terraform init, plan, and apply in Terraform Cloud.
Prerequisite: A GitHub account.
1. Create a GitHub Repository
- Log in to GitHub and click New repository.
- Configure the repository as follows:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Repository name | clumsy_bird |
| Description | Your project description |
| Visibility | Private |
| Initialize with | README |
| .gitignore template | Terraform |
- Click Create repository.
2. Generate a GitHub Personal Access Token
You need a Personal Access Token (PAT) withrepo scope to allow Terraform Cloud to read your repository.
- In GitHub, go to Settings > Developer settings > Personal access tokens.
- Click Generate new token, select repo scope, then Generate token.
- Copy the token now—you won’t be able to see it again.
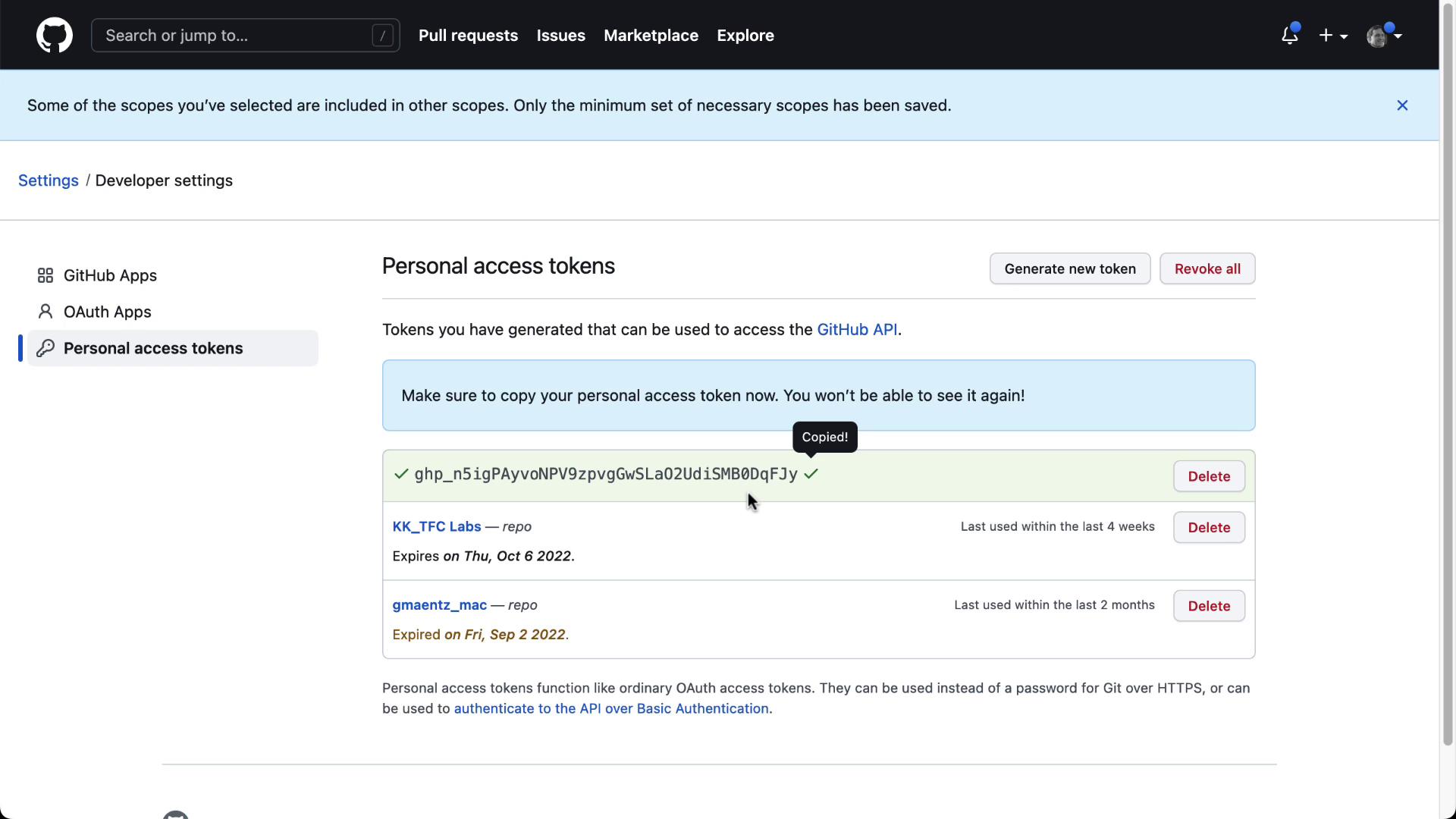
Keep your PAT secure. Do not commit it to any repository or share it publicly.
3. Clone the Repository Locally
In your local or lab environment, clone and push the initial commit:README.md, .gitignore, your Terraform code) in GitHub:

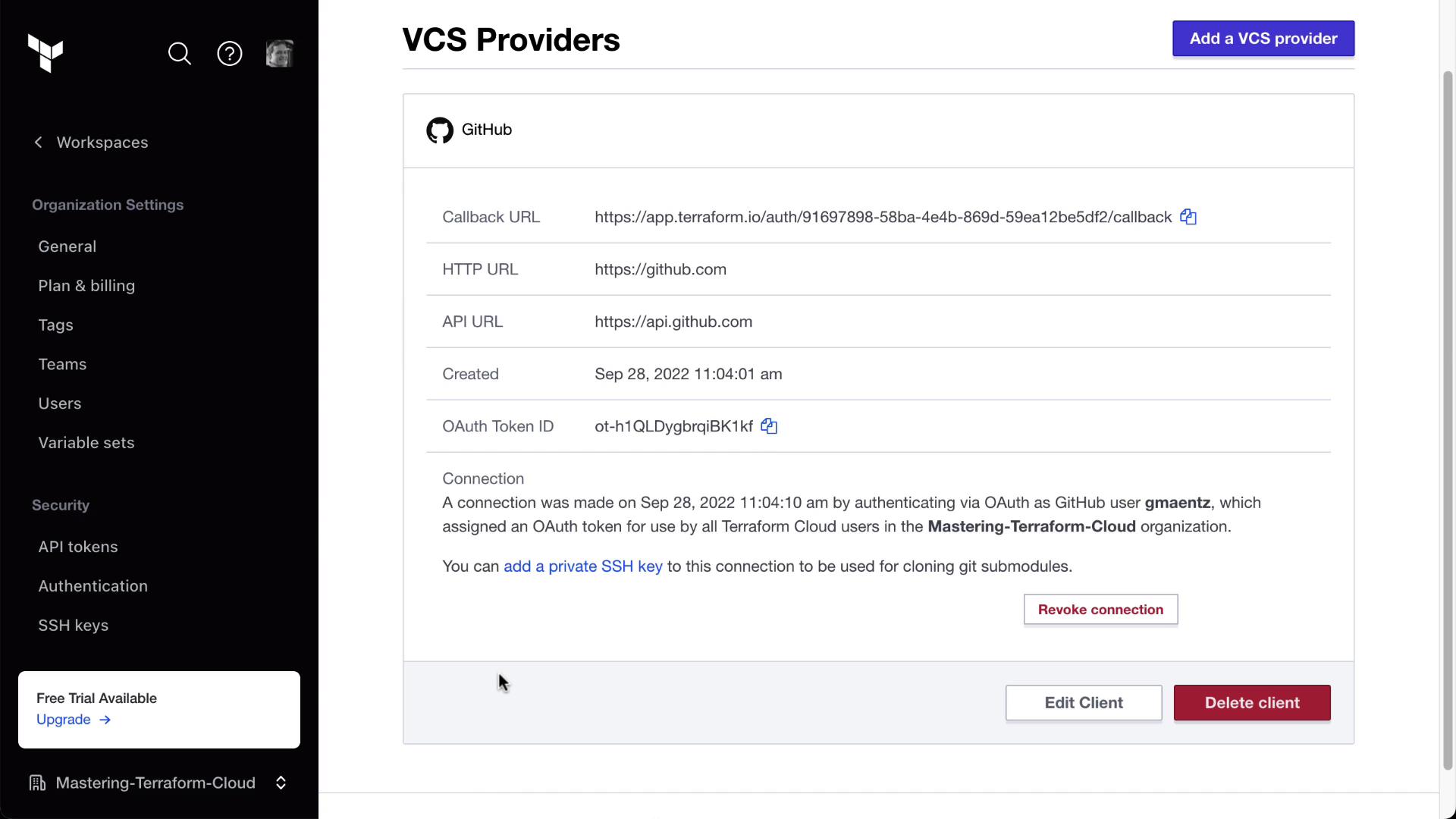
4. Configure GitHub as a VCS Provider in Terraform Cloud
- In Terraform Cloud, navigate to Settings > VCS Providers.
- Click Connect new provider → GitHub.
- Follow the instructions to register a new OAuth application on GitHub:
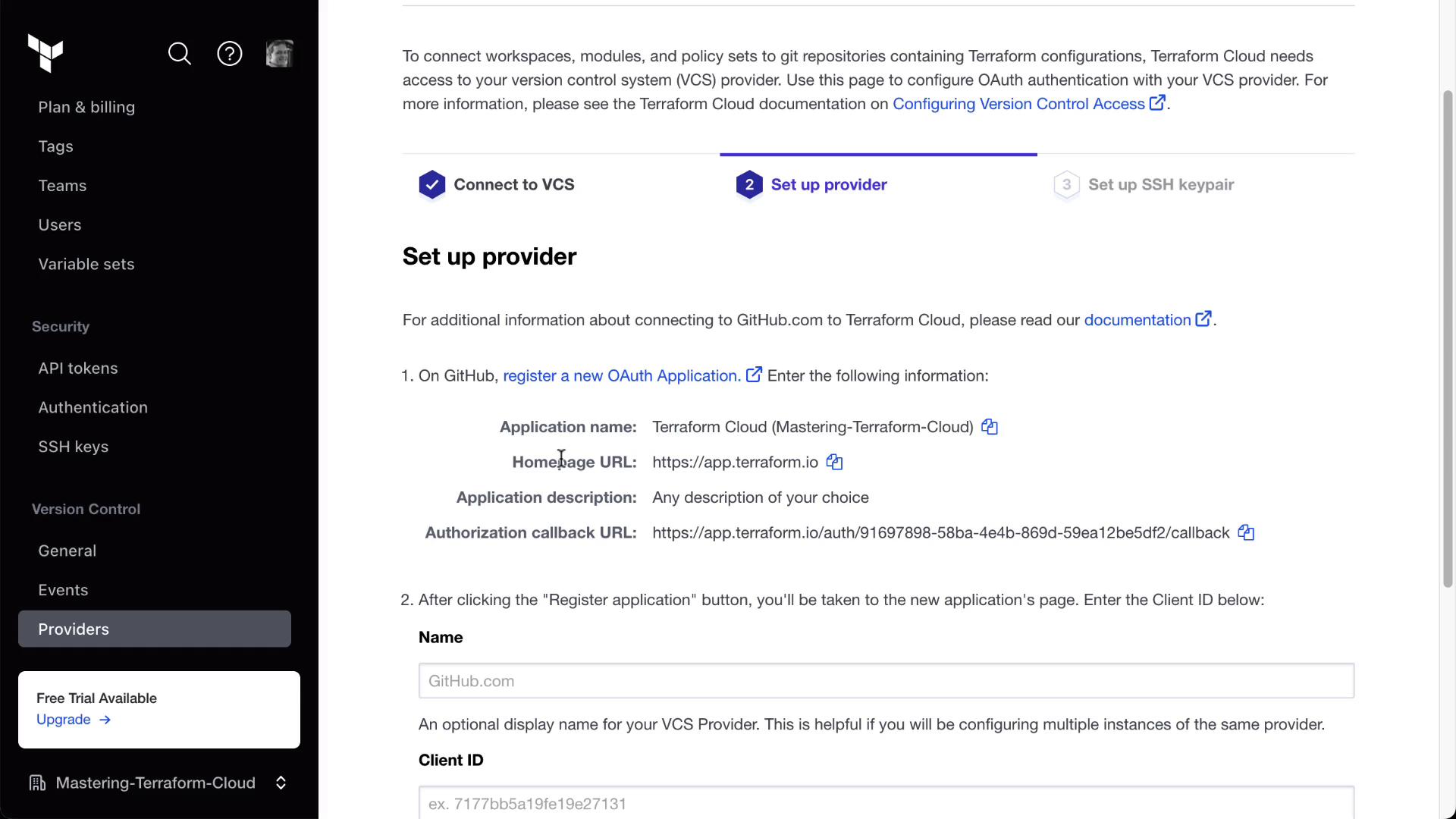
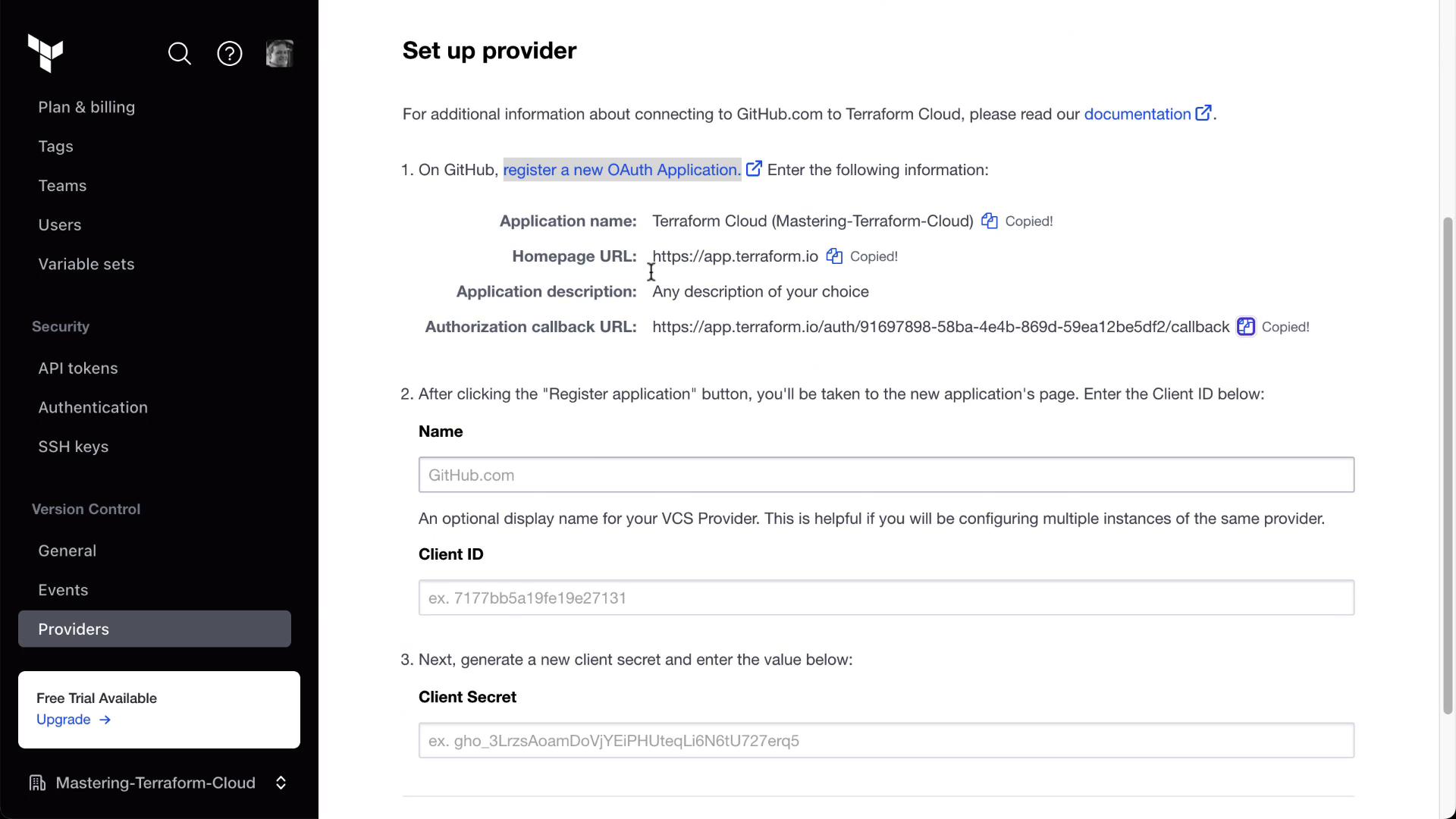
- After registering the app, copy the Client ID and Client Secret:
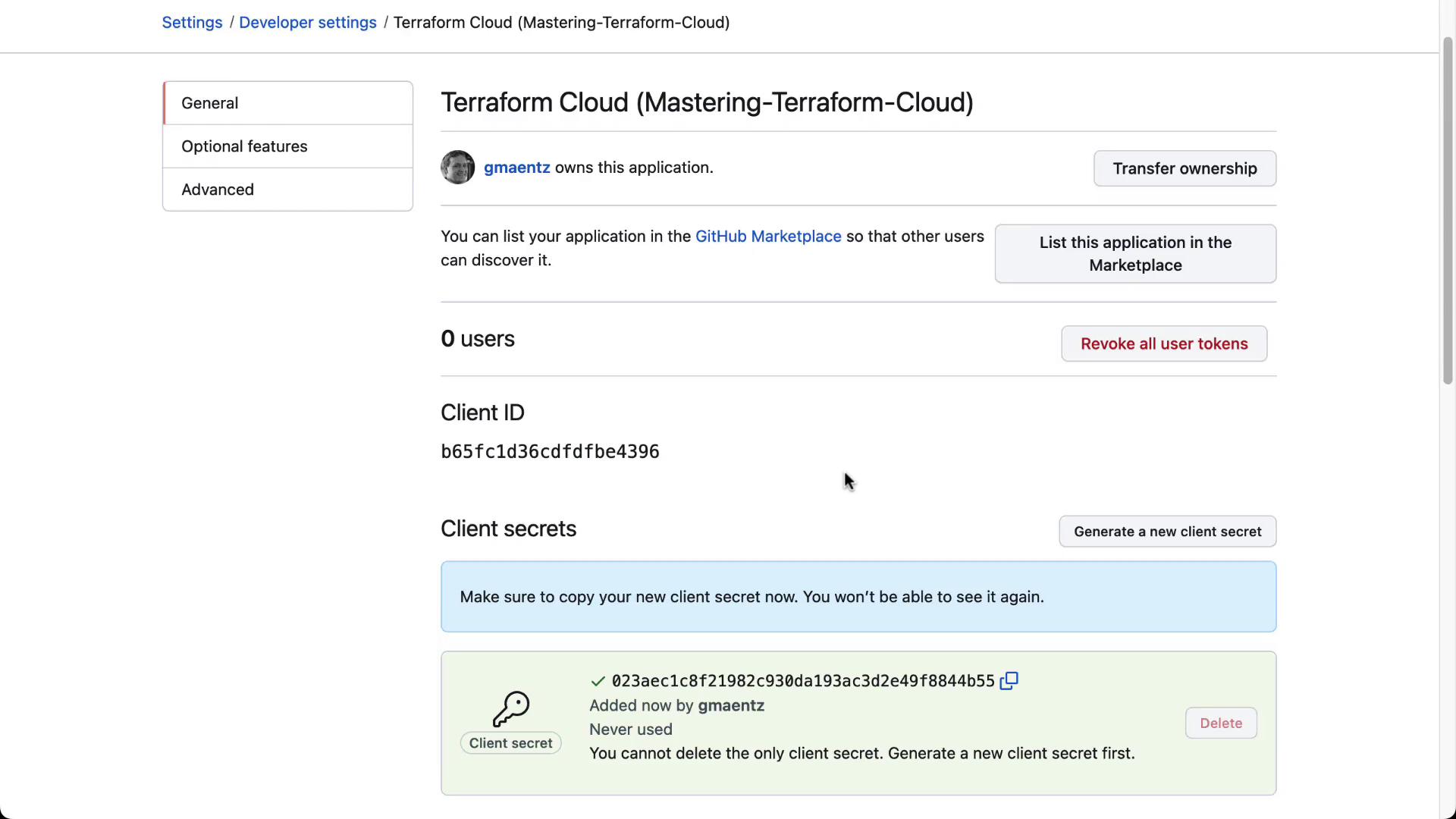
- Back in Terraform Cloud, enter the Client ID, Client Secret, and click Connect and continue. Then authorize the OAuth app.
If you prefer SSH-based access instead of HTTPS, generate an SSH key pair and upload the public key in your GitHub OAuth settings:
5. Associate the Workspace with Your GitHub Repository
- In your Terraform Cloud workspace, go to Settings > Version Control Workflow.
- Select the GitHub provider and choose your repository (
<your-org>/clumsy_bird).

- Enable the following options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Auto Apply | Automatically apply approved plans |
| Automatic Run Triggers | Trigger runs on VCS events |
| Speculative Plans | Create a plan on pull requests without applying |
- Click Save settings.

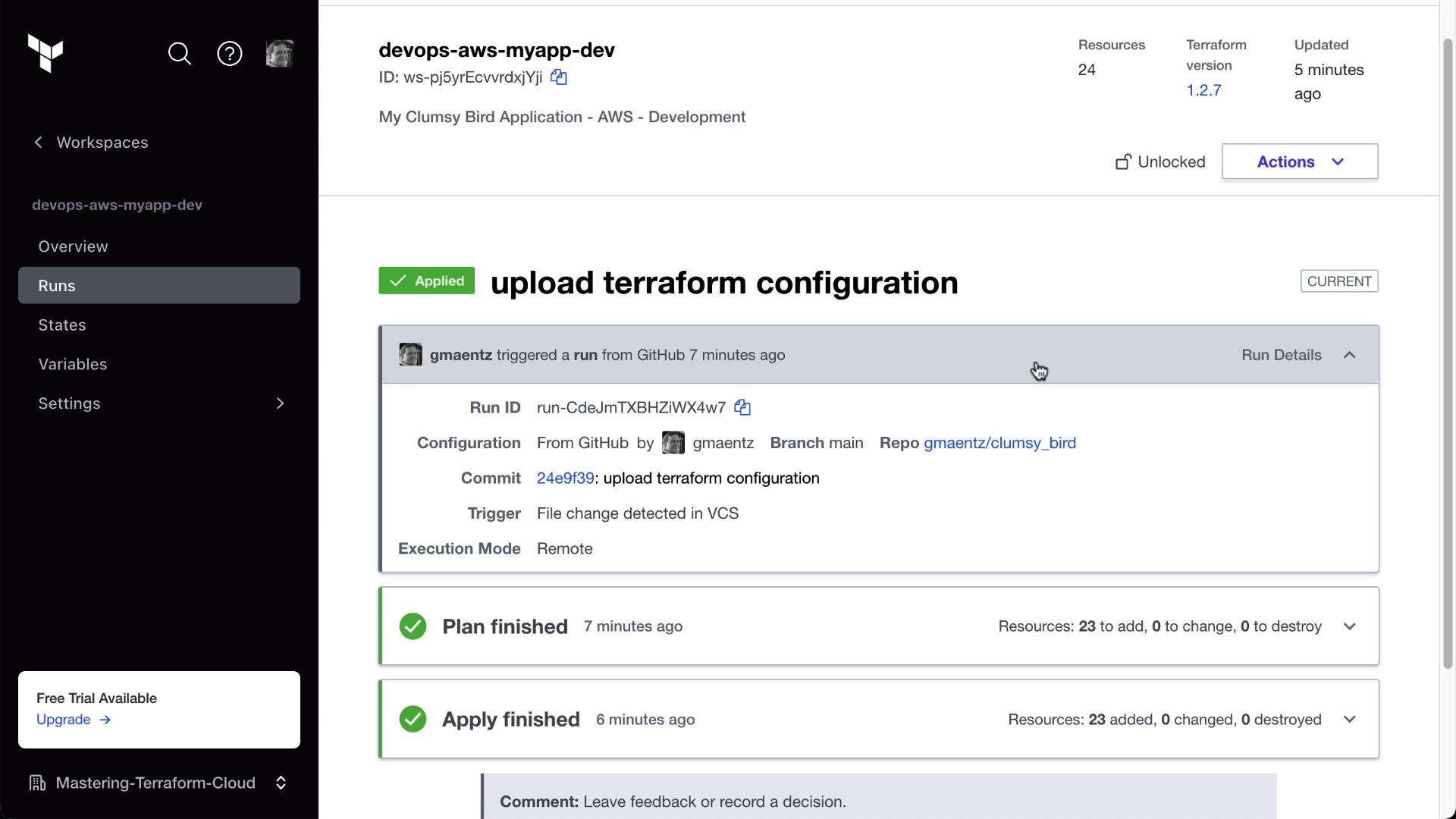
6. Verify the Connection and Trigger a Run
After saving, Terraform Cloud will detect the latest commit and automatically start a run. In the workspace overview, you’ll see the plan and apply details:
clumsy_bird will kick off terraform init, plan, and apply in Terraform Cloud: