. Teams, Users & VCS Providers
Invite users or teams, assign roles, and add version control providers under Organization Settings > VCS Providers.
12. Exploring the Private Module Registry
Terraform Cloud’s Private Module Registry lets your team browse, version, and share modules securely within your organization.

Use a private module in your configuration:
module "vpc" {
source = "app.terraform.io/EnterpriseCloud/vpc"
version = "2.34.0"
# insert required variables here
}
credentials "app.terraform.io" {
# valid user API token
token = "xxxxxx.atlasv1.zzzzzzzzzzzzz"
}
Browse and filter modules by provider and registry to find exactly what you need.

13. Monitoring Workspace Health
Keep track of workspaces that need attention, currently running environments, or those with failed runs. Use filters to quickly locate specific environments like “dev.”



Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content