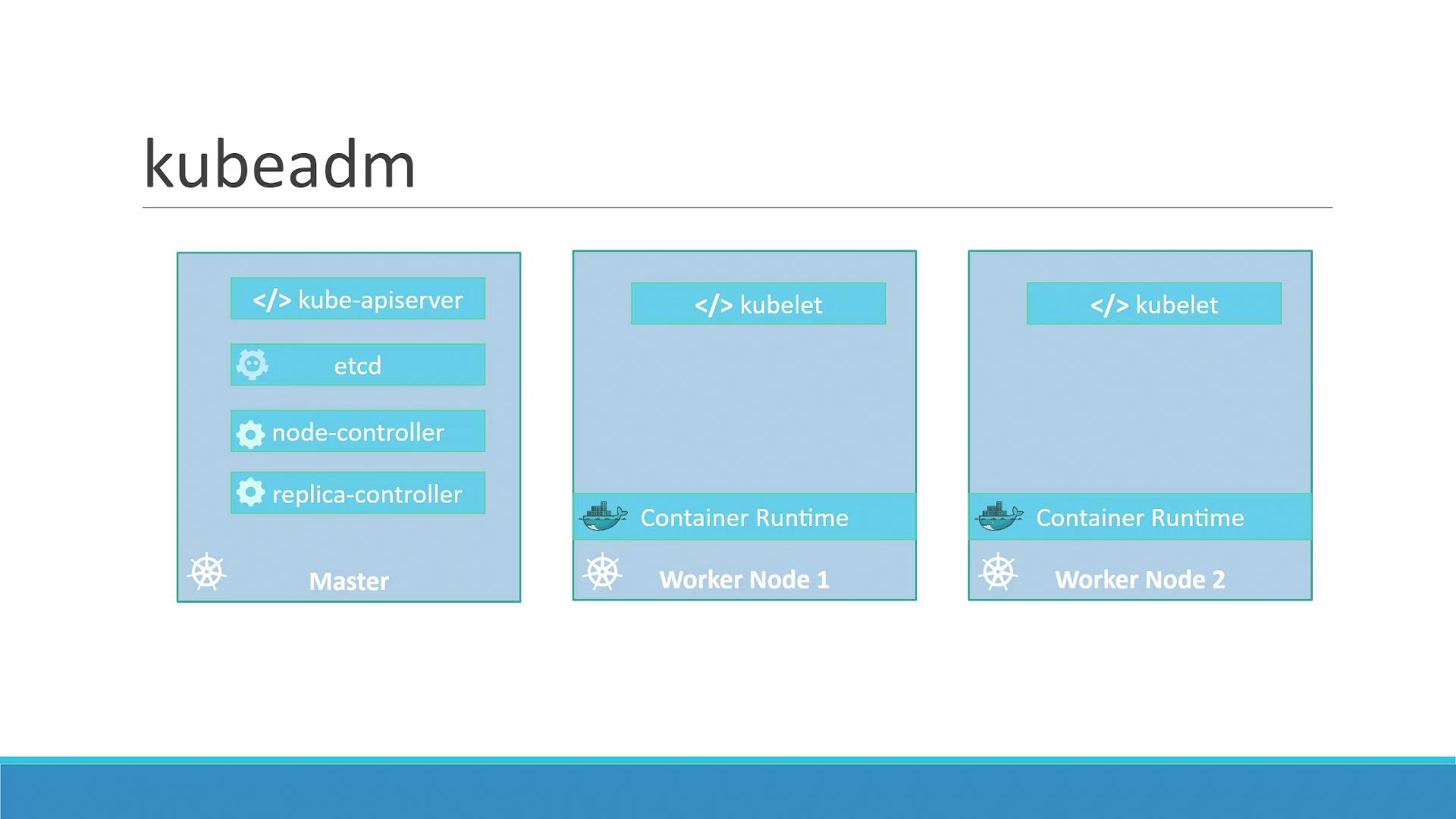
Manually installing and configuring each component across multiple nodes can be error-prone and time-consuming. Kubeadm automates this process by synchronizing installations, configurations, and certificate setups, leading to a streamlined cluster creation process.
High-Level Setup Steps
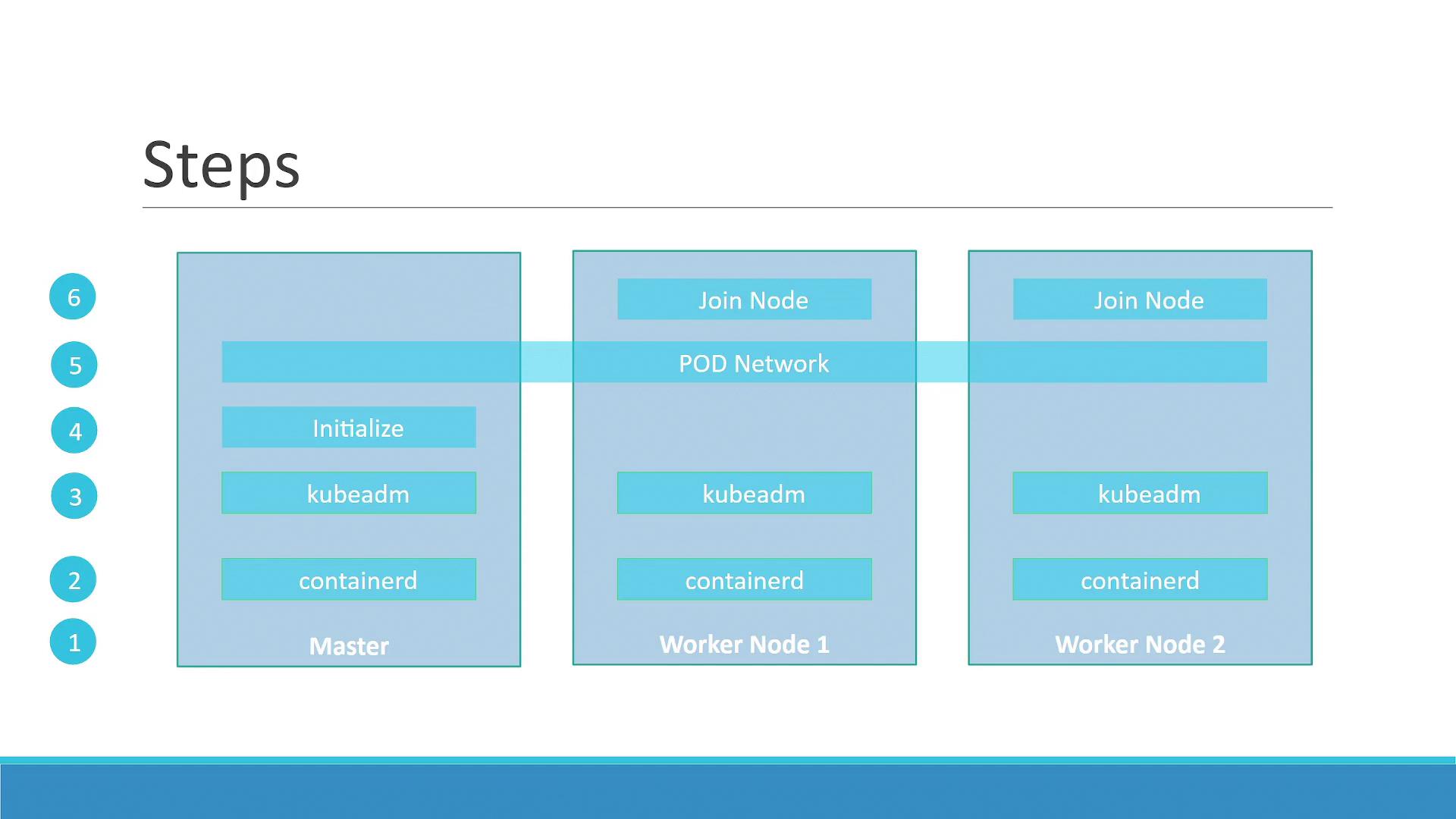
Follow these steps to create a Kubernetes cluster using kubeadm:- Provision Nodes: Set up multiple physical or virtual machines. These nodes will form your Kubernetes cluster.
- Designate Roles: Identify one node as the master and assign the remaining nodes as workers.
- Install Container Runtime: Deploy a container runtime on every node. In this tutorial, we use ContainerD.
- Deploy Kubeadm: Install the kubeadm tool on all nodes. Kubeadm orchestrates the installation of the necessary Kubernetes components.
- Initialize the Master Node: Run the initialization process on the master node. Kubeadm installs and configures all components required to control the cluster.
- Set Up Networking: Before adding worker nodes, ensure your pod network prerequisites are satisfied. Kubernetes requires a dedicated pod network for inter-node communication beyond basic connectivity.
- Join Worker Nodes: Add worker nodes to the cluster once the pod network is configured.
- Deploy Applications: With your cluster up and running, you can now deploy and manage your applications seamlessly.
This guide provides a foundational overview to help you set up a local Kubernetes cluster using kubeadm. For detailed configuration and advanced setups, refer to the Kubernetes Documentation.