

Explore the interactive map at cnsmap.netfly.app to discover security tools and best practices organized by Develop, Distribute, Deploy, and Runtime phases.
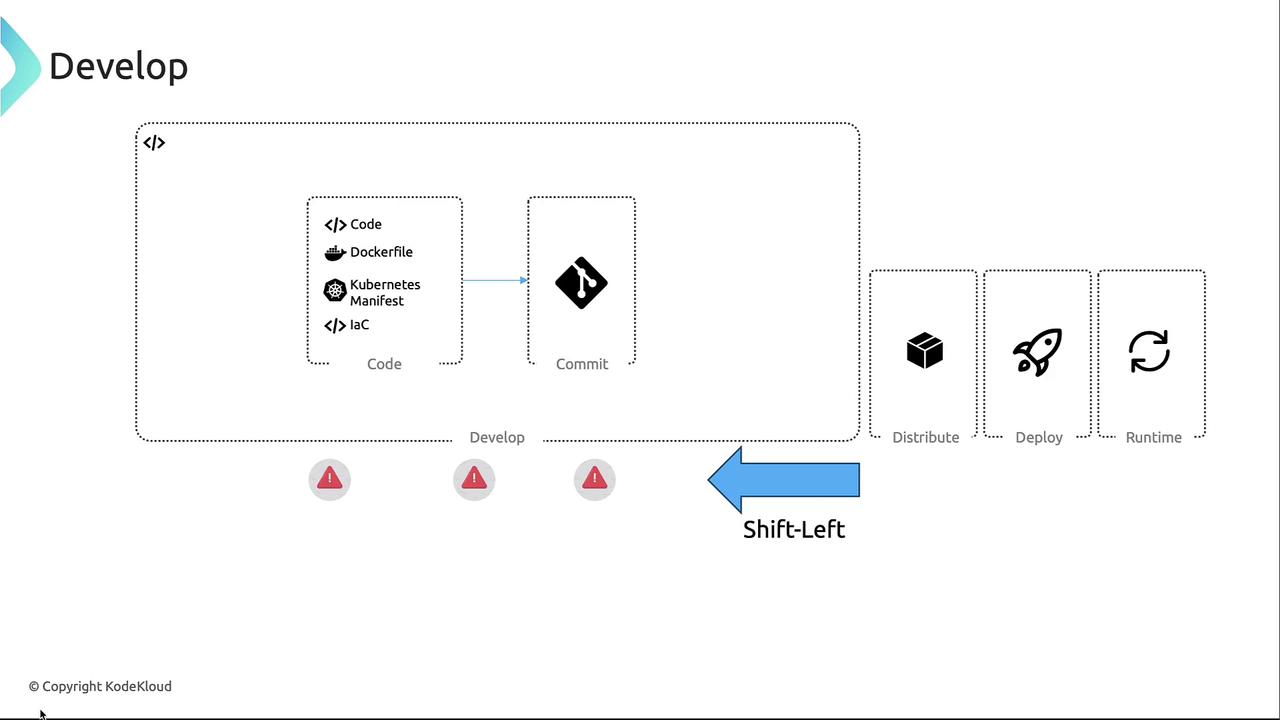
Development Phase
The Develop phase emphasizes “shift-left” testing by integrating security early in code, Dockerfile, and infrastructure-as-code creation. Commit artifacts to repositories (GitHub, GitLab, etc.) with automated checks to:- Block high-severity vulnerabilities when fixes exist
- Enforce non-root container execution
- Restrict allowed base images
Fuzz Testing with OSS-Fuzz
Google’s [OSS-Fuzz][oss-fuzz] automates fuzz testing of open source projects to discover crashes and undefined behavior.parse_integer:
IDE & CLI Security Extensions
- [Snyk VS Code Extension][snyk-vscode]
- Fabricate by Red Hat (VS Code plugin)
- [kube-linter][kube-linter] – Scan Kubernetes YAML:
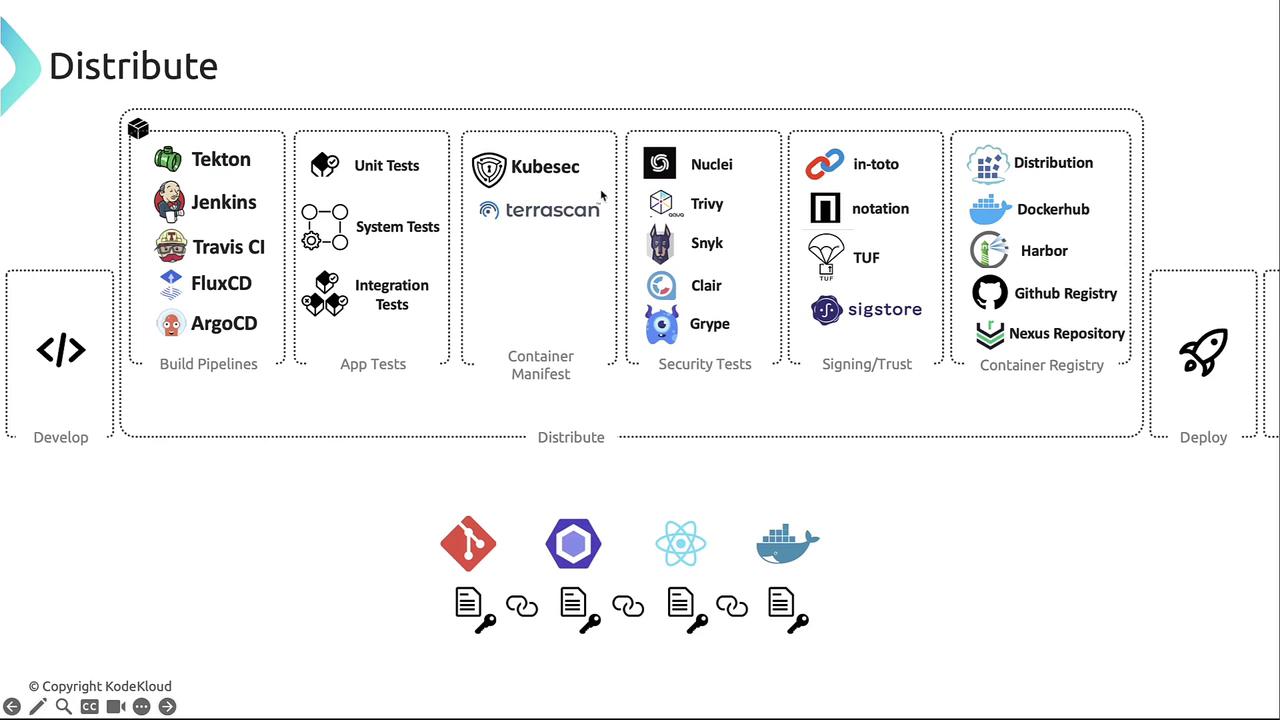
Distribution Phase
In the Distribute phase, CI/CD pipelines build, test, and push container images to registries. Common tools include:| CI/CD Pipeline Tool | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Tekton | Kubernetes-native pipelines |
| Jenkins | Extensible automation server |
| Travis CI | Cloud-hosted continuous testing |
| CircleCI | Container-based CI |
| Flux CD | GitOps continuous delivery |
| Argo CD | Declarative GitOps controller |
- [KubeSec][kubesec] scans Kubernetes YAML for misconfigurations.
- TeraScan validates IaC (Terraform, Dockerfile, Helm, CloudFormation) against CIS, NIST, GDPR, HIPAA.
Always validate manifests before image builds to prevent deployment of insecure configurations.
| Scanner | Scope | Example Command |
|---|---|---|
| Trivy | Container images, filesystems, Git repos | trivy image myapp:latest |
| Clair | Static image analysis via API | API integration |
| Grype | Images & filesystem scanning | grype myimage:tag |
| Nuclei | Custom checks via YAML templates | nuclei -t templates/ |
- [in-toto][in-toto] – End-to-end supply chain security
- [Notary][notary], [TUF][tuf], [Sigstore][sigstore]
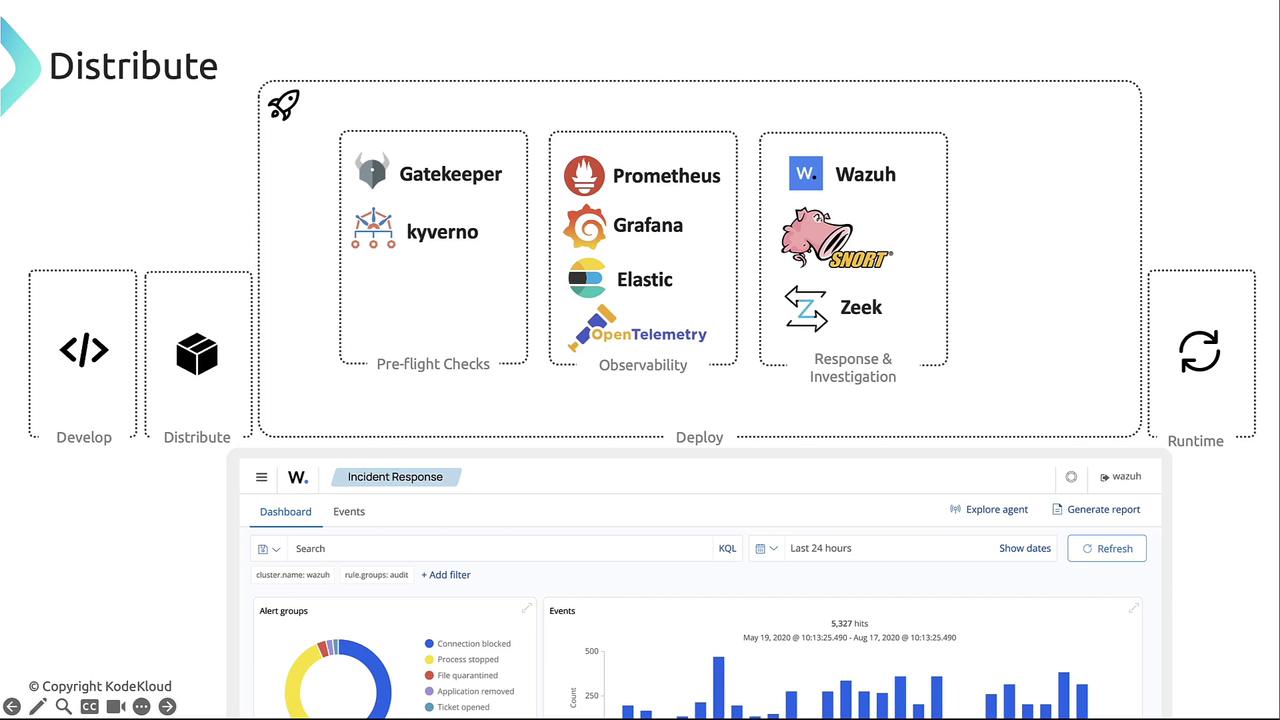
Deployment Phase
The Deploy phase covers pre-flight checks, observability, and incident response:-
Pre-flight Checks
- [OPA Gatekeeper][gatekeeper] – Policies in Rego
- [Kyverno][kyverno] – YAML-based policy management
-
Observability
- [Prometheus][prometheus] + [Grafana][grafana]
- [Elasticsearch][elasticsearch] + [Kibana][kibana]
- [OpenTelemetry][otel]
-
Response & Investigation
- [Wazuh][wazuh]
- [Snort][snort]
- [Zeek][zeek]
Runtime Phase
Once applications are live, enforce continuous security and reliability:- CIS Benchmarking
- [kube-bench][kube-bench] – CIS checks for Kubernetes clusters:
-
Runtime Security
- Falco – System call monitoring
- Trivy – Continuous workload scanning
- SPIFFE – Workload identity via certificates
-
Service Mesh
- Istio, Linkerd
-
Storage Orchestration
- Rook, Ceph, Gluster
-
Access Management
- Keycloak, Teleport, HashiCorp Vault
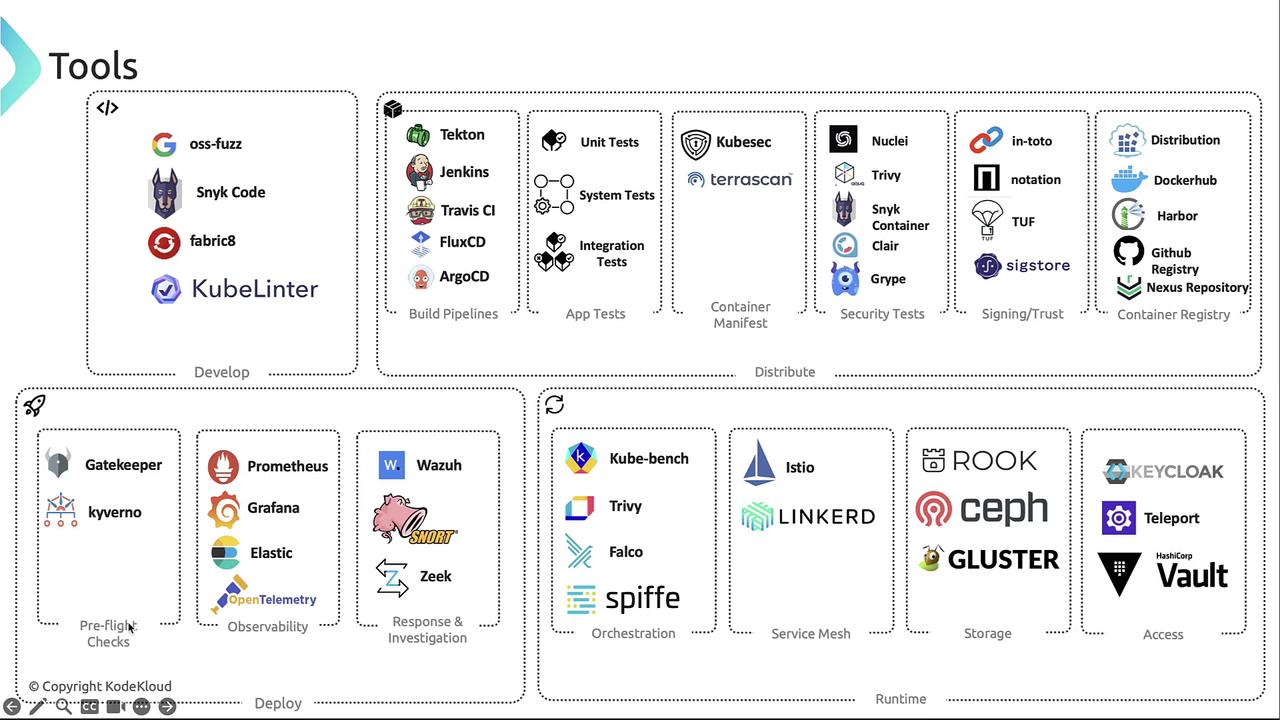
Summary
Map these tools to your cloud-native lifecycle for improved security and efficiency:- Develop: Shift-left scanners & IDE plugins
- Distribute: CI/CD pipelines, manifest & image scanners, signing frameworks
- Deploy: Policy enforcement, observability, incident response
- Runtime: Continuous monitoring, service mesh, access & storage management
Links and References
- OSS-Fuzz: https://github.com/google/oss-fuzz
- Snyk VS Code Extension: https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=snyk-security.snyk-vulnerability-scanner
- kube-linter: https://github.com/stackrox/kube-linter
- KubeSec: https://github.com/controlplaneio/kubesec
- in-toto: https://github.com/in-toto/in-toto
- Notary: https://github.com/theupdateframework/notary
- The Update Framework (TUF): https://theupdateframework.io/
- Sigstore: https://sigstore.dev/
- OPA Gatekeeper: https://github.com/open-policy-agent/gatekeeper
- Kyverno: https://kyverno.io/
- Prometheus: https://prometheus.io/
- Grafana: https://grafana.com/
- Elasticsearch: https://www.elastic.co/elasticsearch
- Kibana: https://www.elastic.co/kibana
- OpenTelemetry: https://opentelemetry.io/
- Wazuh: https://wazuh.com/
- Snort: https://www.snort.org/
- Zeek: https://zeek.org/
- kube-bench: https://github.com/aquasecurity/kube-bench
- Tekton: https://tekton.dev/
- Jenkins: https://www.jenkins.io/
- Travis CI: https://travis-ci.org/
- CircleCI: https://circleci.com/
- Flux CD: https://fluxcd.io/
- Argo CD: https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/
- Docker Hub: https://hub.docker.com/
- Harbor: https://goharbor.io/
- GitHub Container Registry: https://github.com/features/packages
- Nexus Repository: https://www.sonatype.com/product-nexus-repository