Understanding the Hierarchy
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad field focused on designing systems that emulate human reasoning, learning, and problem-solving. It incorporates a range of techniques—from rule-based systems to advanced algorithms that power ML and DL—all geared towards enhancing productivity and transforming industries. Machine Learning, a subset of AI, centers on the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from data. By identifying patterns, these models can predict outcomes and enable smarter decision-making in applications such as spam filtering, fraud detection, and predictive maintenance. Deep Learning, a specialized area within machine learning, utilizes multi-layered neural networks to capture intricate data patterns. Drawing inspiration from the human brain, these networks learn hierarchical representations from large datasets and robust computational power. Deep learning is crucial for tasks like speech and facial recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous vehicle navigation.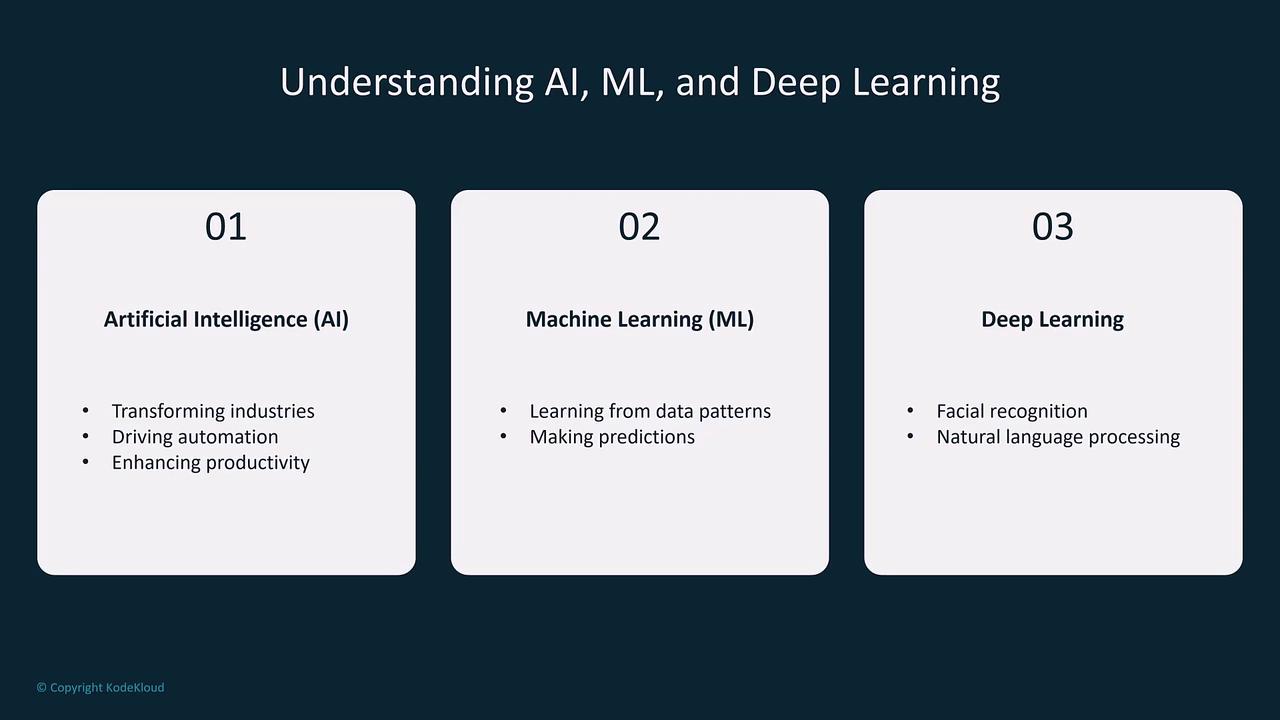
The Relationship Between AI, ML, and Deep Learning
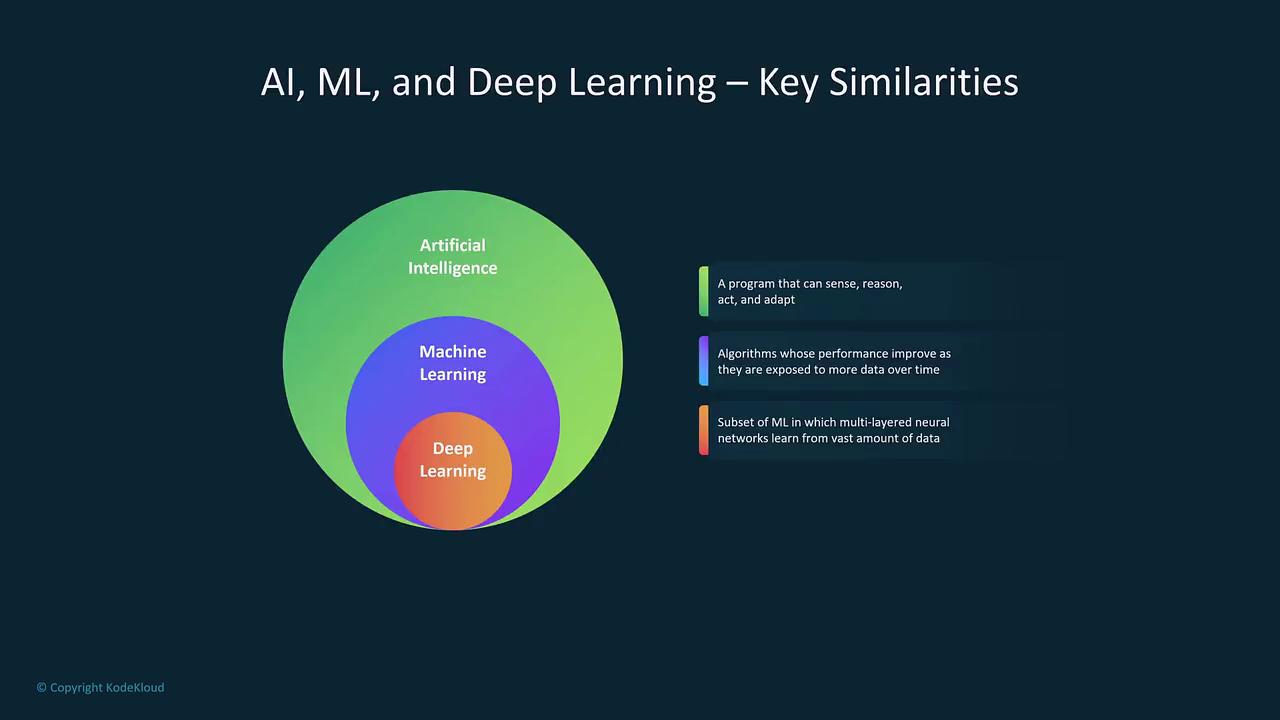
The relationship among these fields can be visualized as nested circles, each layer representing a deeper level of specialization:- Artificial Intelligence: The overarching field encompassing all systems that simulate human intelligence.
- Machine Learning: A subset focused on predictive analysis by learning from data patterns.
- Deep Learning: A further specialized subset that leverages complex neural networks to execute high-precision tasks.
Choosing the Right Approach
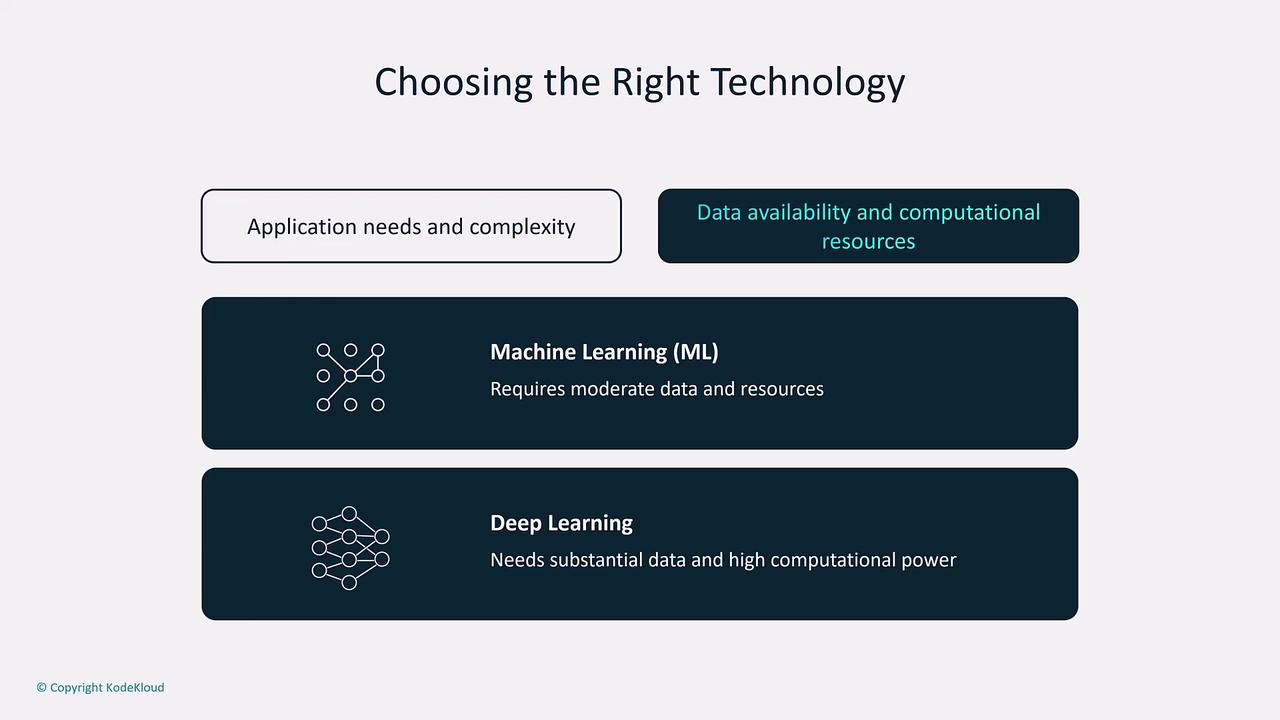
When selecting an approach for your project, consider the complexity of the task, the data available, and the computational resources at hand.- Machine Learning is ideal for applications that require moderate data and computational power, such as predicting customer behavior or detecting fraudulent transactions.
- Deep Learning is best suited for applications demanding high accuracy in complex tasks—like multi-object recognition in autonomous driving—where large data volumes and significant computational resources are necessary.
When deciding between ML and DL, evaluate your application’s requirements, including the type and amount of data available as well as your computational capacity.
Summary
To recap the distinctions:- Artificial Intelligence: Encompasses all methods and systems that imitate human intelligence, including both rule-based and learning algorithms.
- Machine Learning: Focuses on algorithms that predict and infer outcomes from data.
- Deep Learning: Employs complex multi-layer neural networks to analyze large volumes of unstructured data and deliver precise results.
Understanding the distinctions between AI, ML, and Deep Learning is critical for building effective and efficient systems. Evaluating your project’s specific requirements will guide you in choosing the most suitable approach.