kubectl, client libraries, or direct REST calls—route through this component. As the first line of defense, you must tightly control who can communicate with the API server and what operations they can perform.
Key Access-Control Decisions
- Authentication: Verify the identity of users or processes.
- Authorization: Determine which actions authenticated subjects can execute.
Authentication
Kubernetes supports multiple authentication mechanisms. Choose methods based on your environment’s security requirements:| Method | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Static Credentials | Username/password pairs defined in files | Small test clusters |
| Bearer Tokens | Secrets or service account tokens | Automated clients, CI/CD pipelines |
| Client Certificates | X.509 certificates for users and components | Production clusters with strong security |
| External Providers | Integrate with LDAP, OIDC, or webhook token authentication | Enterprise SSO |
| Service Accounts | Automatically managed tokens for in-cluster workloads | Pods requiring API access |
Service accounts are the default identity for workloads inside a cluster. Always assign the minimal set of permissions.

Authorization
After a user or process is authenticated, Kubernetes must decide which API operations they can perform. The most common authorization module is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), but other options exist:| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| RBAC | Grant roles to users or service accounts, defining allowed API groups and resources |
| ABAC | Policy-based on user attributes |
| Node Authorization | Restricts kubelet actions to pods running on the same node |
| Webhook Mode | Delegates authorization to an external service |

Misconfigured RBAC rules can inadvertently grant excessive privileges. Always follow the principle of least privilege.
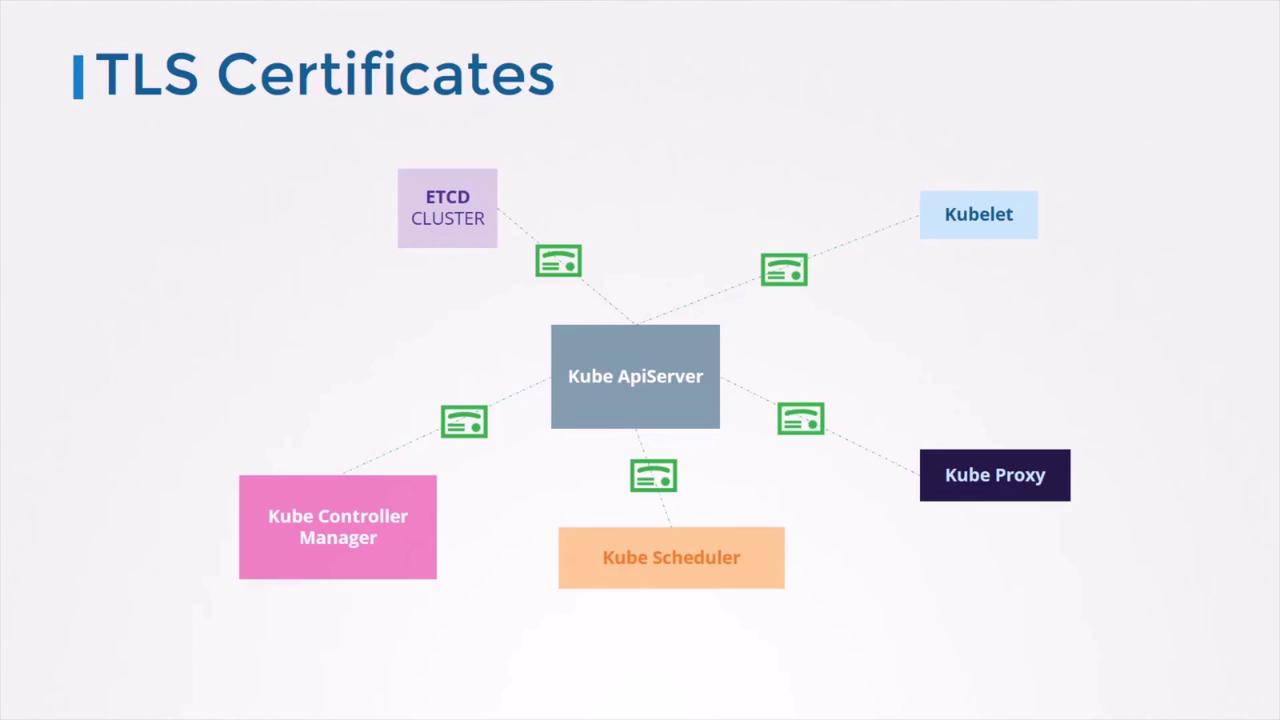
TLS Encryption Between Components
All communication between the API server and other cluster components is encrypted via TLS. This includes:- etcd cluster
- kube-controller-manager
- kube-scheduler
- kubelet and kube-proxy on worker nodes