High-Level Architecture
Imagine your Kubernetes cluster as a growing city:- Deployments are neighborhoods.
- Pods are individual houses.
- Applications run inside those houses, serving end users.
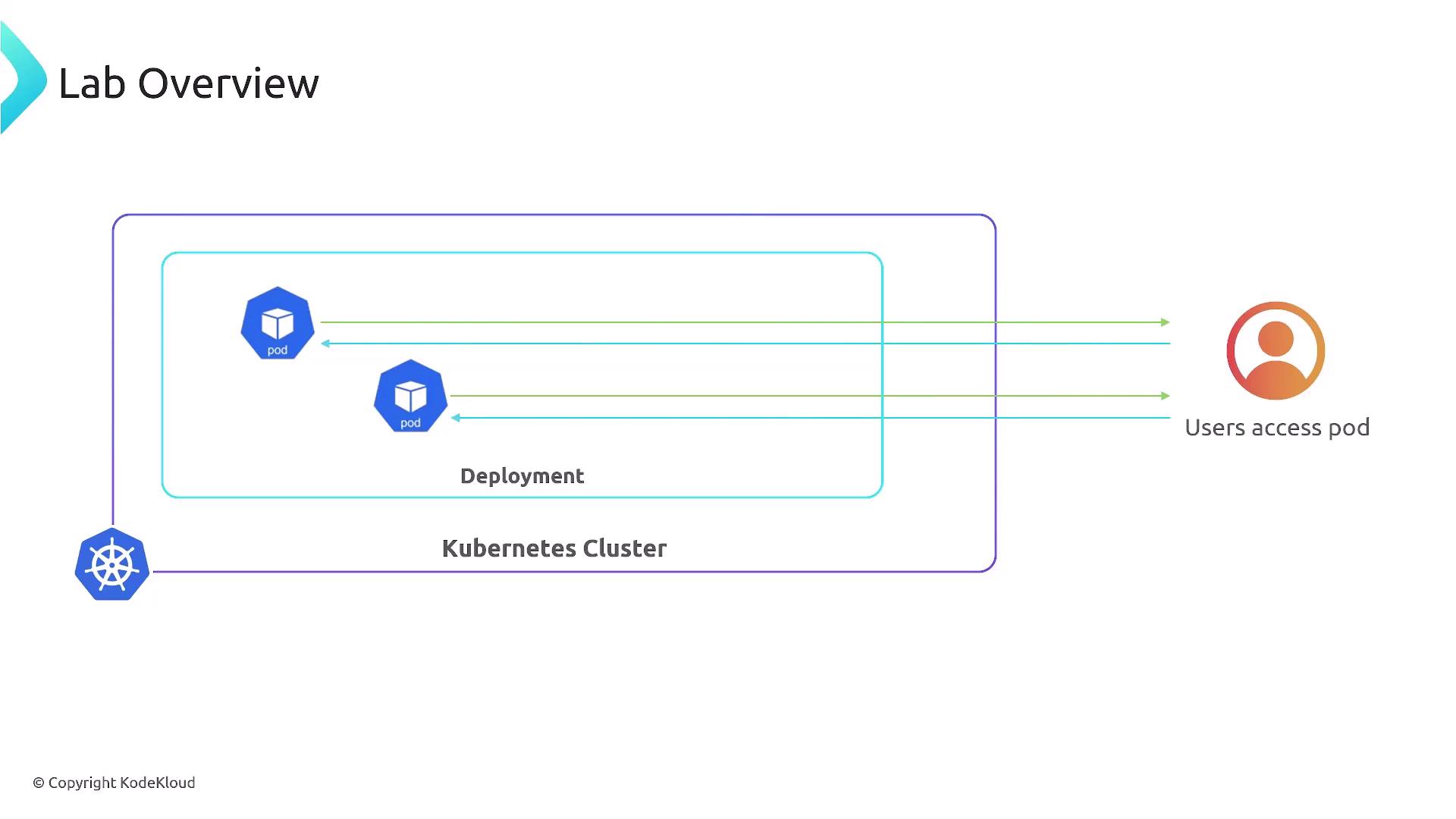
Lab Objectives
In this hands-on lab, you will:- Scale a Deployment up and down by changing its replica count.
- Observe how each pod receives a unique hostname.
- Understand the effects of replication on application throughput and identity.

Ensure you have a running Kubernetes cluster and
kubectl configured to interact with it.Demonstrating Manual Scaling
1. Scale the Deployment
Run the following command to increase replicas to three:2. Verify the New Pods
List the pods and confirm there are three running instances:3. Common Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
kubectl scale deployment ... --replicas | Adjusts the number of pod replicas. |
kubectl get pods | Lists all pods with status and age. |
Pods are ephemeral. Their hostnames and IPs can change on restart or rescheduling. For stable network IDs, consider using a StatefulSet.
Key Takeaways
- Manually scaling a Deployment is like adding or removing houses in a neighborhood.
- Each pod gets its own hostname; they’re not preserved across restarts.
- More replicas boost capacity but can affect apps that rely on host-specific data.
- For stateful applications, use StatefulSets or external storage to maintain stable identities.