Features of Device Management in Azure AD
Azure AD offers several core features to facilitate effective device management:-
Device Identity and Access Management
Azure AD assigns a unique identity to organizational devices, similar to the identities given to users and groups. This allows administrators to control resource access with the same precision and security. -
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) Support
Personal devices can be registered with Azure AD. Once registered, these devices receive an identity, allowing secure access to corporate resources such as OneDrive files, emails, and more. -
Device Authentication and Resource Access
During user sign-in, Azure AD authenticates the device to ensure that only secure and authorized devices gain access to sensitive data. -
Mobile Device Management (MDM) Integration
By integrating with MDM solutions such as Microsoft Intune, organizations can centrally manage devices and enforce compliance policies throughout the enterprise. -
Enhanced Security and Access Control
Administrators can enforce strict policies to deny access to non-compliant devices. For instance, if a device is running a vulnerable OS version, access to corporate resources can be restricted until the necessary updates are applied.
If a vulnerability is discovered in a specific Windows version, device management policies can automatically exclude those devices, marking them as non-compliant until updates are installed.
Benefits of Joining Devices to Azure AD
Joining devices to Azure AD enhances security and provides multiple benefits, including:- Single Sign-On (SSO)
When devices are joined to Azure AD, users enjoy a seamless sign-in experience across applications without being prompted for credentials repeatedly.
- User Settings Roaming
Changes made to user settings on one device automatically synchronize with other Azure AD-joined or enrolled devices, ensuring consistency across the board.
- Windows Store for Business
Organizations can leverage the Windows Store for Business, allowing users to download applications using their corporate credentials. Administrators have full control over app availability and can even publish internal apps, such as a leave management system.
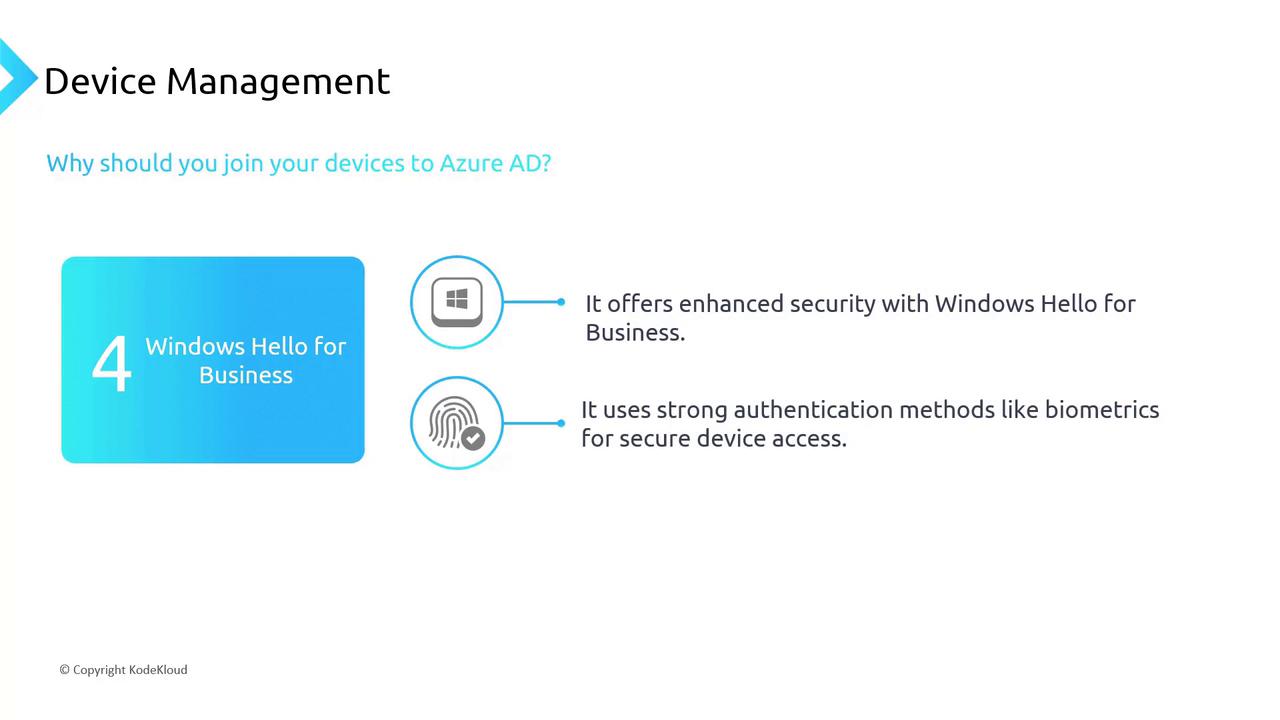
- Windows Hello for Business
Boosting security, Windows Hello for Business uses biometric authentication methods like facial recognition and fingerprint scanning. This multi-factor approach ensures that even if passwords are compromised, unauthorized access is prevented.
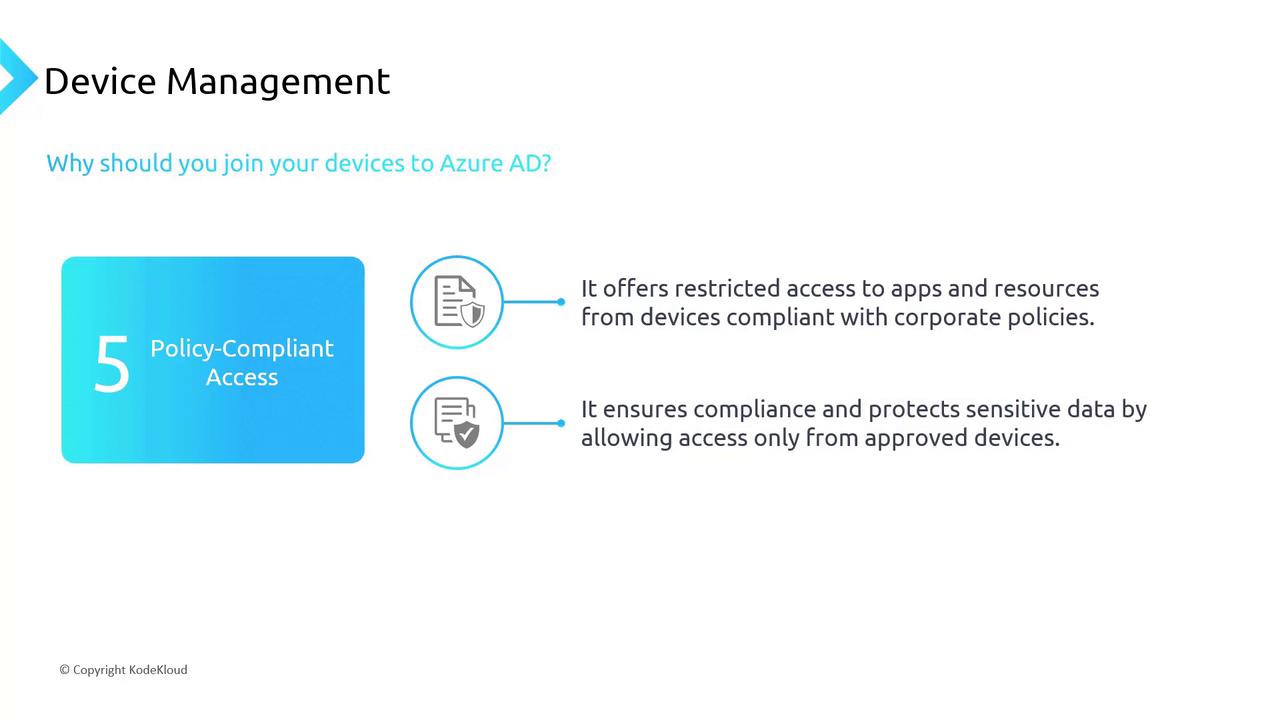
- Policy-Compliant Access
Policy-based controls ensure that only devices meeting specific criteria—such as running a minimum OS version—can access corporate resources. Non-compliant devices are automatically denied access, effectively safeguarding organizational data.
A Practical Walkthrough
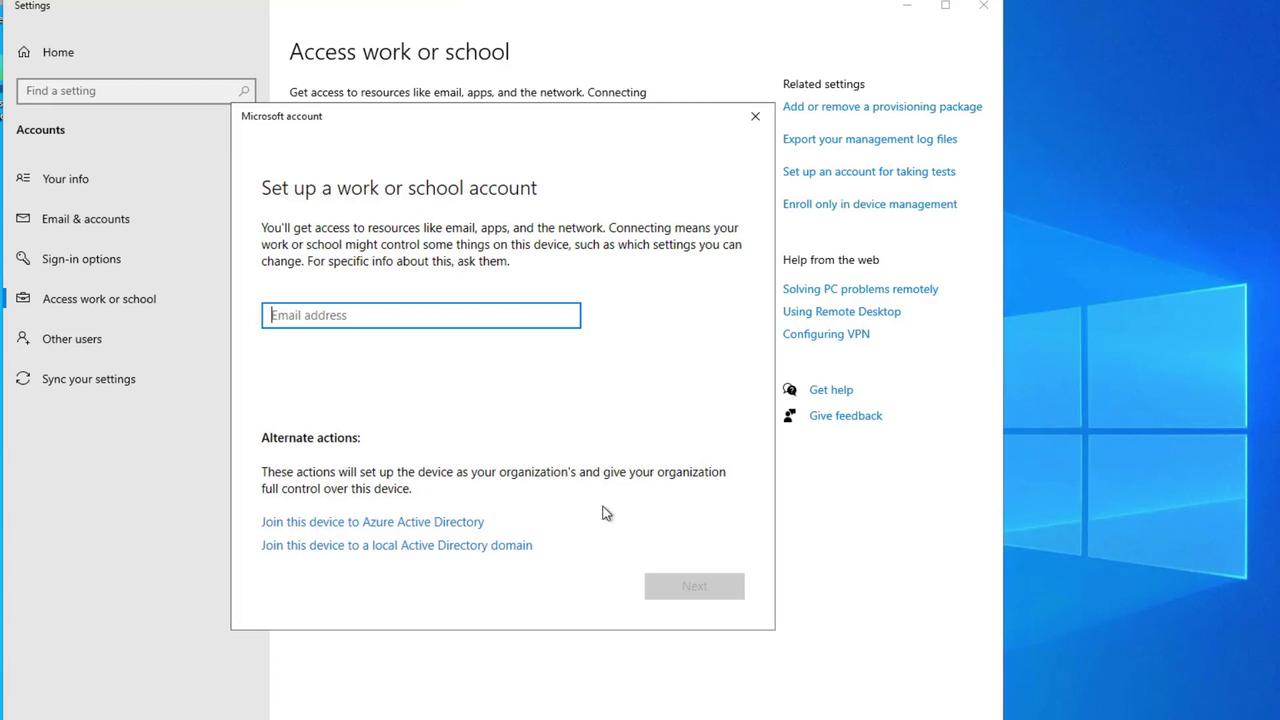
Let’s explore a practical scenario to understand how device management works in Azure AD:- Setting Up a Virtual Machine (VM)
Assume you are working with an Azure virtual machine. From any device, navigate to the “Sign-in options” and select “Access work or school accounts.” Clicking “Connect” prompts you to log in with your Azure AD credentials to enroll the device into management. Once authenticated, the VM becomes managed by your organization.
-
Joining the Device
Select the option to join the device to Azure AD. After completing the sign-in process, your device becomes linked to your organization (e.g., KodeKloud). Note that while the cloud account password cannot be reset via the Control Panel, alternative secure methods such as Ctrl+Alt+Delete can be used to change it. -
Using Azure AD on a Local Machine
On physical machines or local laptops, joining Azure AD enables a full sign-in experience using Azure AD credentials. For example, on a Windows 11 machine running on Hyper-V, once you sign in and configure basic settings, you can further secure your session with Windows Hello and multi-factor authentication (MFA). -
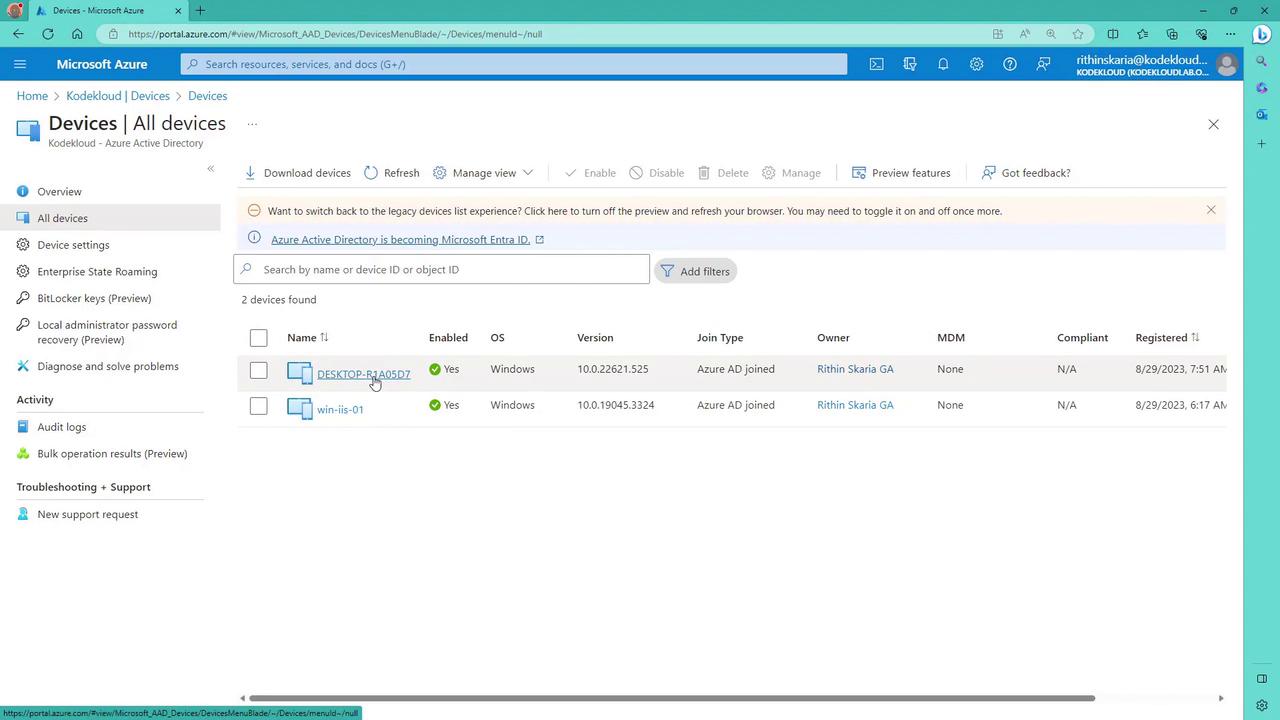
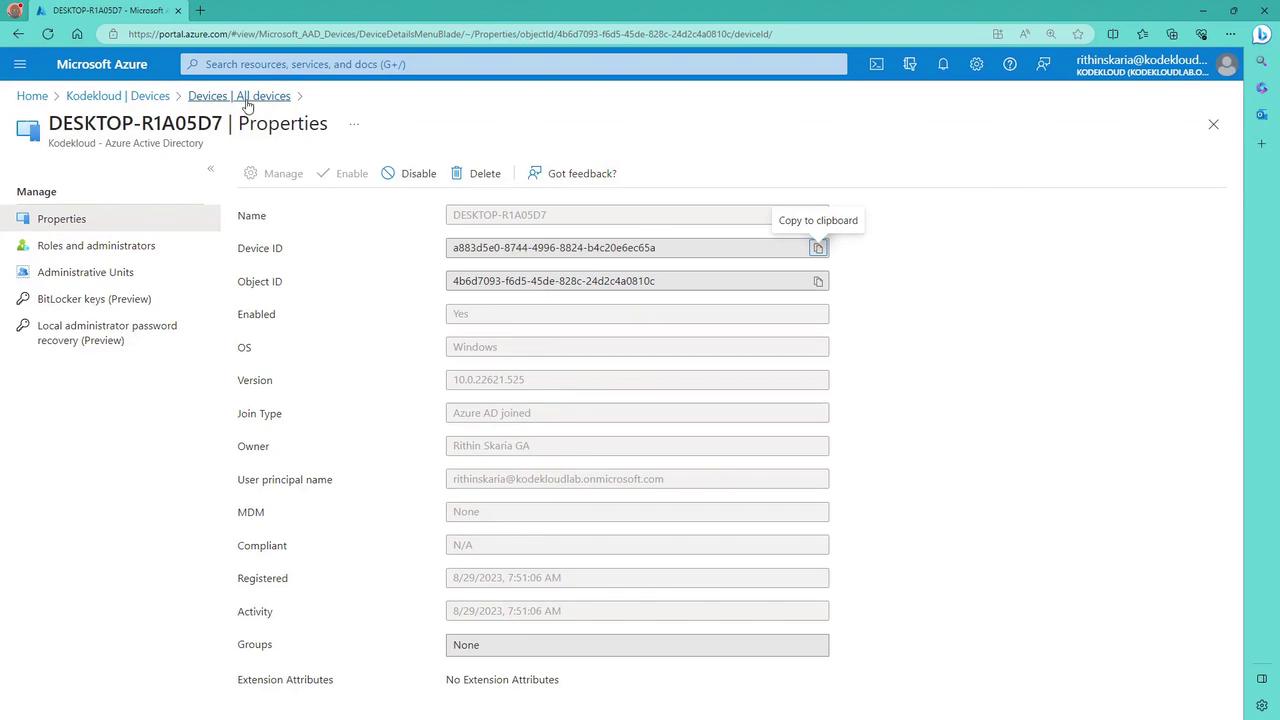
Verifying Device Enrollment in the Azure Portal
Once enrolled, you can monitor the device status in the Azure portal. Navigate to Azure Active Directory > Devices > All devices, and review details like device name, operating system, version, owner, and enrollment date. This comprehensive monitoring is essential for setting up dynamic groups and efficient device management.
Conclusion
Device management in Azure AD is a robust system that combines security, central control, and enhanced user experience. By providing features such as SSO, roaming settings, access to the Windows Store for Business, Windows Hello for Business, and strict policy-compliant access, Azure AD ensures that only secure and compliant devices can connect to organizational resources.In the next lesson, we will delve into passwordless authentication and administrative units, further strengthening your organization’s security posture.