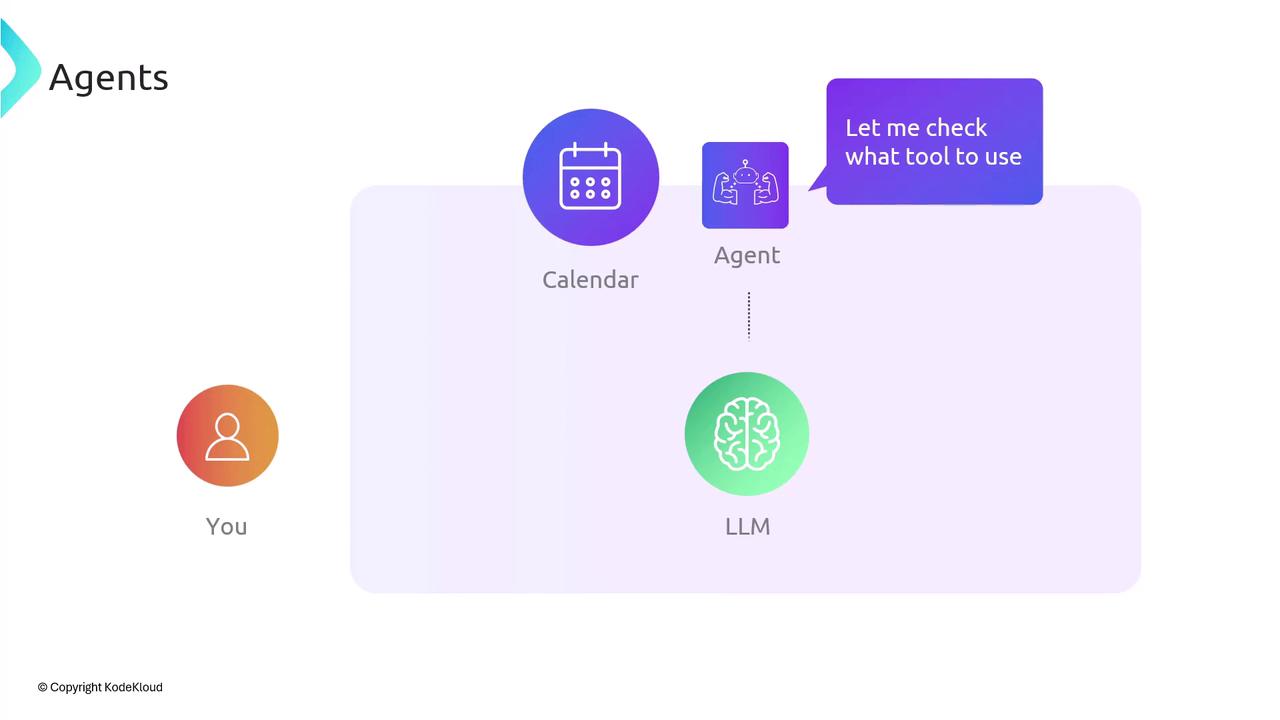
Agents operate in a loop: they consult the LLM for reasoning, invoke tools (APIs, databases, etc.), and feed results back into the LLM until the task is complete.
Agent Workflow
When a user issues a high-level request—such as:“Book me a cab for my return flight.”—the agent breaks it down into sub-steps by interacting with the LLM and external tools:
- Receive Request
The user’s input is sent to the agent’s controller. - Clarify with the LLM
The agent asks the LLM questions:- What is the flight number?
- When does the flight depart?
- What’s the destination city?
- Select Tools
Based on the LLM’s clarifications, the agent chooses required integrations (e.g., a calendar API). - Query External Services
The agent invokes chosen tools, retrieves data, and forwards answers to the LLM. - Generate Plan
The LLM synthesizes a detailed step-by-step plan. - Execute Actions
Finally, the agent uses the plan to call the appropriate APIs (ride-hailing, email confirmation, etc.).
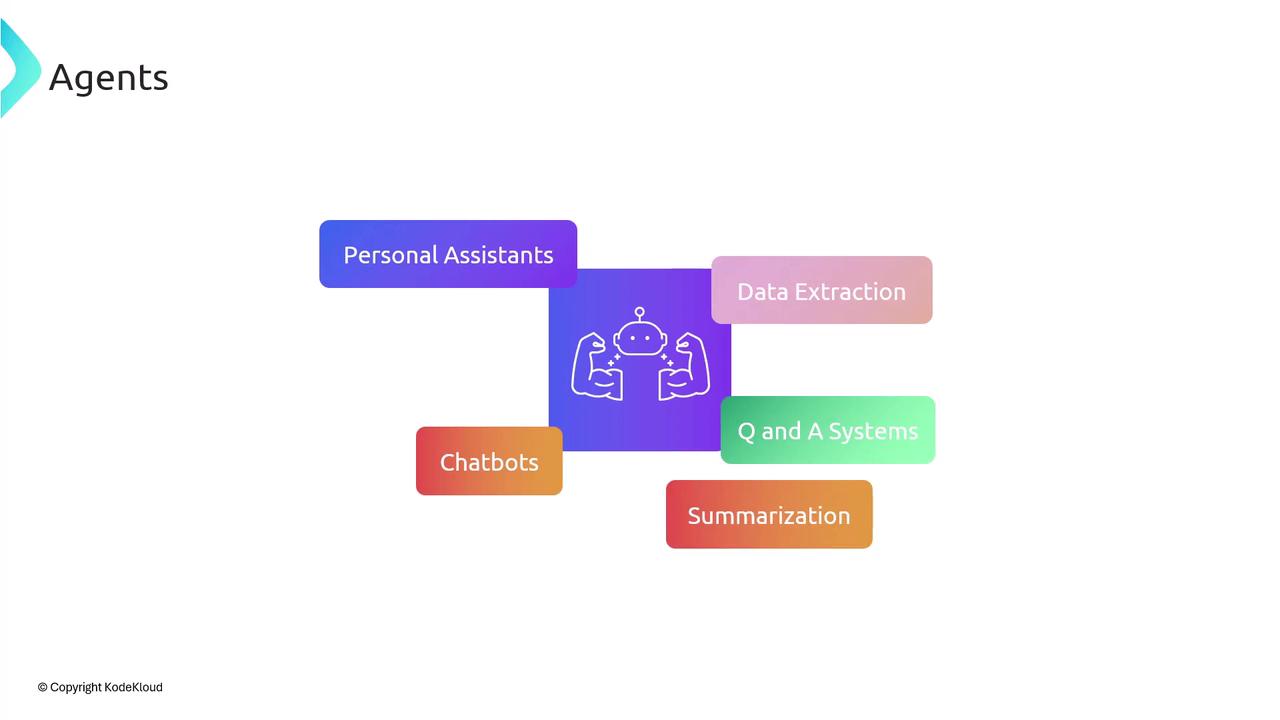
Common Agent Use Cases
Because agents can loop between LLM reasoning and external tools, they excel at:| Use Case | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Assistants | Automate scheduling, reminders, and travel planning | Book flights, reserve hotels, manage calendars |
| Data Extraction | Pull structured data from documents or websites | Extract tables from PDFs, scrape web pages |
| Q&A Systems | Answer domain-specific questions with tool-augmented context | Internal knowledge-base querying |
| Chatbots | Maintain multi-turn dialogue with external API lookups | Order tracking, support ticket status |
| Summarization | Generate concise summaries of long texts or conversations | Meeting notes, research article digests |
Built-in Agent Support
LangChain ships with robust agent frameworks out of the box:- Function Calling: Define and register custom functions that the LLM can invoke.
- Tool Integration: Seamlessly plug in any API or service as a “tool” for the agent.
- Custom Workflows: Combine multiple tools and conditional logic into one orchestrated pipeline.
LangChain Building Blocks
Below is the big-picture view of core LangChain components covered so far:- Model I/O: Designing prompts and processing LLM responses.
- Memory: Managing conversational context, both short-term and long-term.
- Retrieval: Connecting to external data sources and fetching relevant content.
- Chains: Chaining together prompts, APIs, and logic into a cohesive pipeline.
- Tools: Exposing APIs and services for agents to interact with.
- Agents: Orchestrating LLM reasoning with tools to solve complex tasks.