Prerequisites
- Terraform v1.0+ installed
- A valid Linode API token
kubectlinstalled and configured
Store your Linode API token securely. We recommend using environment variables (
TF_VAR_token) or a protected .tfvars file instead of hard-coding credentials.1. Terraform Configuration
1.1 Required Provider
Specify the Linode provider and lock its version:1.2 Provider & Variables
Configure the provider to use your API token:1.3 LKE Cluster Resource
Create an LKE cluster named my-cluster inus-central, using Kubernetes v1.23 and a three-node pool:
If you enable the
autoscaler, ensure your account has sufficient quota for scaling nodes.1.4 Output Kubernetes Configuration
Expose the generated kubeconfig for use withkubectl:
2. Deploying the Cluster
Initialize, plan, and apply your configuration:| Command | Description |
|---|---|
terraform init | Download provider plugins |
terraform plan | Preview changes |
terraform apply -auto-approve | Provision resources automatically |
3. Monitoring Provisioning
You can track cluster creation progress in the Linode Cloud Manager. Provisioning typically takes 5–15 minutes.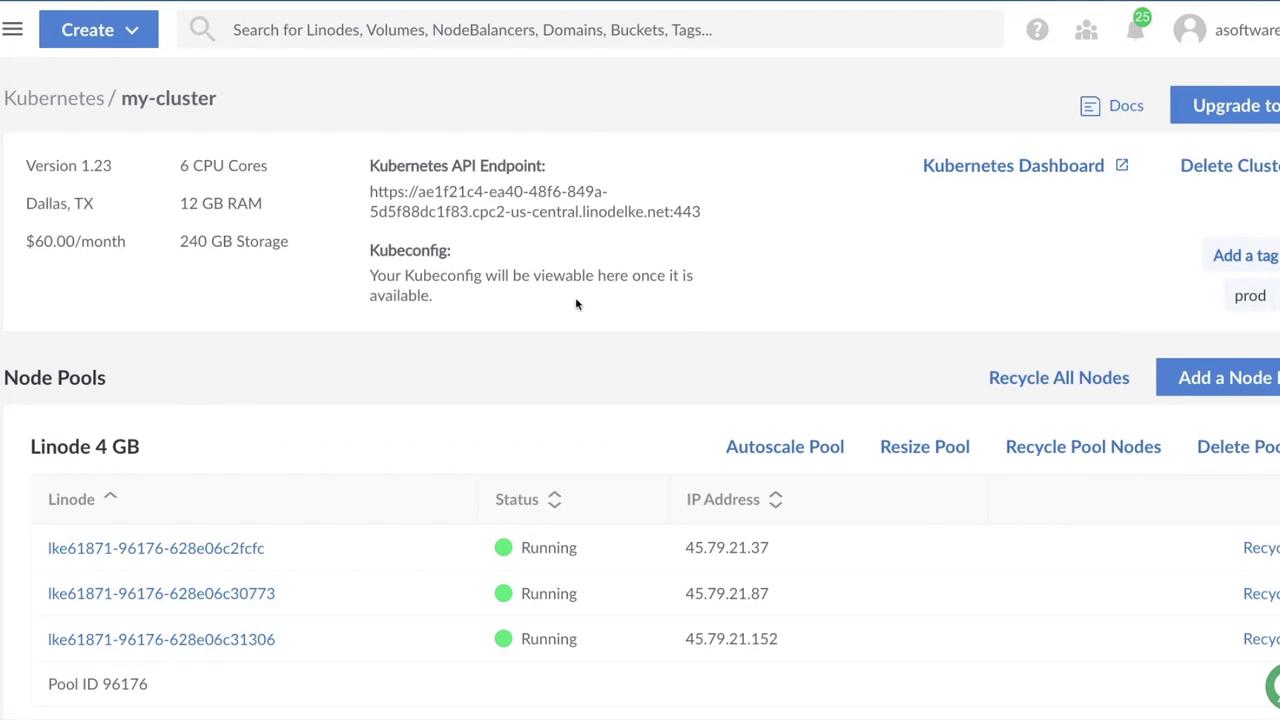
4. Explore the Code on GitHub
View the full Terraform configuration in theLinode folder of the Kubernetes-Quickstart-Environments repo.