| Metric Category | Description | API Endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| Resource | CPU & memory usage | metrics.k8s.io |
| Custom | In-cluster application metrics | custom.metrics.k8s.io |
| External | Third-party or cloud metrics | external.metrics.k8s.io |
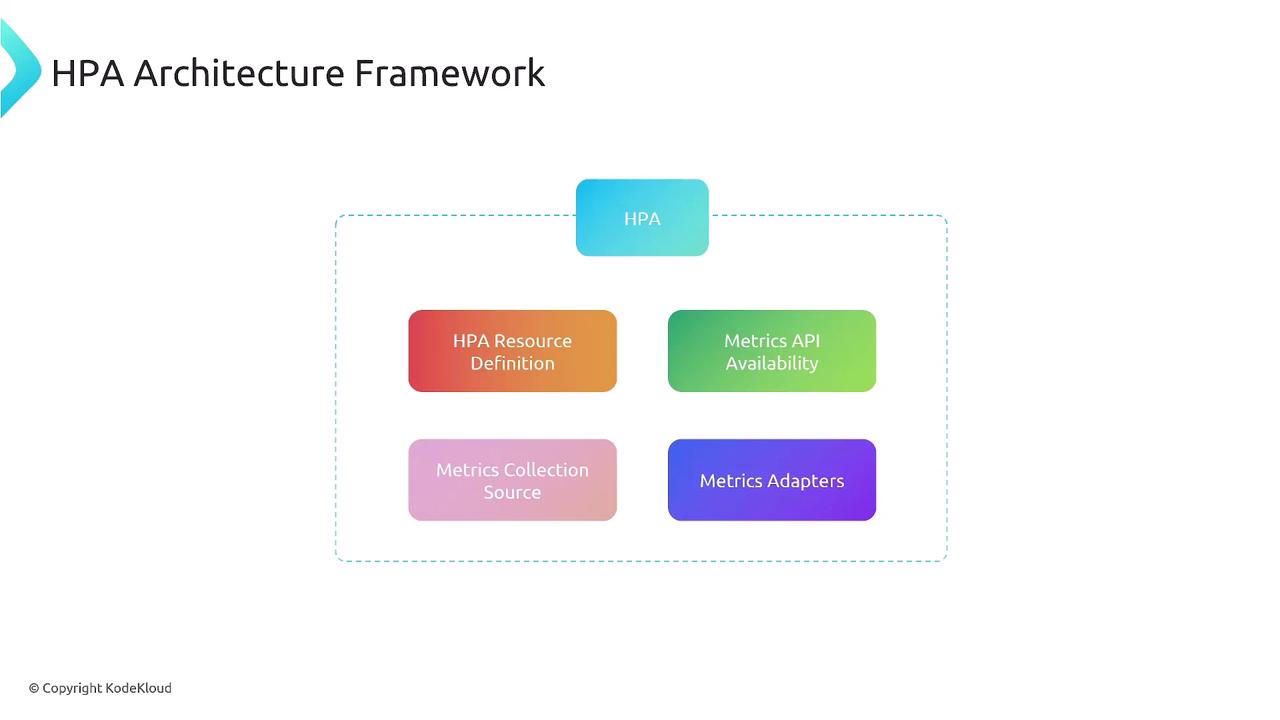
1. HPA Resource Definition
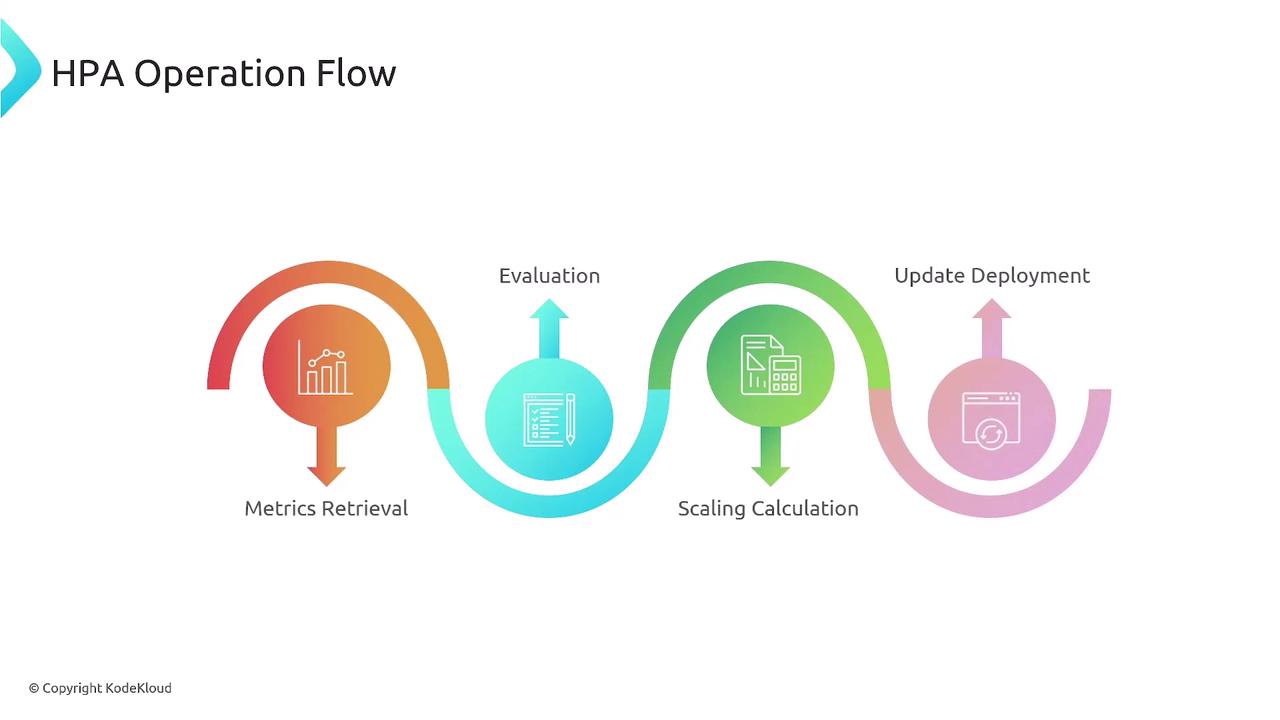
Define which workload to scale, the minimum/maximum replicas, and the metric targets.2. Native Resource Metrics Collection
By default, HPA retrieves CPU and memory metrics from the Kubernetes Metrics Server viametrics.k8s.io.
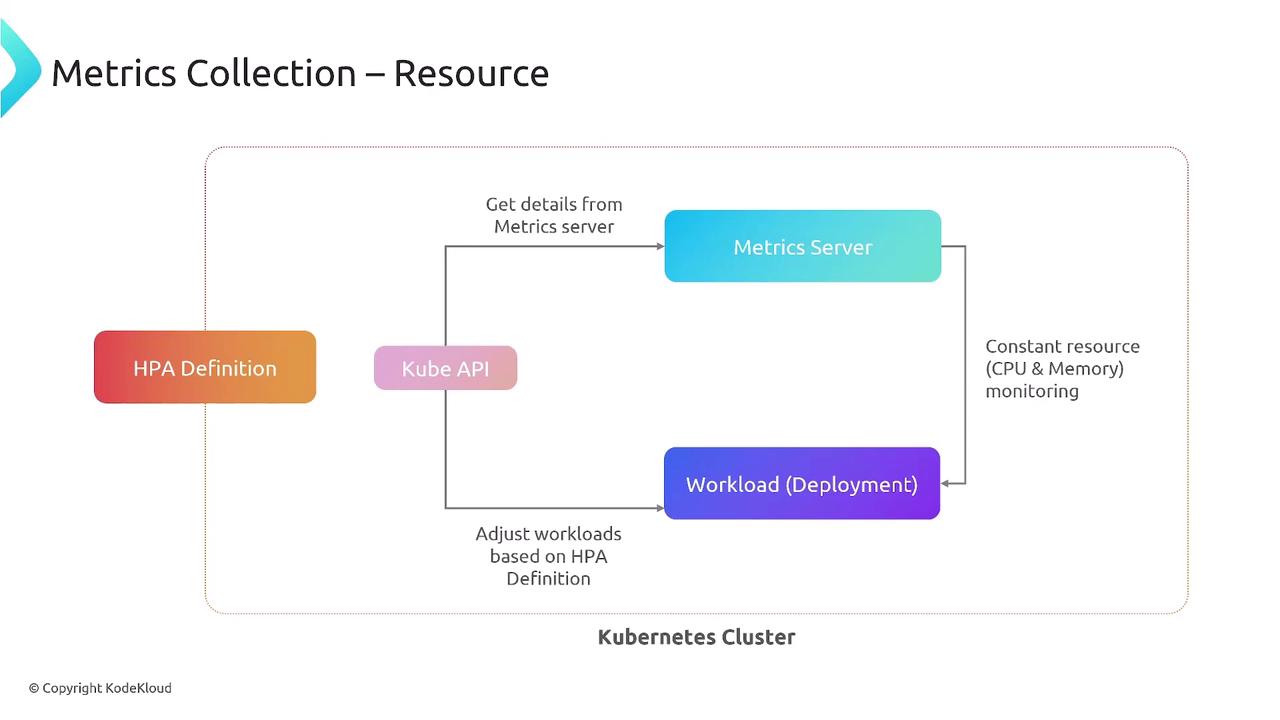
- Fetch metrics (CPU/memory) from Metrics Server
- Compare to target thresholds
- Compute desired replica count
- Patch the target workload
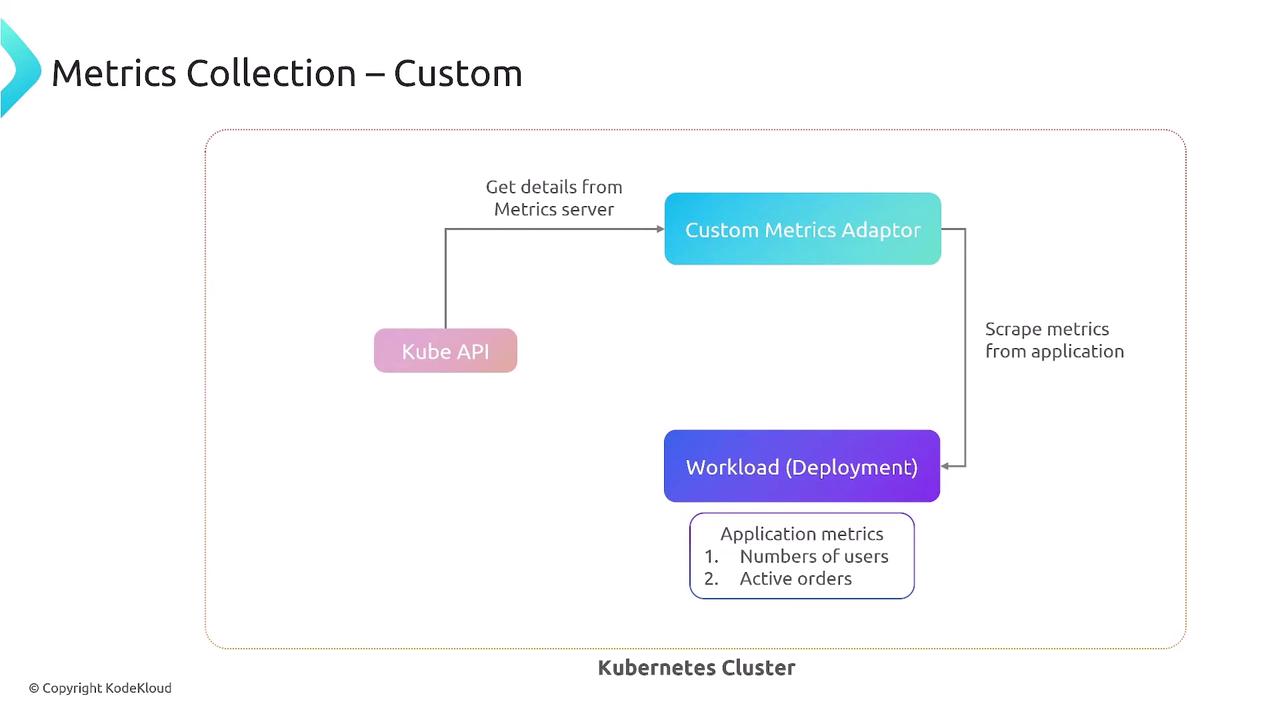
3. Custom Metrics (In-Cluster)
Usecustom.metrics.k8s.io and an adapter (e.g., Prometheus Adapter) to scale on application-specific metrics.
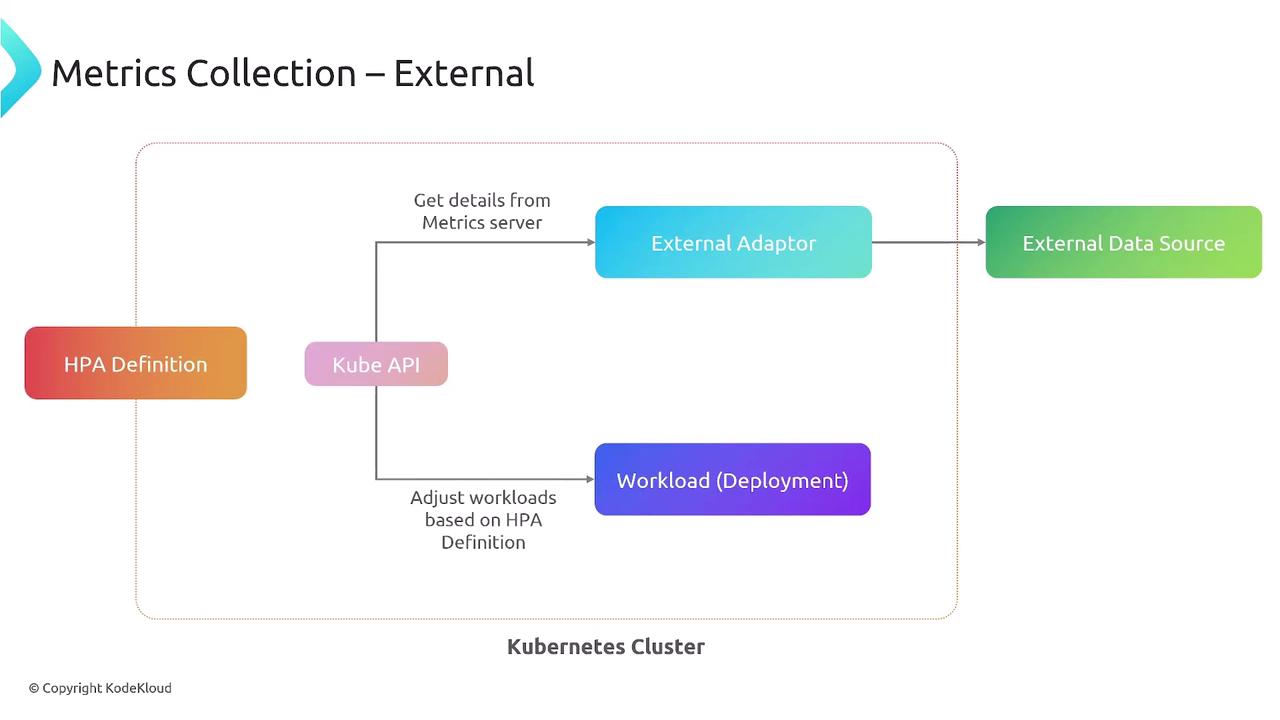
4. External Metrics (Outside Cluster)
Leverage metrics from external systems—cloud providers, SaaS tools—viaexternal.metrics.k8s.io and a suitable adapter.
5. Metrics APIs and Adapters
Kubernetes exposes three metric APIs:| Metric Type | API Endpoint | Adapter Example |
|---|---|---|
| Resource | metrics.k8s.io | Metrics Server |
| Custom | custom.metrics.k8s.io | Prometheus Adapter |
| External | external.metrics.k8s.io | New Relic Adapter, AWS CloudWatch Adapter |
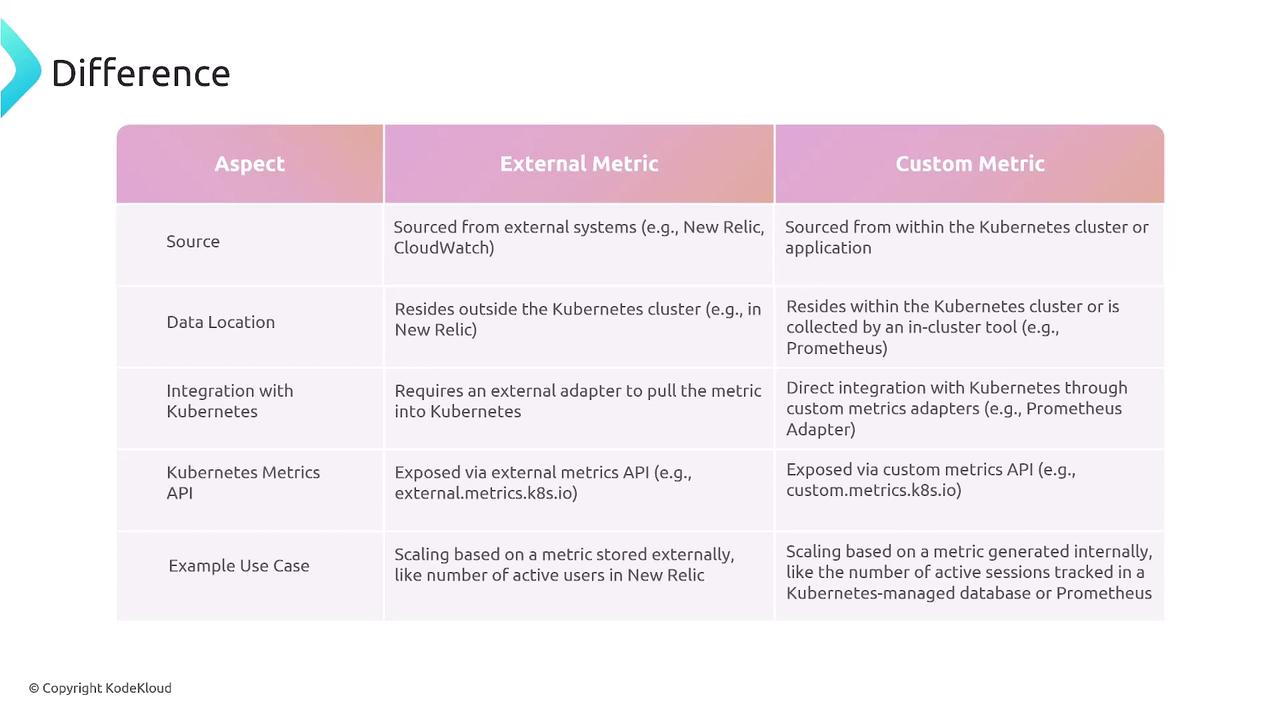
Adapters translate between Kubernetes and metric providers, enabling HPA to consume non-native metrics.
6. HPA Control Loop and Operation Flow
The HPA controller continuously runs a loop to keep your pods scaled to demand.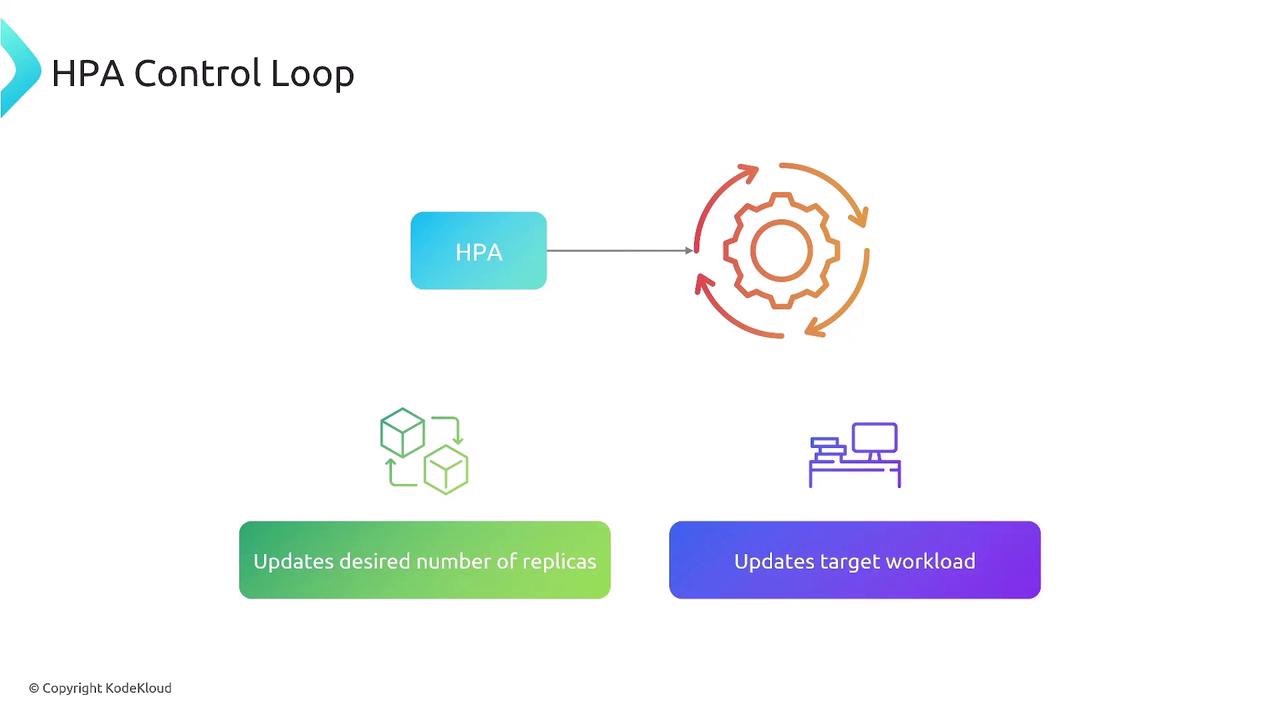
Key Considerations
- Ensure the Metrics Server is installed for resource metrics.
- Deploy custom/external adapters before referencing their APIs.
- Configure scale-up/down policies and stabilization windows to avoid flapping.
- Tune the control loop interval and thresholds based on workload patterns.
Incorrect thresholds or missing adapters can lead to no scaling or unexpected behavior. Always test HPA configurations in a staging environment.