Microsoft Azure Security Technologies (AZ-500)
Secure Azure solution with Azure Active Directory
Investigate roles in Azure AD
In this lesson, we dive deep into the roles available in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). Understanding these roles and their specific permissions is key to managing your resources securely and efficiently.
Azure AD-Specific Roles
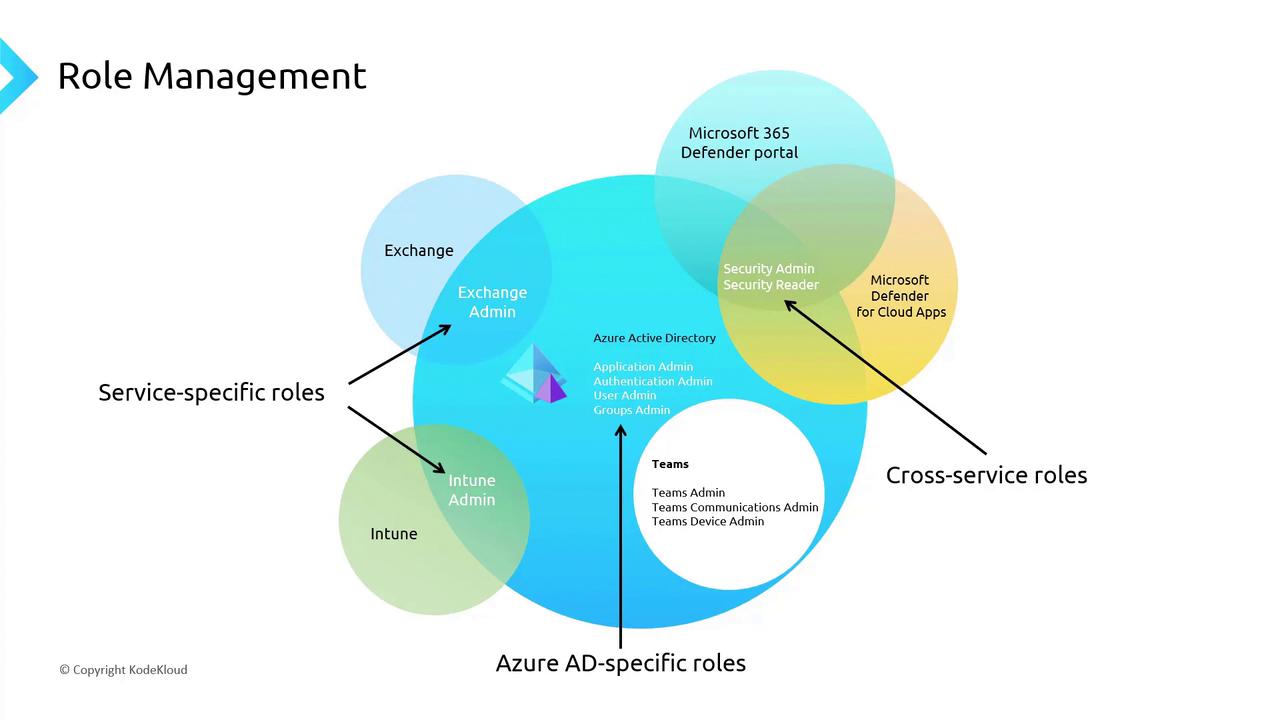
Azure AD-specific roles are designed to manage tasks that are unique to the Azure AD environment. These roles serve as specialized tools for managing users, applications, and groups within Azure AD. Common examples include User Administrator, Application Administrator, and Group Administrator.
Service-Specific Roles
Service-specific roles are tailored to individual Microsoft 365 services. Think of these roles as dedicated captains, each steering their respective service. Examples include the Exchange Administrator, Intune Administrator, SharePoint Administrator, and Teams Administrator, each offering precise control over their designated service.
Cross-Service Roles
Cross-service roles extend across multiple services, providing a unified management experience across Microsoft 365 and Azure AD. These roles serve as ambassadors by ensuring consistency in administration. Global roles such as Global Administrator and Global Reader operate universally across services. In addition, security and compliance roles, like Security Administrator, oversee protection settings and regulatory compliance across platforms.

Role Categories in Depth
Azure Active Directory is structured into several role categories, each designed for distinct management areas:
| Role Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Azure AD-Specific Roles | Roles focused solely on managing Azure AD functions. | Application Administrator, User Administrator |
| Service-Specific Roles | Roles that manage individual Microsoft 365 services. | Exchange Administrator, Teams Administrator |
| Cross-Service Roles | Roles with permissions that span multiple Microsoft 365 services and Azure AD. | Global Administrator, Global Reader, Security Administrator |
Built-In Roles in Azure AD
Azure AD includes both administrative and non-administrative roles:
- Administrators: Responsible for critical tasks such as user creation, group management, and device policy enforcement.
- Non-administrators: Users without administrative privileges.
Key Built-In Roles
Global Administrator
The Global Administrator is the highest authority within Azure AD. This role provides full access to manage users, groups, application settings, and security configurations, along with the authority to delegate administrative tasks.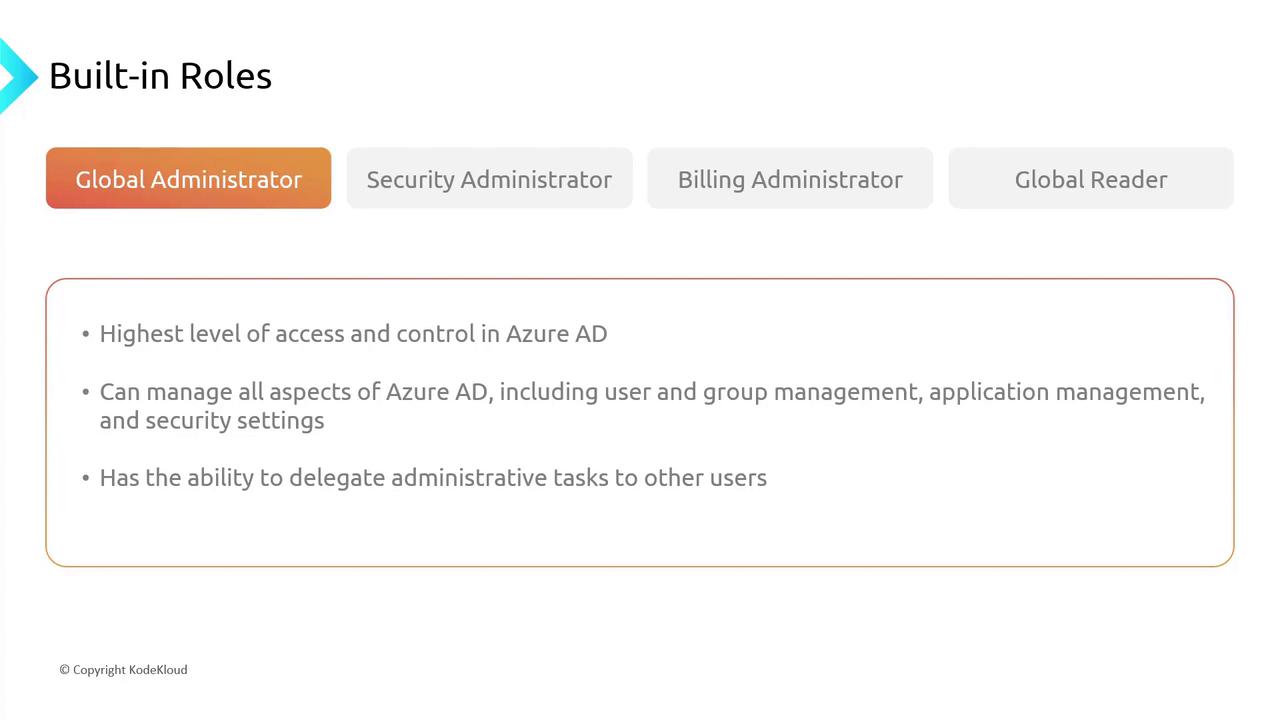
Security Administrator
Serving as the guardian of Azure AD, the Security Administrator manages security settings, policies, and monitors events to ensure the integrity of your environment.
Billing Administrator
The Billing Administrator oversees subscription management, monitors costs, and ensures that resource consumption stays optimized.
Global Reader
With a focus on oversight, the Global Reader has read-only access to configurations, settings, and reports. This role is ideal for auditors and stakeholders who need to review system details without making any changes.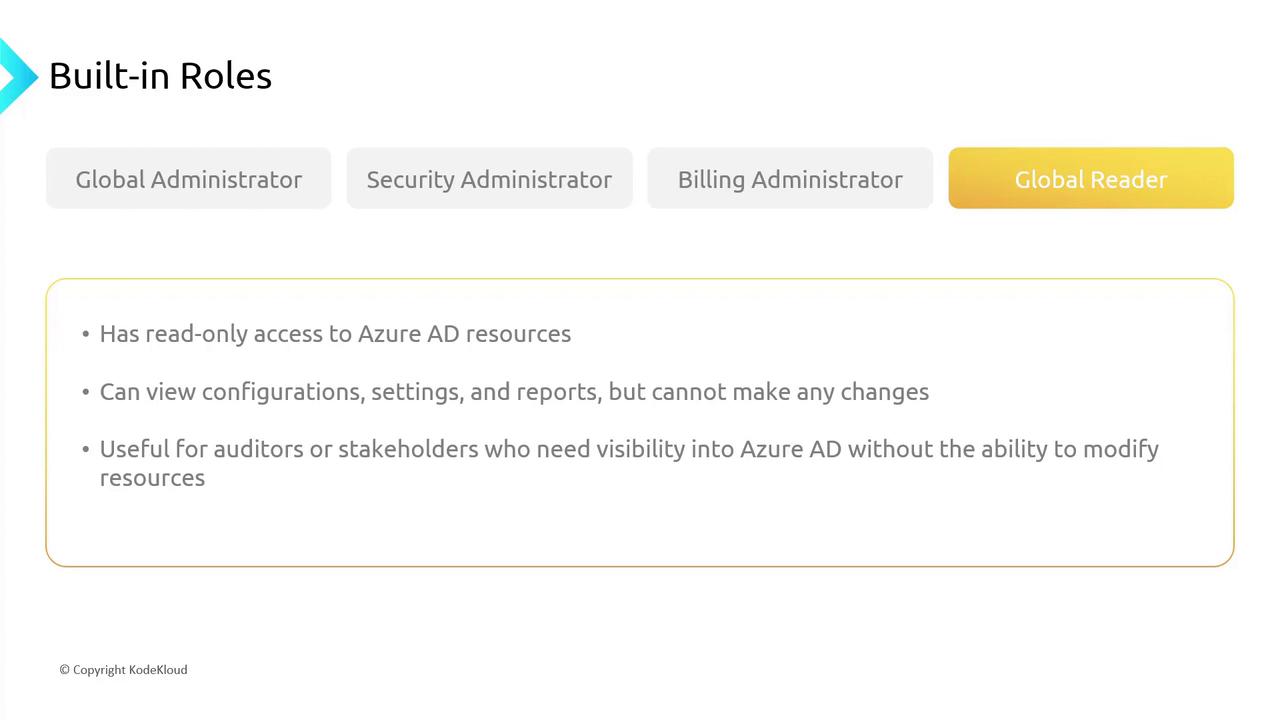
Note
Remember to apply the principle of least privilege when assigning roles. This practice ensures that users receive only the access necessary for their tasks, thereby reducing security risks.
Final Thoughts
Roles in Azure AD are more than just titles—they define the level of responsibility and access within your environment. While some roles, like the Teams Administrator, are service-specific, roles such as Global Administrator and Global Reader offer cross-service capabilities applicable across Microsoft 365 and Azure AD.
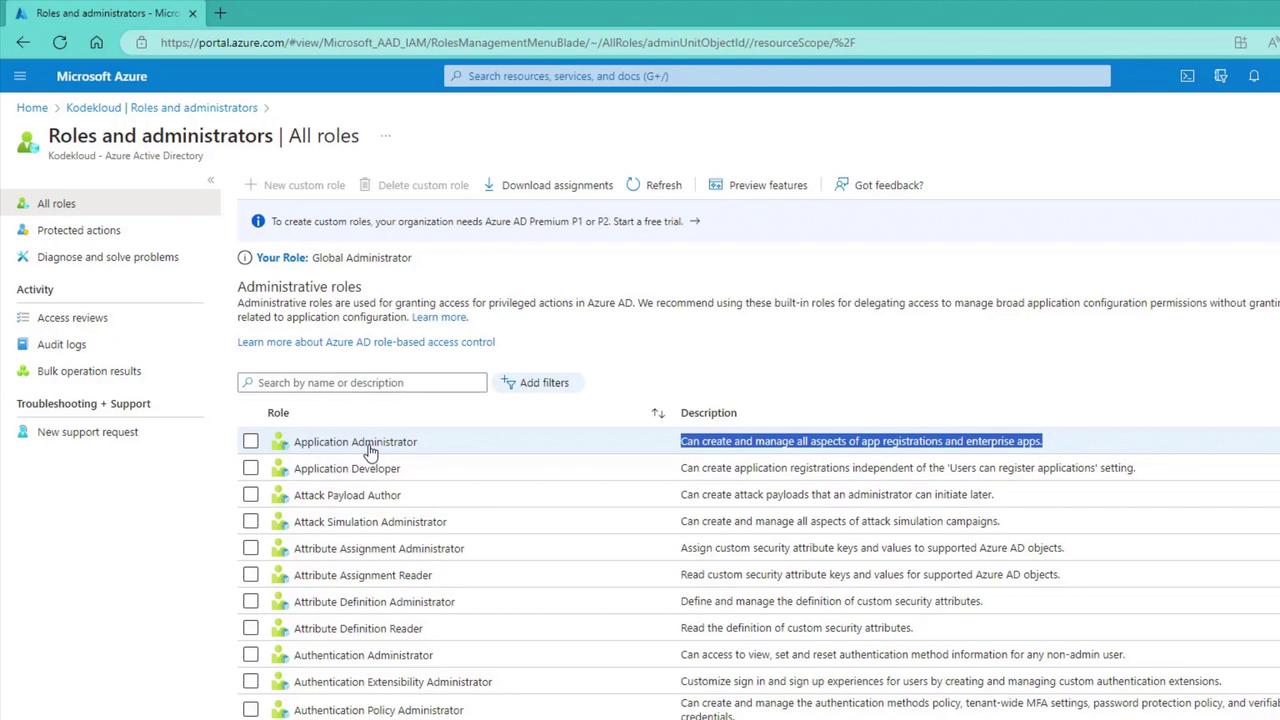
To manage these roles, navigate to the Azure AD section in the Azure Portal. Here, you can review the list of available roles, assign tasks, and maintain operational security by delegating responsibilities appropriately. As you move forward with creating users and groups, you’ll learn how to effectively assign these permissions.
Finally, let's transition to discussing the deployment of Azure AD Domain Services.
Watch Video
Watch video content