Kubernetes Networking Deep Dive
Network Security
Cilium Hubble Overview
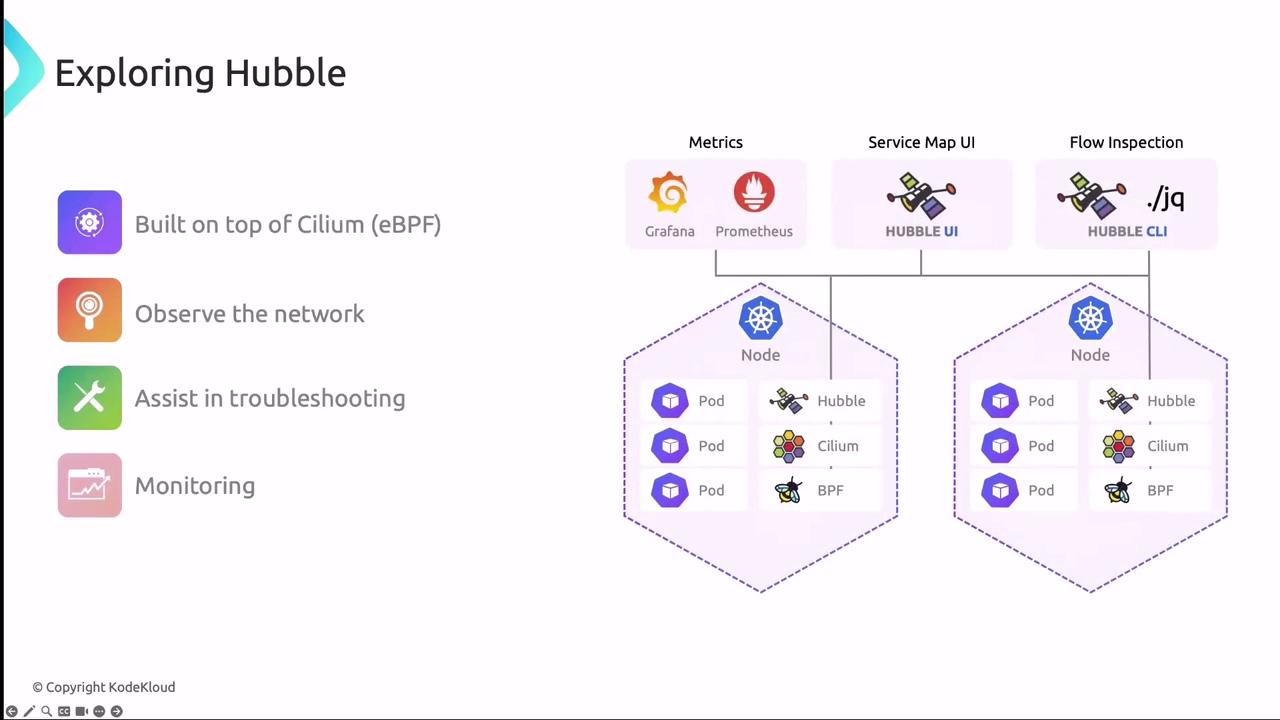
Cilium Hubble extends Cilium’s eBPF datapath to deliver unparalleled network observability, troubleshooting, and security enforcement for Kubernetes clusters. In this guide, we’ll cover Hubble’s architecture, built-in metrics, UI/CLI tools, and how to integrate with Prometheus and Grafana.
Hubble components:
- eBPF datapath on each node for flow and event capture
- Relay to aggregate data across nodes
- Integrations with Prometheus (metrics), Grafana (dashboards, service maps), and Hubble UI/CLI for interactive inspection
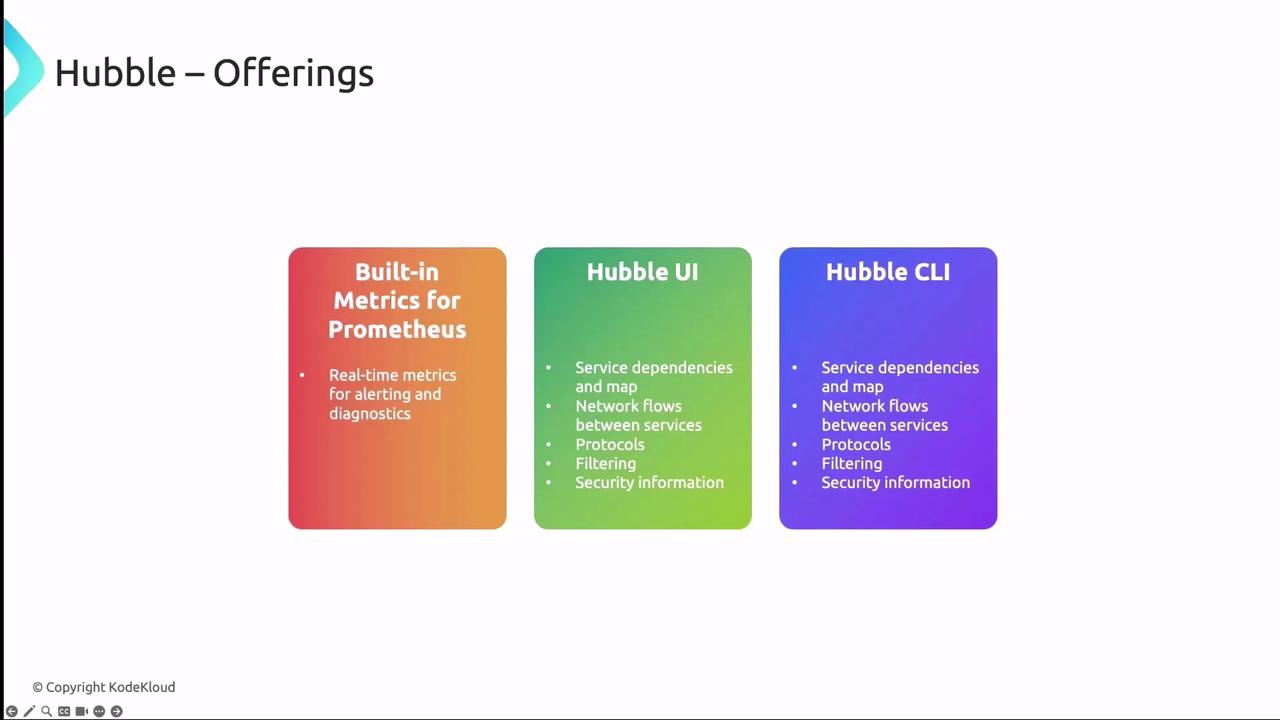
Built-in Metrics for Prometheus
Hubble exports metrics in the Prometheus OpenMetrics format, making it simple to monitor network health and trigger alerts on key events:
| Metric Category | Tracks | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| dns | DNS queries, failures, latencies | Alert on high DNS failure rate |
| drop | Packet drops by policy or error | Identify unintended policy blocks |
| tcp | TCP connections, retransmissions, resets | Detect connection instability |
| flow | Flow counts, throughput, duration | Baseline traffic trends |
| port-distribution | Top port usage across services | Spot unexpected open ports |
| icmp | ICMP echo requests and replies | Monitor ping flood or unreachable hosts |
| httpV2 | HTTP/2 metrics with exemplars and label context | Trace request latencies with context labels |
Note
Enable only the metrics you need to reduce data volume and improve query performance.
Enabling Hubble Metrics via Helm
When installing or upgrading Cilium with Helm, you can enable Hubble and Prometheus integration in one step:
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --version CILIUM_VERSION \
--namespace kube-system \
--reuse-values \
--set hubble.enabled=true \
--set hubble.relay.enabled=true \
--set hubble.ui.enabled=true \
--set hubble.metrics.enableOpenMetrics=true \
--set prometheus.enabled=true \
--set operator.prometheus.enabled=true \
--set hubble.metrics.enabled="{dns,drop,tcp,flow,port-distribution,icmp,httpV2:exemplar=true;labelsContext=source_ip\,source_namespace\,source_workload\,destination_ip\,destination_namespace\,destination_workload\,traffic_direction}"
Hubble UI and CLI
Hubble offers both a web-based UI and a scriptable CLI, providing deep visibility into service interactions, network flows, and security policy verdicts.
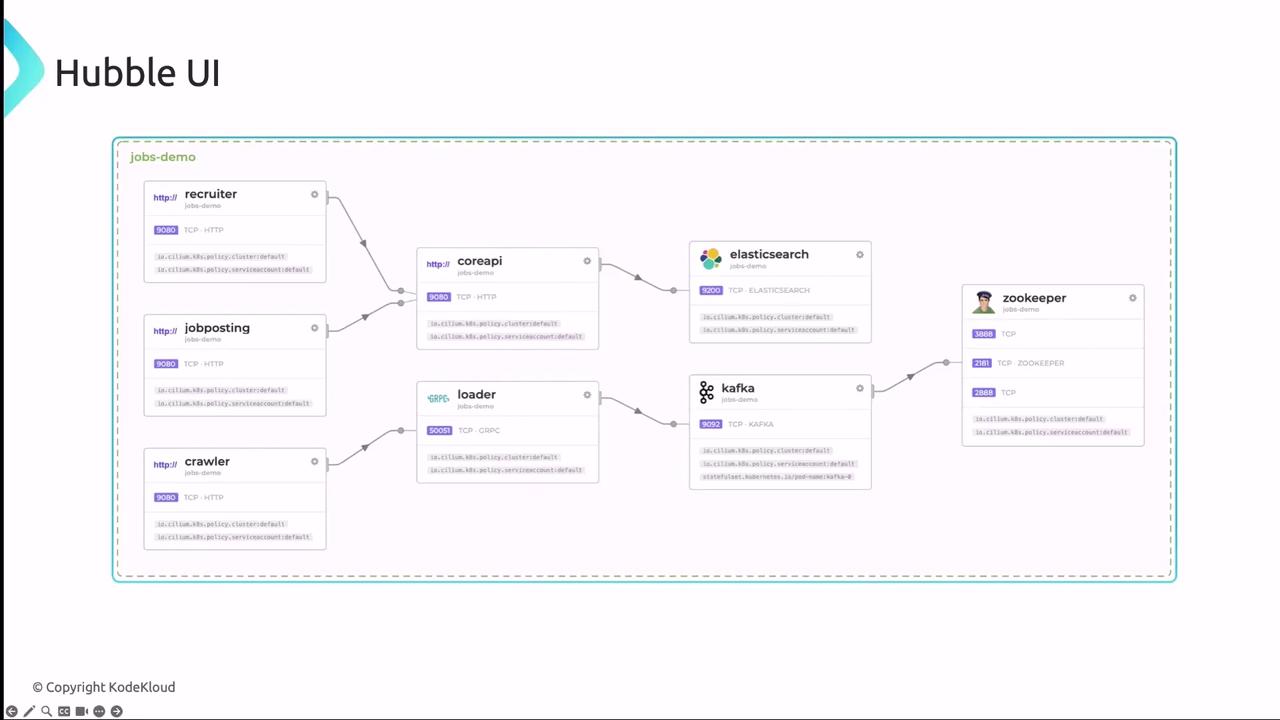
Hubble UI
The Hubble UI delivers interactive dashboards and service maps:
- Service Dependency Map
Visualize inter-service communication to spot bottlenecks or misconfigurations. - Flow Table
Inspect individual network flows with source/destination, protocol details, performance metrics, and policy verdicts. - Security Events
Review blocked connections, policy violations, and external access attempts.
Example service dependency graph:
Warning
Avoid exposing the Hubble UI publicly without proper authentication. Use port-forwarding or an ingress with strong access controls.
Launching Hubble UI Locally
Forward the UI port to your workstation:
cilium hubble ui
# Forwarding from 0.0.0.0:12000 -> 8081
# Forwarding from [::]:12000 -> 8081
Then browse to http://localhost:12000.
Hubble CLI
The Hubble CLI offers the same visibility in a terminal-friendly format, ideal for automation and scripts.
Check the status inside a Cilium agent pod:
kubectl exec -it -n kube-system cilium-xxxxxx -c cilium-agent -- hubble status
# Healthcheck (via unix:///var/run/cilium/hubble.sock): Ok
# Current/Max Flows: 4,095/4,095 (100.00%)
# Flows/s: 4.72
Installing the Hubble CLI on Linux
HUBBLE_VERSION=$(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/hubble/master/stable.txt)
HUBBLE_ARCH=amd64
if [ "$(uname -m)" = "aarch64" ]; then
HUBBLE_ARCH=arm64
fi
curl -L --fail --remote-name-all \
https://github.com/cilium/hubble/releases/download/$HUBBLE_VERSION/hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz \
https://github.com/cilium/hubble/releases/download/$HUBBLE_VERSION/hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256sum
sudo tar xvzf hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin
rm hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256sum
Next, we’ll dive into a hands-on demo to see Hubble in action.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content