1. Review GitHub Repository and Terraform Cloud Workspaces
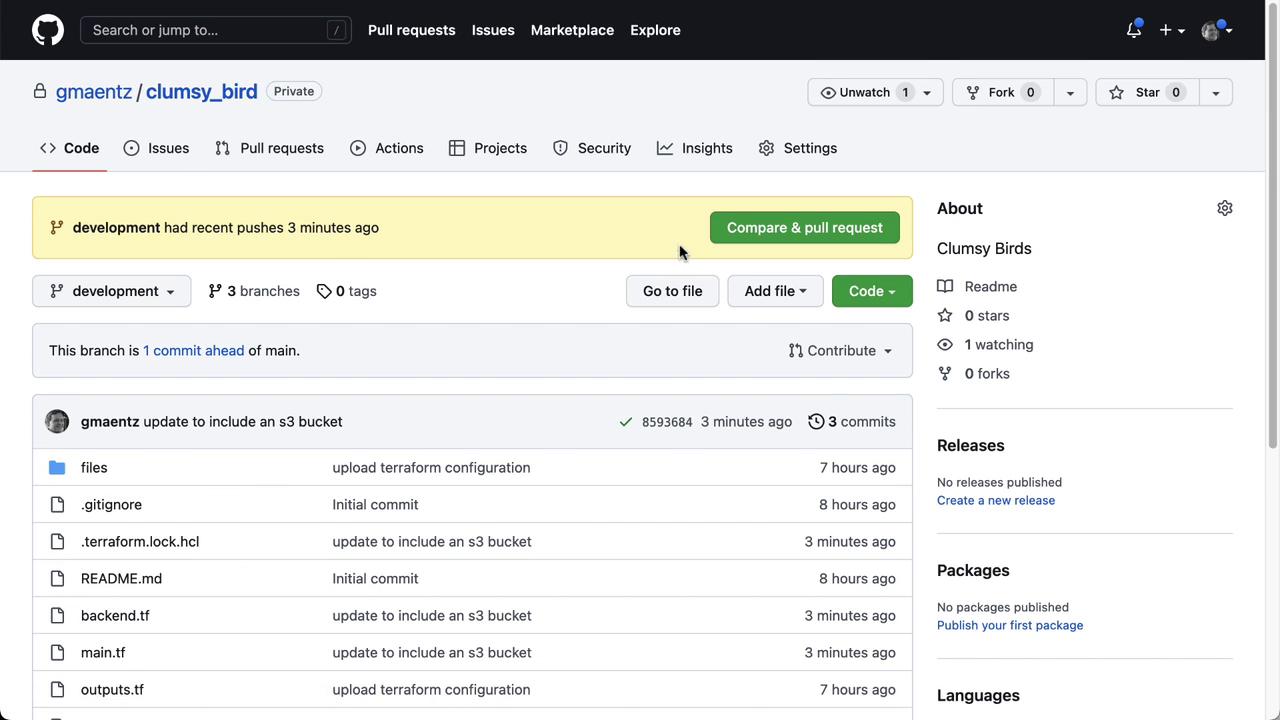
First, inspect the Clumsy Bird repository structure and branch layout:

Each workspace must map to a Git branch (development, staging, main) for GitOps workflows to work seamlessly.
| Workspace | Branch | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| devops-aws-myapp-dev | development | Development environment |
| devops-aws-myapp-staging | staging | Pre-production testing |
| devops-aws-myapp-prod | main | Production environment |
2. Clone the Repository and Checkout the Development Branch
In your terminal (e.g., VS Code integrated terminal), clone the repo and switch todevelopment:

3. Add an S3 Bucket Module in main.tf
Update your Terraform configuration by appending the S3 bucket module:
prefix and environment variables.
4. Configure the Terraform Cloud Backend
Ensure yourbackend.tf points to the dev workspace:
5. Authenticate, Initialize, and Validate
Log into Terraform Cloud, initialize the configuration, and validate:6. Preview Changes with terraform plan
Run a speculative plan in Terraform Cloud:

7. Commit and Push to development
Since this workspace is VCS-driven, CLI apply is disabled. Commit and push your updates:
Do not attempt
terraform apply locally when using a VCS-connected workspace. All applies must occur in Terraform Cloud.8. Observe the Terraform Cloud Run
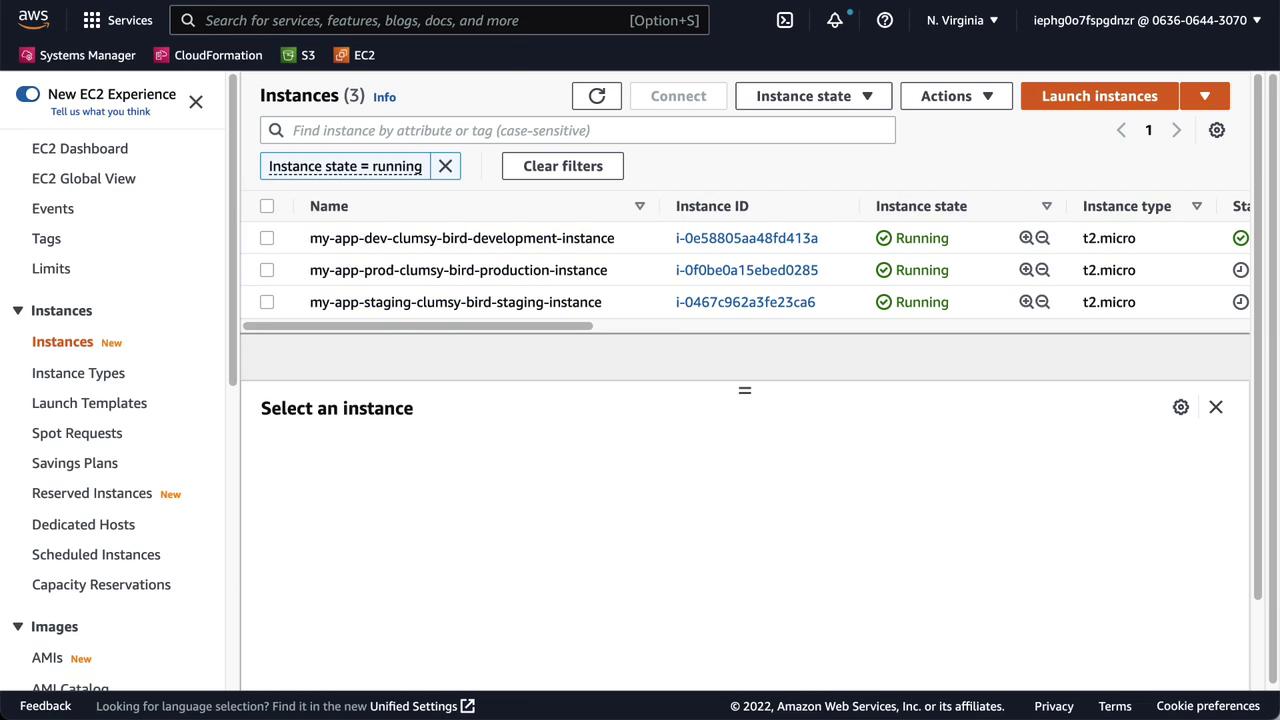
After pushing, Terraform Cloud will automatically plan and apply in the dev workspace. View the run details:
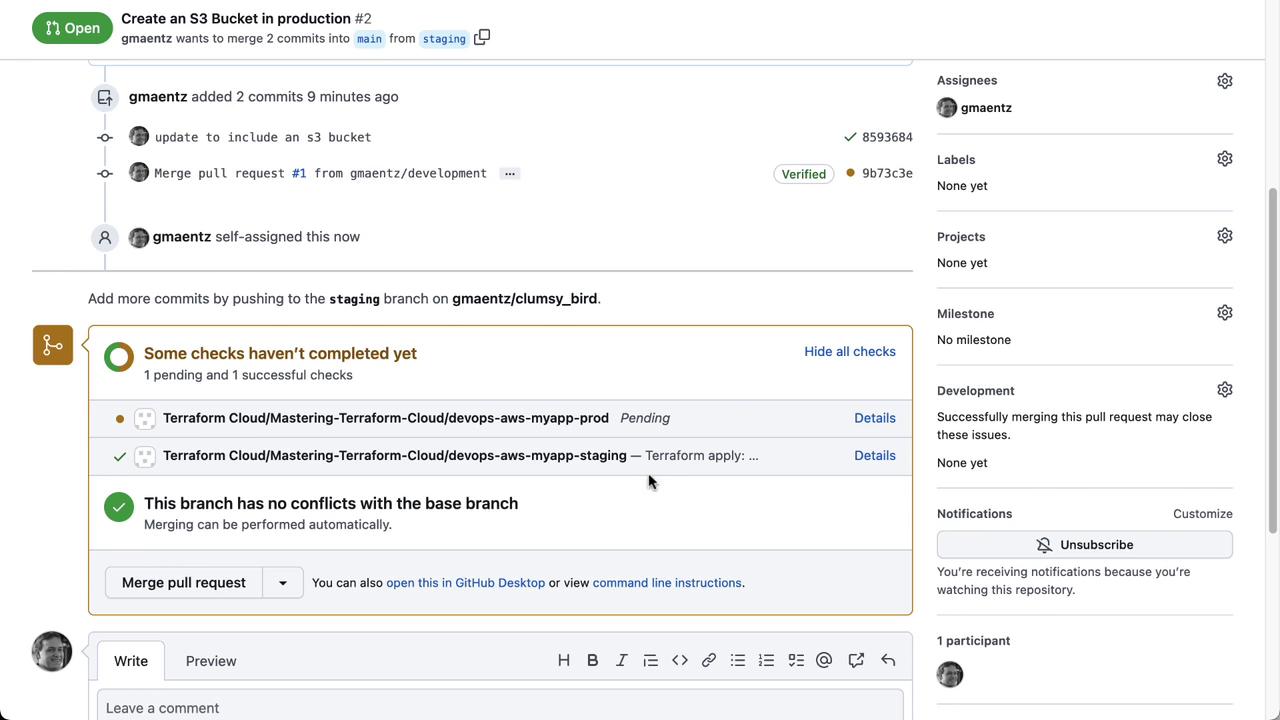
9. Promote to Staging via Pull Request
Create a PR fromdevelopment into staging on GitHub:


10. Verify Staging Apply
After merging, Terraform Cloud detects the newstaging commit and applies the changes:



11. Promote to Production
Repeat the PR process fromstaging into main: