Terragrunt for Beginners
Terragrunt Configuration
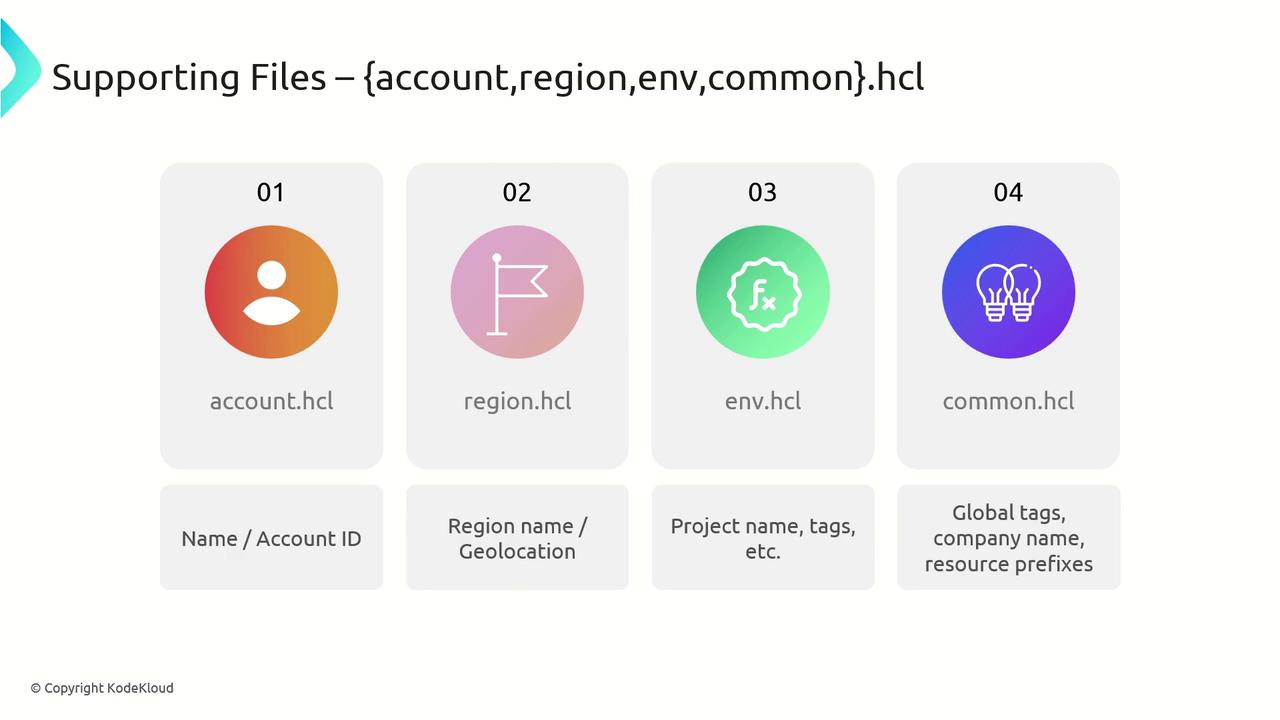
Supporting Files accountregionenvcommon
Terragrunt supporting files let you centralize environment-specific and global settings, promoting consistency and reusability across Terraform configurations. By defining variables in dedicated HCL or YAML files, you tailor deployments to specific accounts, regions, and environments without duplication.
Core Supporting Files
| File | Purpose | Typical Contents |
|---|---|---|
| account.hcl | Account-specific details | account_id, account_name |
| region.hcl | Region-specific parameters | AWS regions like us-east-1, geolocation |
| env.hcl | Environment-specific values | project_name, tag conventions, parameters |
| common.hcl | Global defaults shared across all environments | Company tags, naming conventions |
Note
Supporting files can be written in HCL or YAML. Use HCL for native Terraform/Terragrunt integration, or YAML if you prefer readability and tooling compatibility.
Place these files alongside your Terraform modules:
live
├── account.hcl
├── region.hcl
├── env.hcl
├── common.hcl
└── modules
└── app
└── terragrunt.hcl
Example Configurations
# example-account.hcl
locals {
account_id = "123456789012"
account_name = "production-account"
}
# example-common.yaml
globals:
company_name: "AcmeCorp"
tags:
- "owner:infra"
- "compliance:internal"
Benefits of Supporting Files
- Reusability: Import shared settings across multiple modules and environments.
- Maintainability: Update a value in one file and have it propagate everywhere.
- Consistency: Enforce standard tagging, naming conventions, and defaults.
Warning
Avoid committing sensitive data (like credentials or secrets) directly in these files. Use tools like Vault or encrypt secrets with sops.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content