Telepresence For Kubernetes
Telepresence For Kubernetes
Telepresence Intercept
Learn how to intercept Kubernetes Service traffic and handle requests locally using Telepresence. This guide covers setup, command syntax, traffic flow, and best practices for collaborative development.
Prerequisites
- A running Kubernetes cluster with the Telepresence Traffic Manager installed.
- An active Telepresence session:
This establishes a secure tunnel between your local environment and the cluster.telepresence connect
Creating an Intercept
To redirect Service traffic for local debugging, you create an intercept on a Deployment. In this example, a products-depl Deployment is exposed on port 3000 in the cluster:
Command Syntax
| Argument / Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| products-depl | Name of the Deployment or Service to intercept | products-depl |
--port LOCAL:REMOTE | Forward REMOTE port in the cluster to LOCAL port on your host | --port 8000:3000 |
Run the intercept:
telepresence intercept products-depl --port 8000:3000
Note
If the target Service exposes only one port, you can omit :REMOTE.
For example:
telepresence intercept products-depl -p 8000
Once the intercept is established, Telepresence injects a traffic-agent sidecar into the products-depl Pod. All calls from other Pods (for example, an inventory Service) to port 3000 are proxied through the cluster to your local process on port 8000.
Intercept Details
After running the command, Telepresence prints status information:
telepresence intercept products-depl -p 8000
Using Deployment products-depl
Intercept name : products-depl
State : ACTIVE
Workload kind : Deployment
Destination : 127.0.0.1:8000
Service Port Identifier : 3000/TCP
Volume Mount Point : /tmp/telfs-1147625726
Intercepting : all TCP connections
Listing and Managing Active Intercepts
View all active intercepts:
telepresence list
You can intercept multiple Services in parallel. Just ensure each local port is unique:
telepresence intercept products-depl --port 8000:3000
telepresence intercept inventory-depl --port 9000:3000
Warning
Each intercept binds a unique local port. Reusing a port will cause the command to fail.
Traffic Flow with Multiple Intercepts
When one intercepted Service calls another, traffic may loop through the cluster multiple times:
- Client in cluster → local
products-depl(port 8000) - Local
products-depl→ cluster → localinventory-depl(port 9000) - Local
inventory-depl→ cluster → localproducts-depl→ original caller
This indirect routing can impact performance. While you can manually adjust /etc/hosts or use a local proxy to shortcut these hops, Telepresence does not automate intra-local traffic resolution.
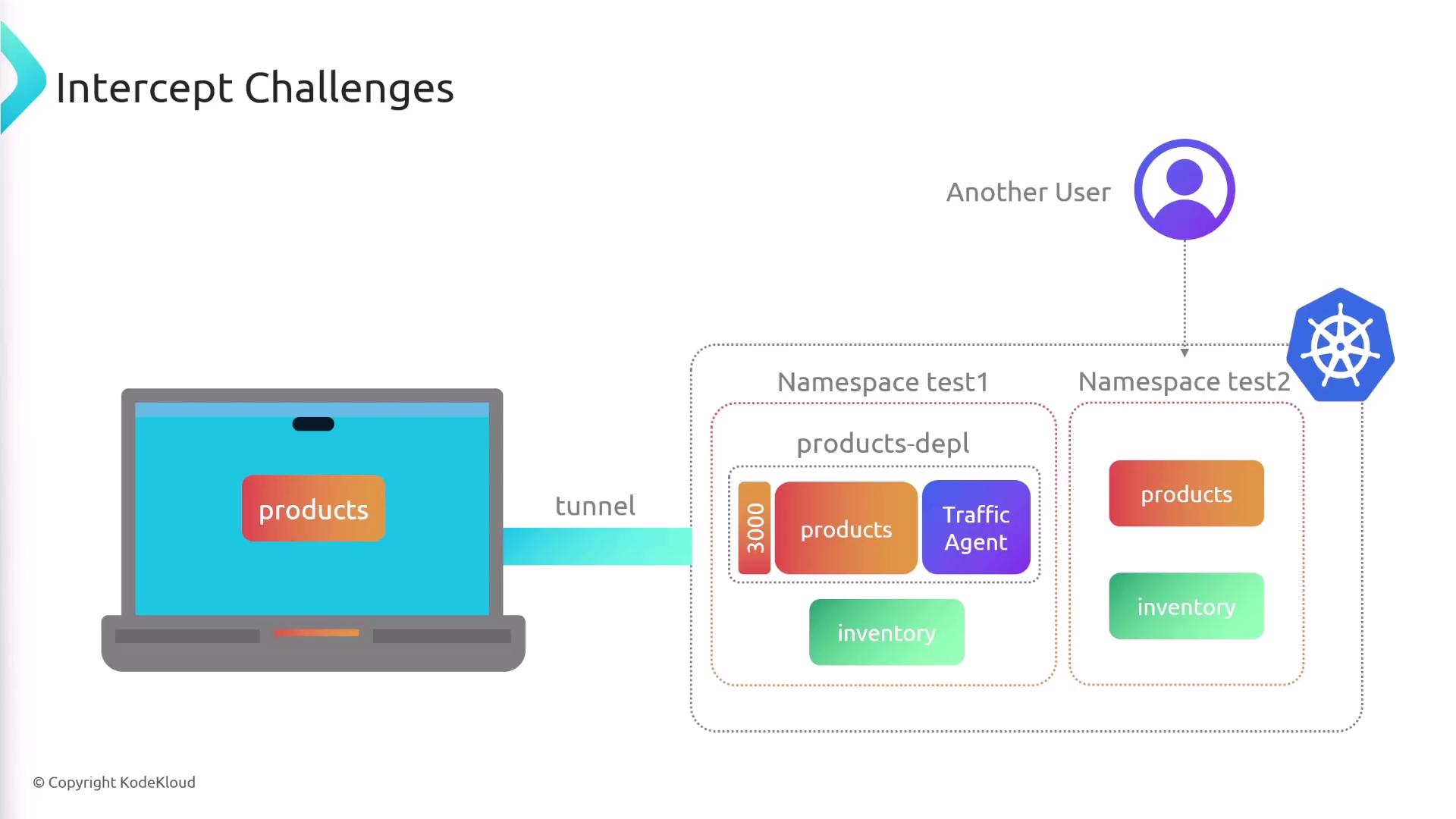
Collaboration Best Practices
Active intercepts route all cluster traffic for a Service to your machine. If multiple developers intercept the same Service in a shared namespace, requests will collide.
- Deploy each developer’s version into a dedicated namespace.
- Instruct teammates to intercept only their namespace’s resources.
Watch Video
Watch video content