- Docker Engine metrics
- Container-specific metrics with cAdvisor
Enabling Docker Engine Metrics
Follow these steps on your Docker host to enable Docker Engine metrics:- Create a file named
daemon.jsonin the/etc/dockerdirectory. - Configure the Docker daemon to expose the metrics endpoint. In this file, specify the metrics adapter, set the IP address and port, and enable experimental features.
- Restart Docker to apply these changes.
- Verify the configuration by curling the metrics endpoint.
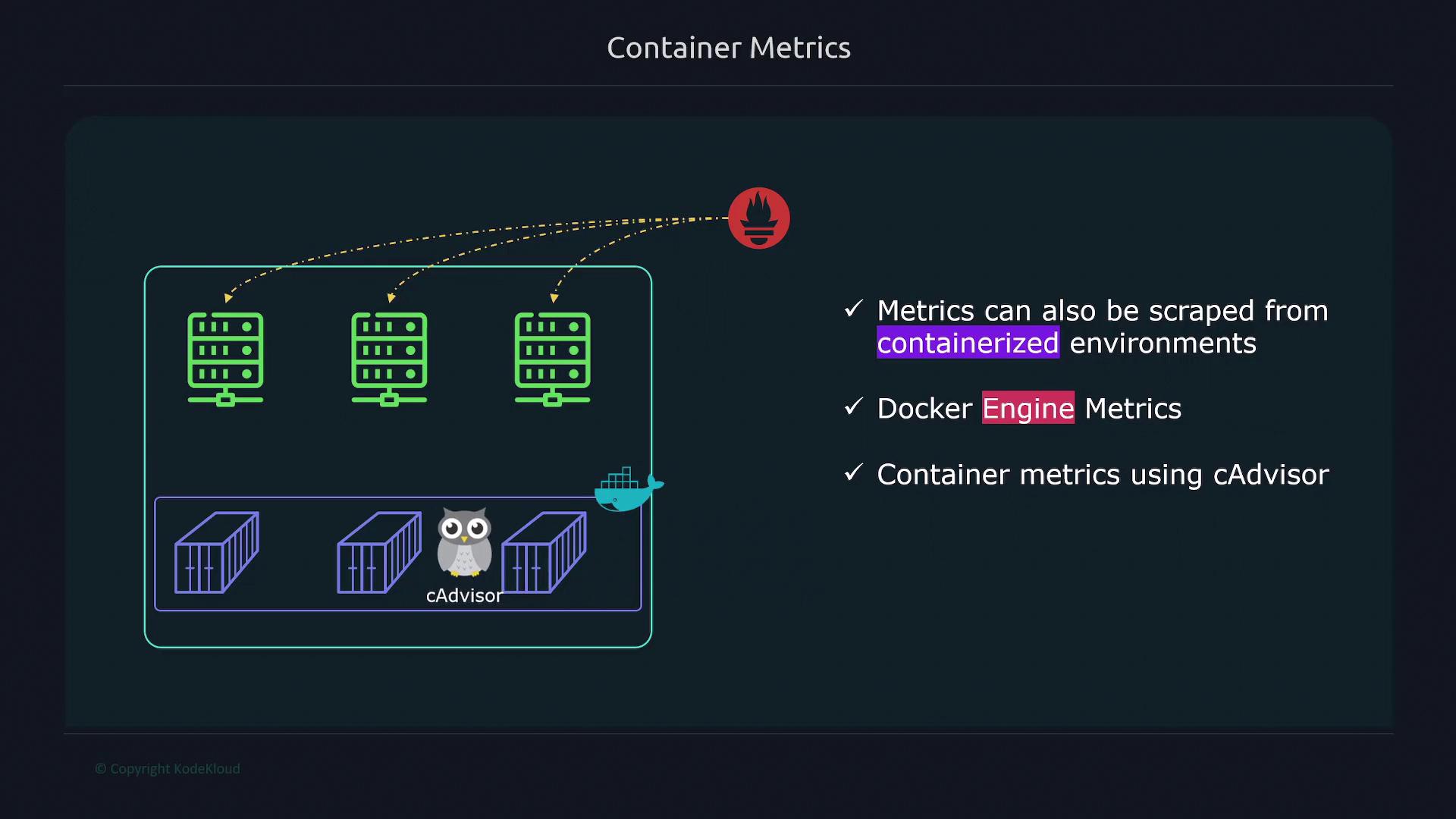
Enabling cAdvisor for Container Metrics
To obtain detailed, container-specific metrics, deploy cAdvisor using Docker Compose. Follow these steps:- Create a Docker Compose file.
- Define a service for cAdvisor, ensuring it has the necessary privileges and mounts to access system metrics.
- Launch cAdvisor on your Docker host.
Comparing Docker Engine and cAdvisor Metrics
Docker Engine metrics provide insights into the performance of the entire Docker engine. These metrics include CPU usage, the total number of failed image builds, and the processing time for container actions. However, they do not offer container-specific details. In contrast, cAdvisor delivers a granular view of individual container performance, covering:- CPU and memory usage per container
- The number of processes running within a container
- Container uptime
| Feature | Docker Engine Metrics | cAdvisor Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Overall engine performance | Detailed container-specific performance |
| CPU & Memory Utilization | General engine metrics | Per-container usage details |
| Process Tracking | Not available | Detailed process count per container |
| Use Case | Monitoring Docker daemon health | In-depth analysis of container behavior |
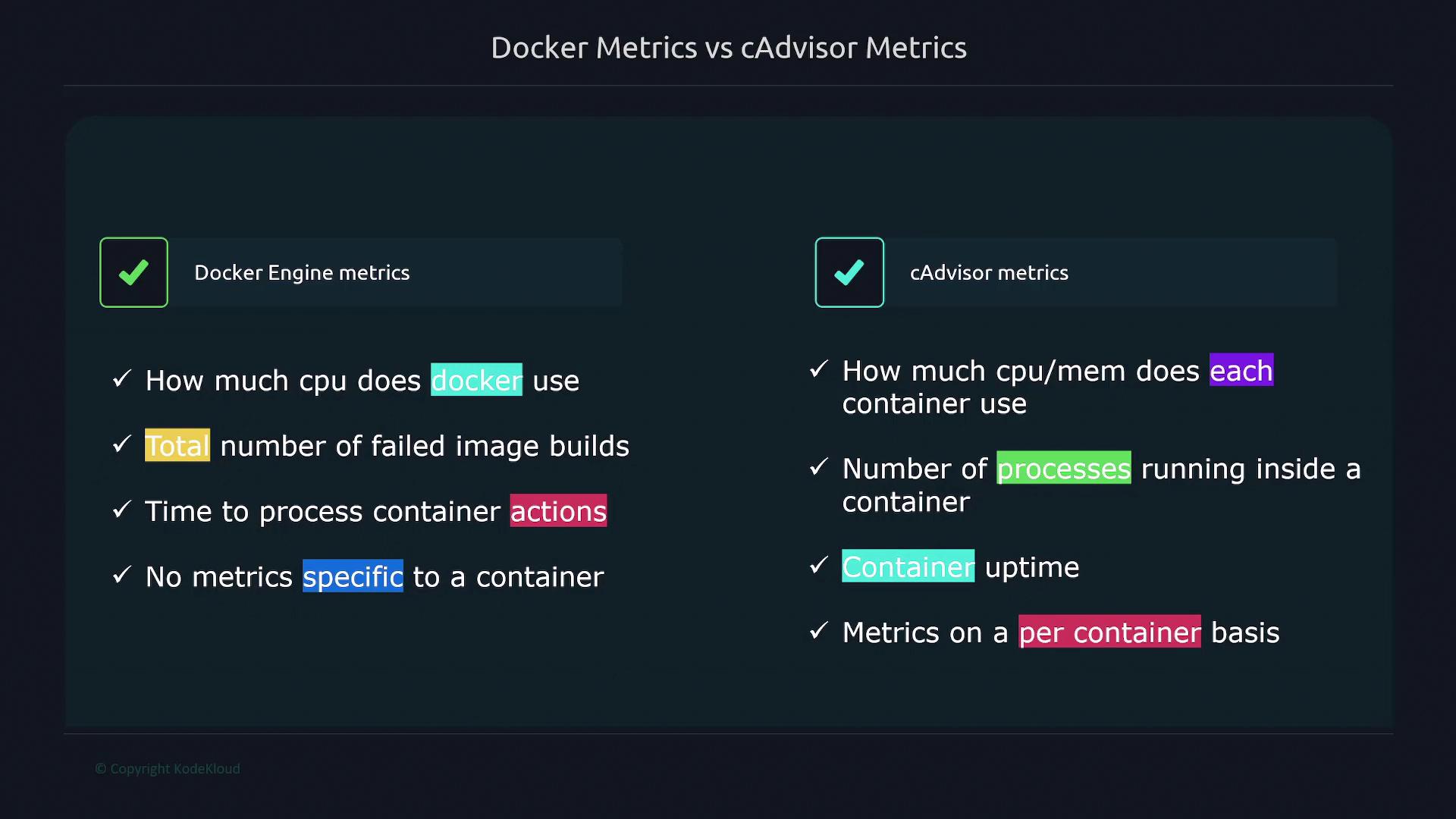
For a comprehensive monitoring solution, use Docker metrics for overall engine health and cAdvisor metrics for detailed container performance insights.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can efficiently monitor both Docker Engine and container-specific metrics using Prometheus. This dual-approach provides you with a robust view that helps optimize performance and troubleshoot issues in containerized environments.