HashiCorp : Terraform Cloud
Securing Variables with Terraform Cloud
Terraform Cloud Variables
Terraform variables in HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) let you parameterize your infrastructure code without changing module source files. By centralizing values in Terraform Cloud workspaces, you can:
- Keep secrets out of version control
- Reuse the same configurations across environments
- Simplify CI/CD with remote execution
Warning
Never commit sensitive data (API keys, credentials, or tokens) directly in your .tf files. Always mark secrets as Sensitive in Terraform Cloud.
Workspace Variables vs. Organization Variable Sets
Terraform Cloud offers two scopes for storing variable values:
| Variable Scope | Defined At | Sensitivity Support | Applies To | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workspace Variables | Single workspace | Yes | One workspace only | AWS credentials, DB passwords |
| Organization Variable Sets | Organization level | Yes | Multiple workspaces | Shared cloud provider tokens |
Workspace Variables
- Scoped to an individual workspace.
- Can be flagged Sensitive to hide in UI, CLI output, and logs.
- Ideal for per-environment secrets like
aws_access_key_id.
Organization Variable Sets
- Defined at the organization level for reuse.
- Supports both Terraform input variables and environment variables.
- Workspaces must opt in to inherit the set.
- Perfect for credentials or settings shared by multiple projects.
Input Variables vs. Environment Variables
Terraform Cloud recognizes two types of variables:
| Variable Type | Reference in HCL | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Terraform Input Variable | var.<name> | var.subscription_id, var.db_connection |
| Environment Variable | <NAME> env var | AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, TF_LOG, GOOGLE_CRED |
All variables can be marked Sensitive to prevent exposure in logs or the web UI. Terraform also supports HCL types like string, number, list, and map.
Setting Variables Locally
Even with remote execution, you can still supply values from your workstation:
# Single variable
terraform plan -var="name=value"
# Load from a file
terraform apply -var-file="env.prod.tfvars"
# Export as environment variable
export TF_VAR_region=us-west-2
terraform apply
Terraform 0.10.0+ automatically loads any *.auto.tfvars in your working directory:
# Rename your terraform.tfvars
mv terraform.tfvars terraform.auto.tfvars
Note
Using terraform.auto.tfvars lets you track non-sensitive defaults in Git while still overriding them via the CLI or workspace UI.
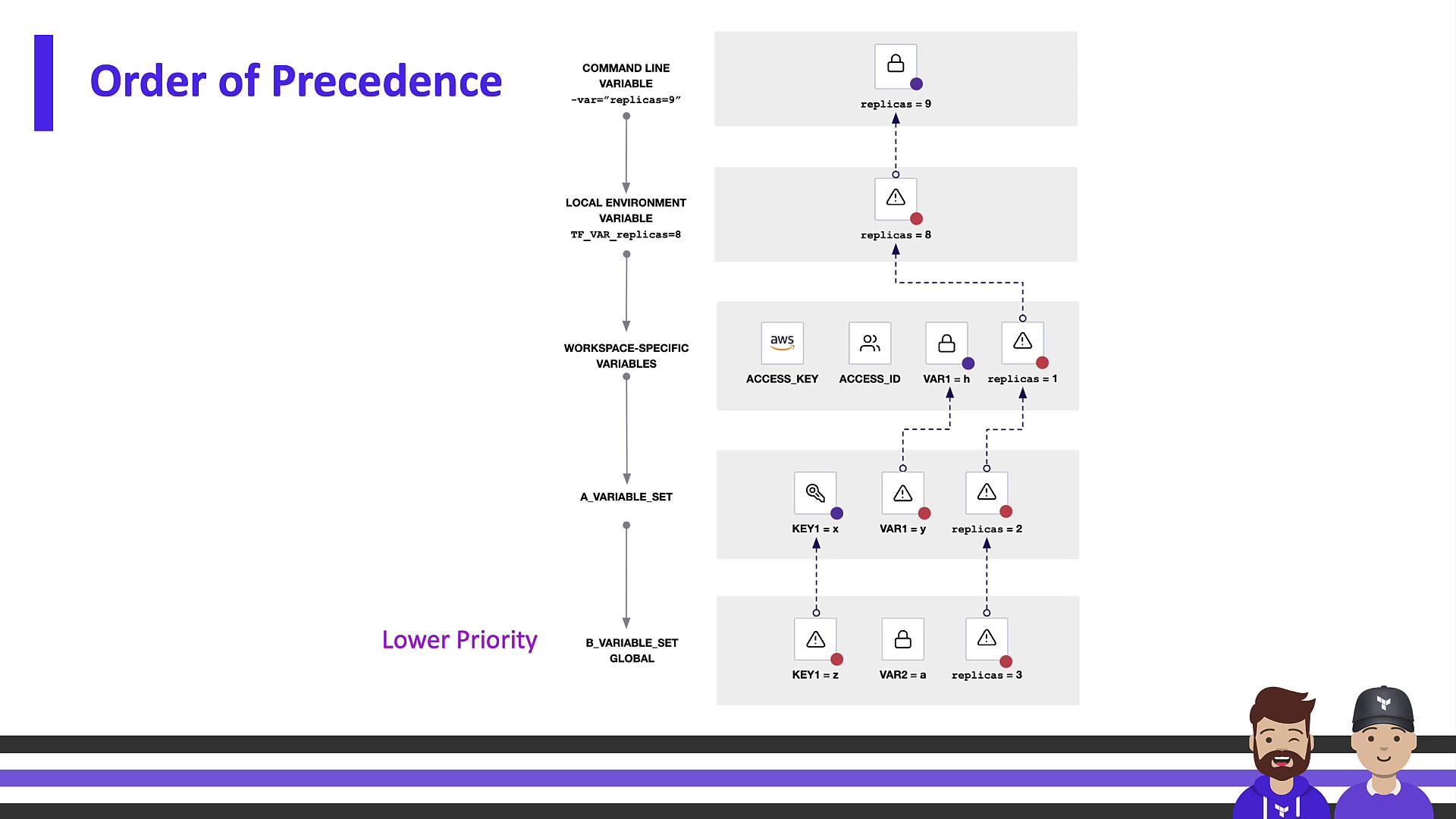
Variable Precedence
When a variable exists in multiple locations, Terraform applies values based on this hierarchy (highest → lowest):
- CLI flags (
-varor-var-file) - Workspace UI variables
- Organization Variable Sets
- Auto-loaded
*.auto.tfvarsfiles
Command-line inputs override workspace settings, which override organizational sets, which in turn override auto.tfvars defaults.

For more details, see the Terraform Cloud Variable Precedence documentation.
Best Practices & Recommendations
- Store non-sensitive defaults in
*.auto.tfvarsfiles and commit them to Git. - Keep sensitive values in Terraform Cloud—either at the workspace level or via Organization Variable Sets.
- Regularly rotate credentials and audit workspace variable access.
Links and References
- Terraform Cloud Variables Guide
- Terraform Input Variables
- Terraform CLI Docs
- HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL)
- Terraform Cloud Best Practices
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab