The Impact of AI-Powered Applications
AI-powered applications are revolutionizing various fields by enhancing efficiency, reducing operational costs, and accelerating decision-making. Companies are adopting AI solutions—from chatbots to automated data analysis—to serve as force multipliers, enabling smarter and faster business operations.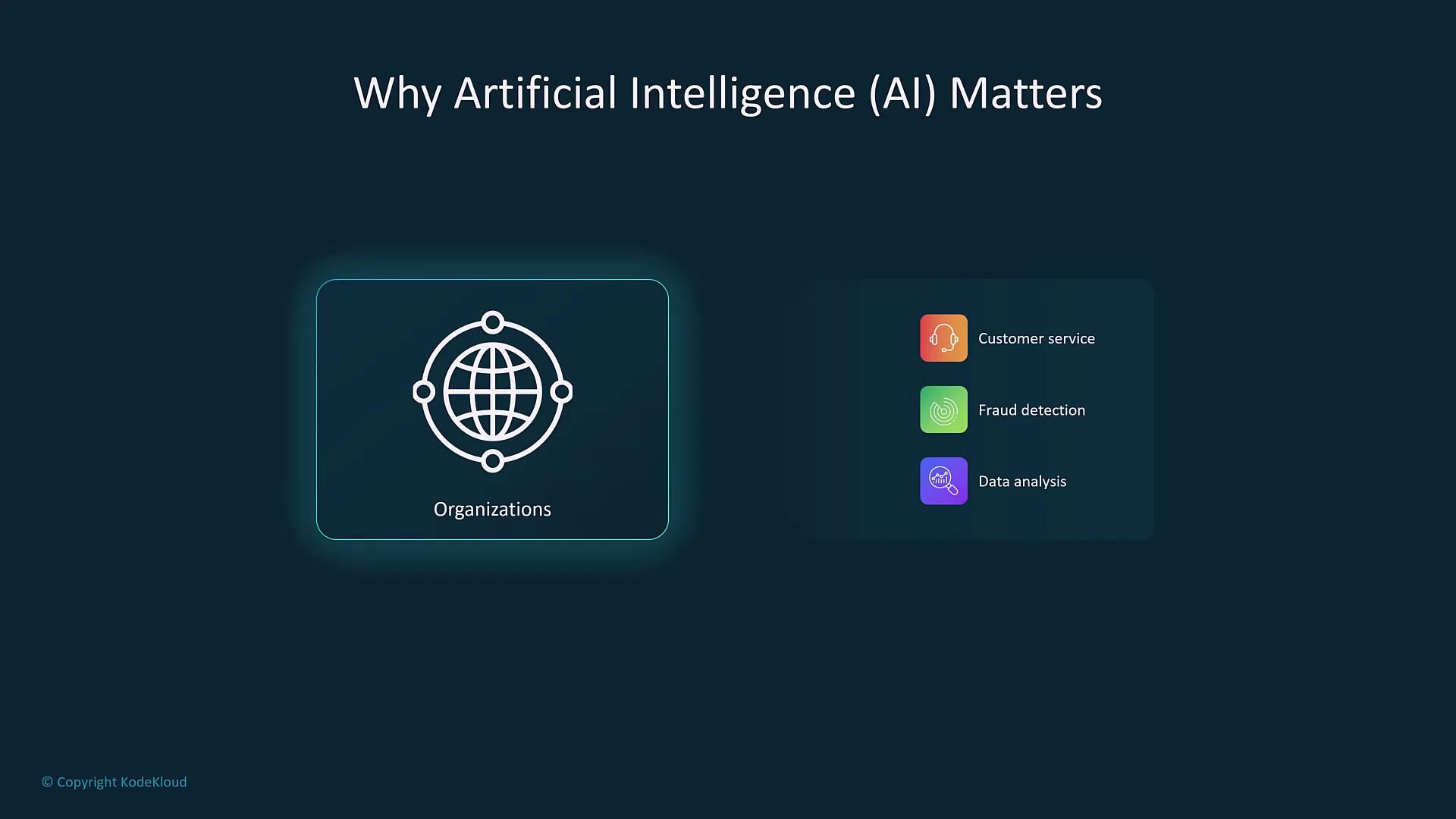
AWS and Its Role in Advancing AI
AWS is a major enabler of AI innovation with services such as SageMaker for machine learning and Rekognition for image analysis. These tools democratize access to advanced data processing and categorization, even for non-experts, breaking down previous barriers.
Transition to Machine Learning Systems
Since around 2015-2016, there has been a significant shift from traditional rule-based software to machine learning systems. Rule-based systems follow fixed logic—for instance, credit approval based on pre-set thresholds—whereas machine learning (ML) systems learn probabilistically from historical data, adapting to unseen scenarios.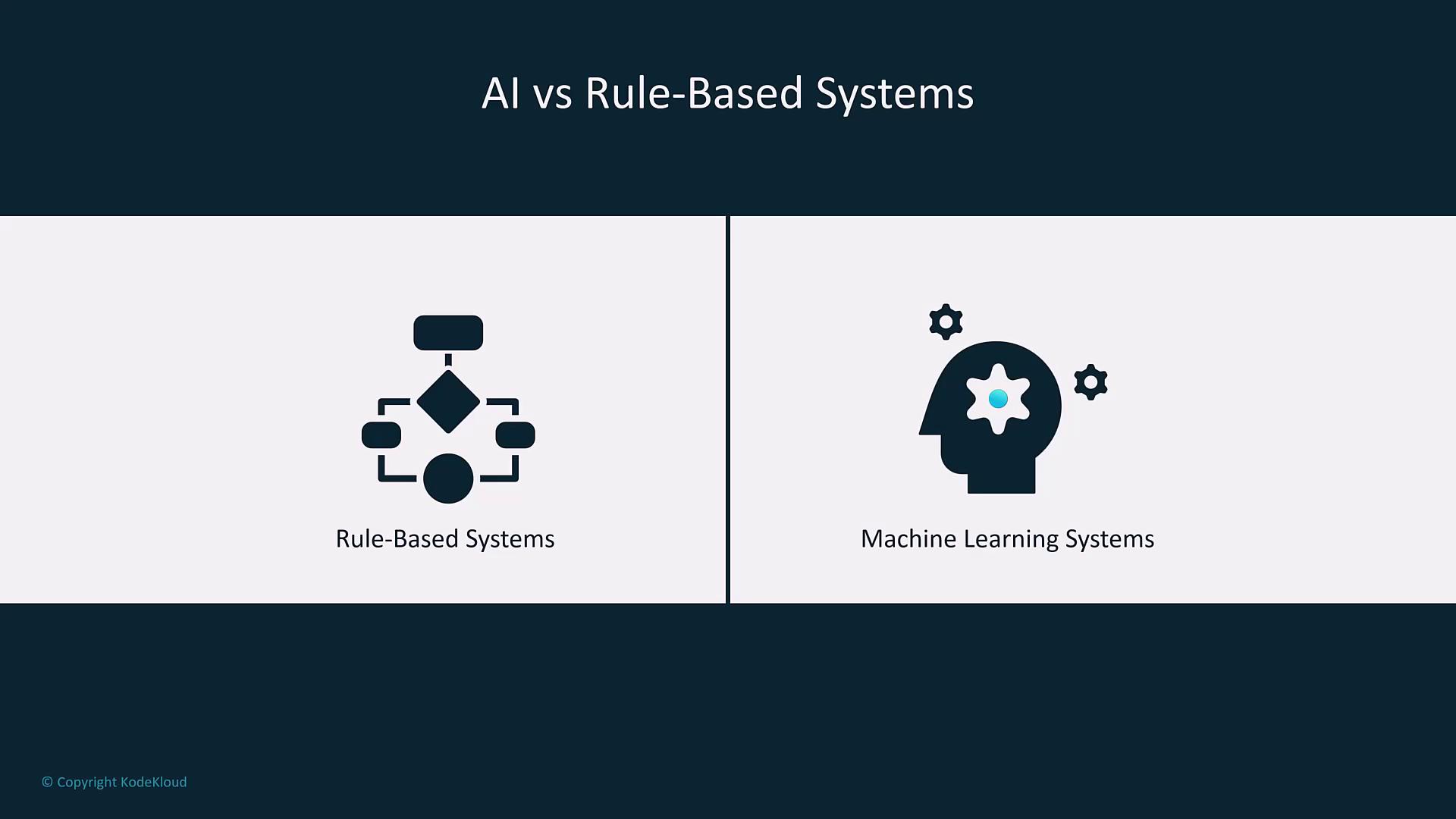
While rule-based systems provide consistent outputs for straightforward tasks, machine learning offers superior capabilities for applications such as recommendations, predictions, and forecasts.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science that creates systems capable of performing tasks that traditionally require human intelligence. Modern AI encompasses areas including visual perception, speech recognition, decision making, and language translation.
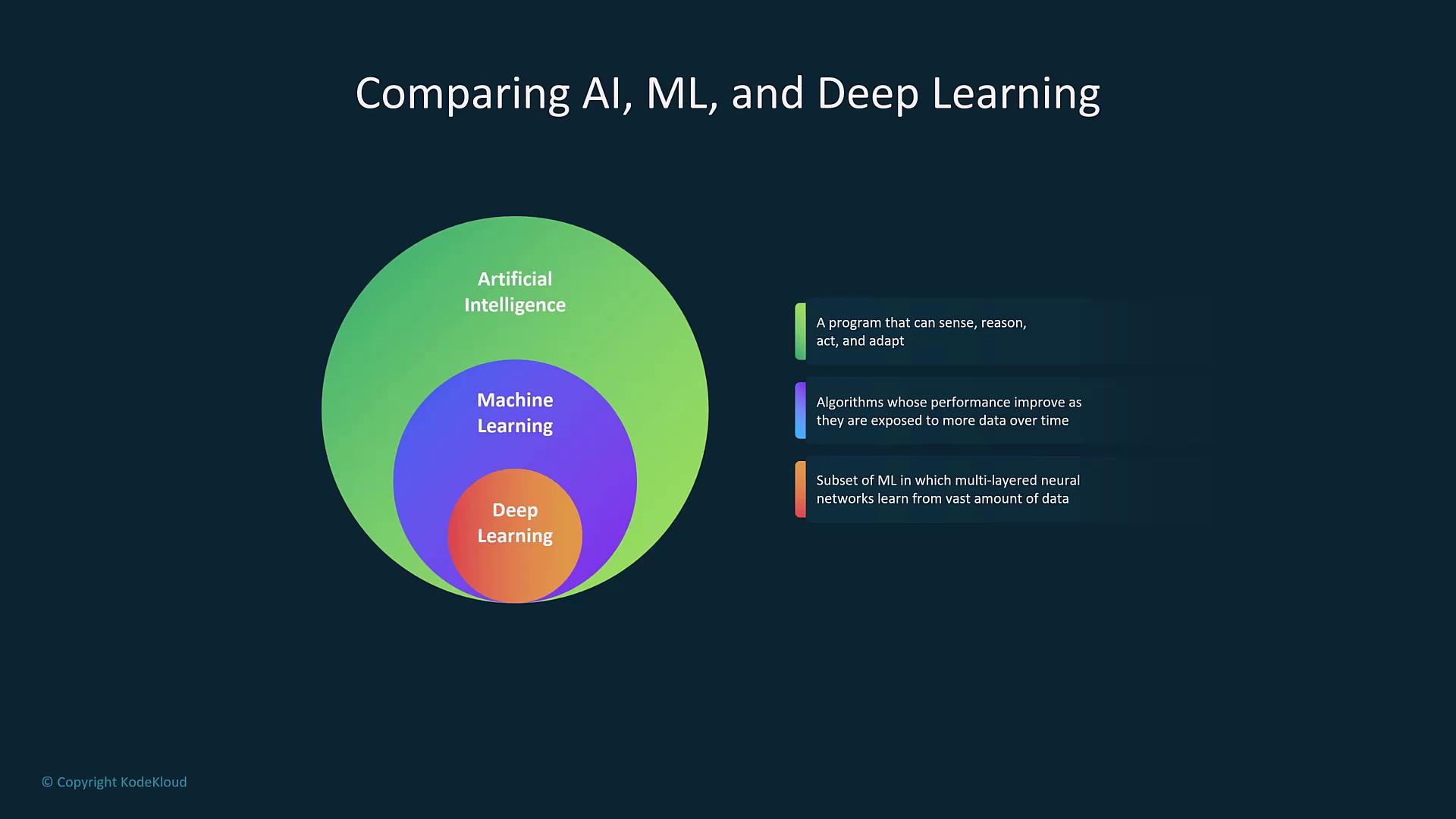
Exploring AI Subfields: Machine Learning and Deep Learning
AI can be broadly divided into subfields such as Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL):
Narrow AI vs. General AI
- Narrow AI: Focused on specific tasks such as product recommendations or personalized interactions (e.g., AI assistants like Alexa, Siri, or personalized content on platforms like Netflix).
- General AI: Represents a theoretical system with broad problem-solving abilities akin to human intelligence. Although generative AI is making strides toward broader capabilities, true general AI remains a long-term goal.

Machine Learning: Learning from Data
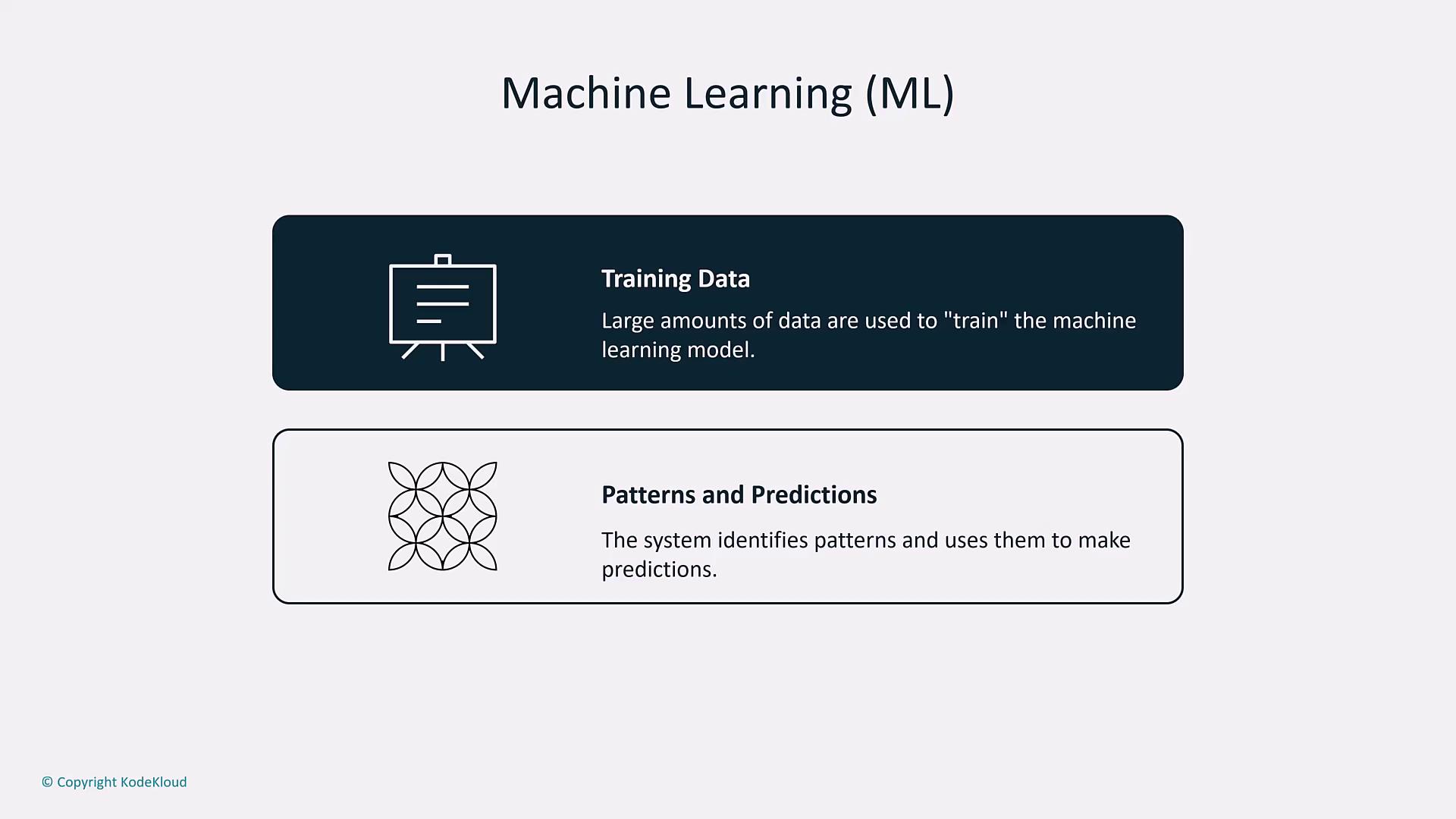
In practical applications, AI can perform binary classification tasks (e.g., identifying spam emails) or probabilistic predictions (e.g., forecasting market trends). This data-driven approach is known as machine learning. ML employs mathematical algorithms and statistical models to identify patterns within both structured and unstructured data. Unlike traditional software that strictly executes programmed instructions, ML models continually improve as they process more data and receive feedback.
Deep Learning: A Specialized Subset
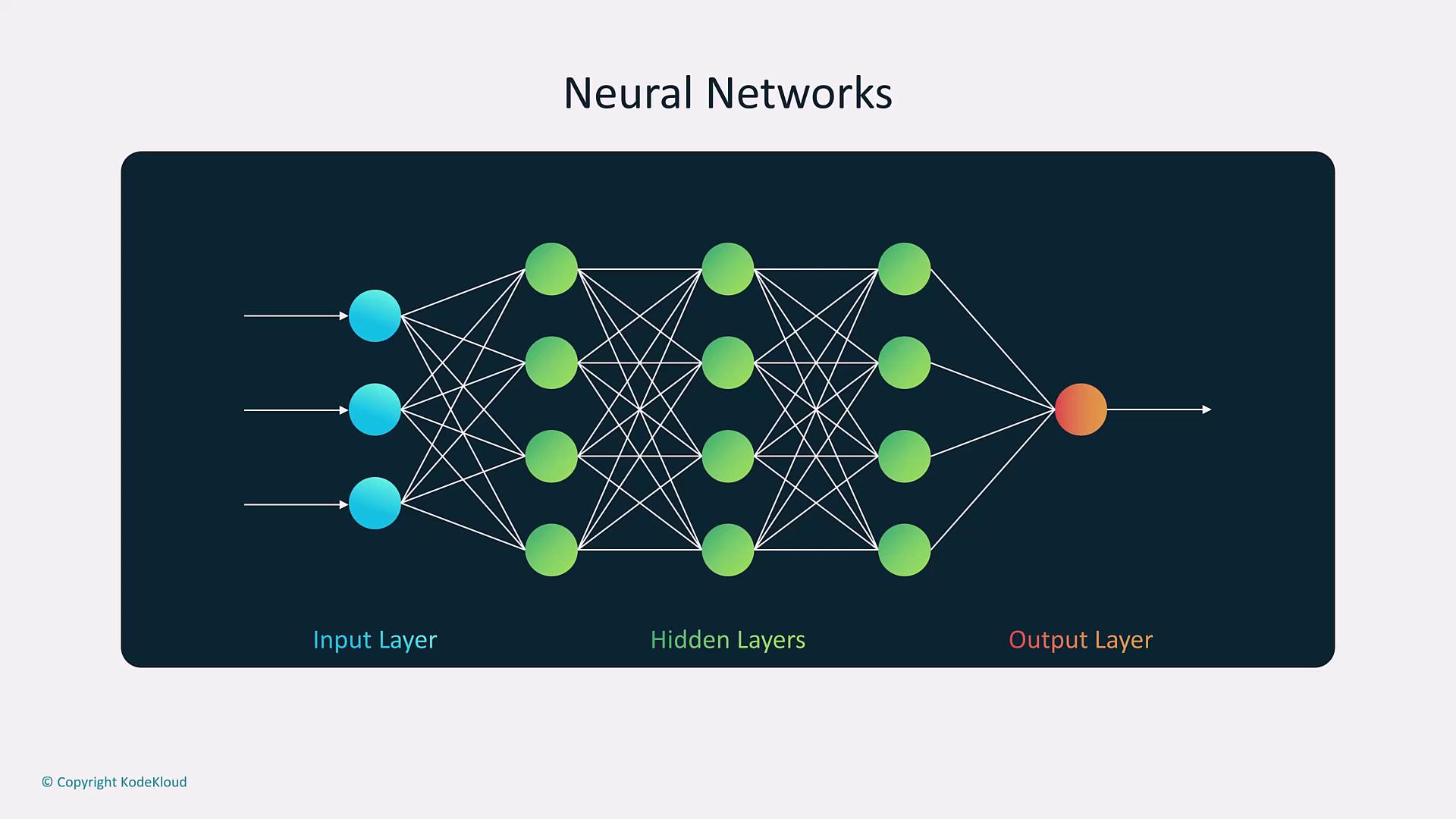
Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, leverages multi-layered neural networks. These networks, composed of interconnected artificial neurons, process data through multiple layers—similar to an intricately weighted decision tree—to solve complex problems.
Summary
Artificial intelligence is an overarching field that includes machine learning and deep learning. In essence:- AI refers to any technology that can replace or augment human effort.
- Machine learning utilizes algorithms to learn from historical data.
- Deep learning refines these capabilities using multi-layered neural networks that mimic human reasoning.