Kubernetes Networking Deep Dive
Kubernetes Services
Services Overview
Kubernetes Services provide a stable network endpoint for pods, abstracting their dynamic IPs and ensuring consistent communication across the cluster.
A Service definition looks like any other Kubernetes object. You give it a name, set a selector for matching pods, declare ports, and choose a Service type:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-service
namespace: my-namespace
spec:
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80 # Service port
targetPort: 8080 # Pod port
type: ClusterIP
- selector:
app: my-appmatches pods labeled accordingly. - ports: exposes port 80 and forwards traffic to pod port 8080.
- type:
ClusterIP(default) makes the Service reachable only within the cluster.
Note
Kubernetes uses EndpointSlices to track pod endpoints automatically. Clients always connect to the Service IP, unaware of pod restarts or IP changes.
Service Discovery
Kubernetes exposes Service endpoints to pods in two ways:
Environment variables
The kubelet injects:MY_SERVICE_SERVICE_HOSTMY_SERVICE_SERVICE_PORT
into each container at startup.
DNS
With CoreDNS (or another DNS add-on), every Service gets an A record and SRV records:
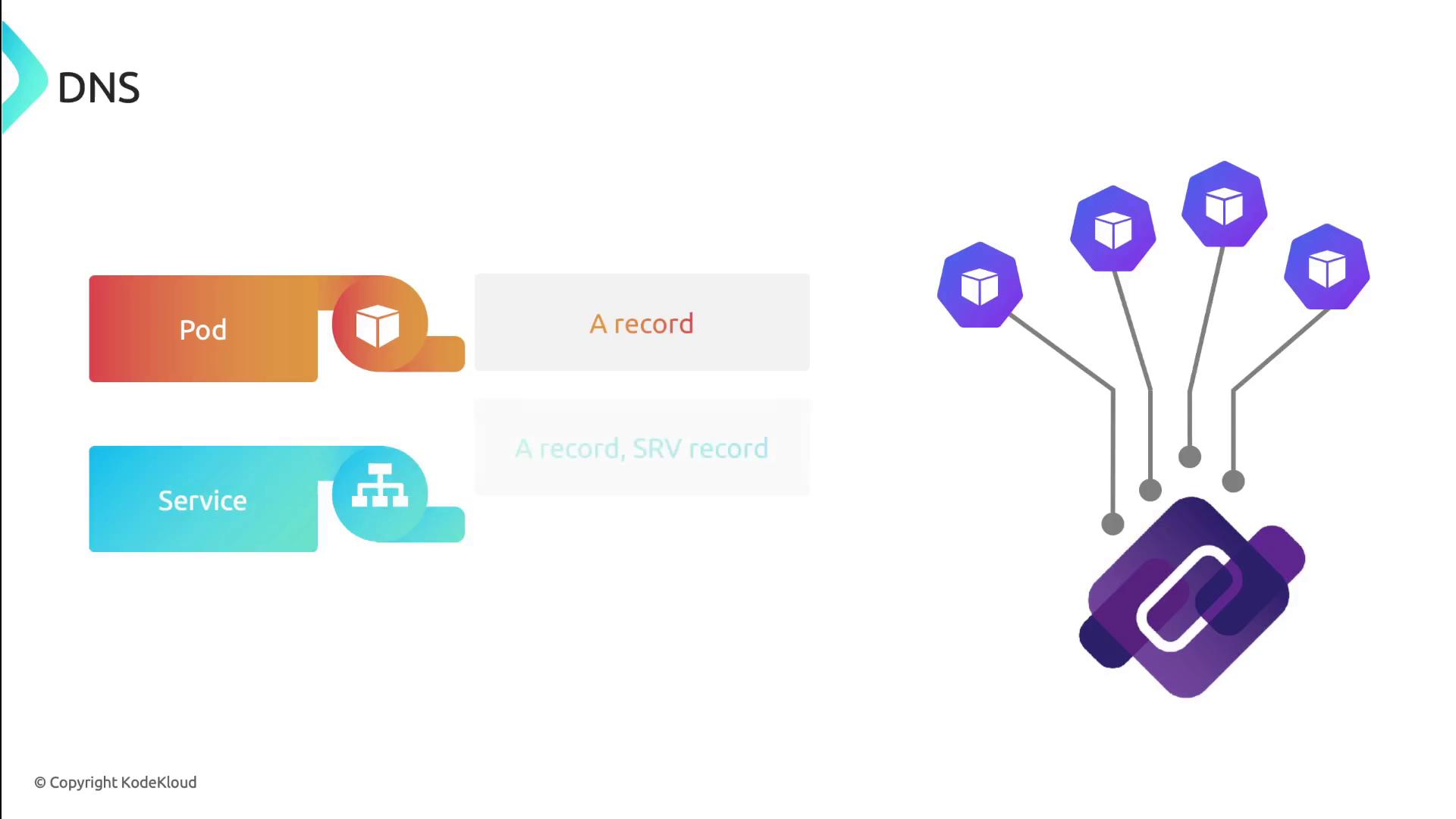
- A record:
service-name.namespace.svc.cluster.local - SRV records: one per named port, for example:
_http._tcp.my-service.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local
![]()
Service Types
Kubernetes supports four Service types, each controlling how traffic reaches your application.
| Service Type | Exposure Scope | Port Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| ClusterIP | Internal cluster only | Virtual cluster IP |
| NodePort | Host nodes | NodeIP:NodePort |
| LoadBalancer | External via LB | Provisioned cloud load balancer IP |
| ExternalName | DNS redirection | CNAME record to external hostname |
1. ClusterIP
Exposes the Service on a cluster-internal IP address. Use it for internal microservice communications or when fronted by an Ingress.

2. NodePort
Allocates a port on each node’s IP. External clients use NodeIP:NodePort to reach the Service.

3. LoadBalancer
Integrates with cloud-provider load balancers. Kubernetes provisions an external load balancer and maps it to your Service.

4. ExternalName
Creates a DNS CNAME record that maps the Service to an external DNS name. No proxies or IPs are provisioned in the cluster.

Warning
ExternalName Services do not support port mapping or protocols. They simply return a DNS CNAME.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content