AI in Healthcare
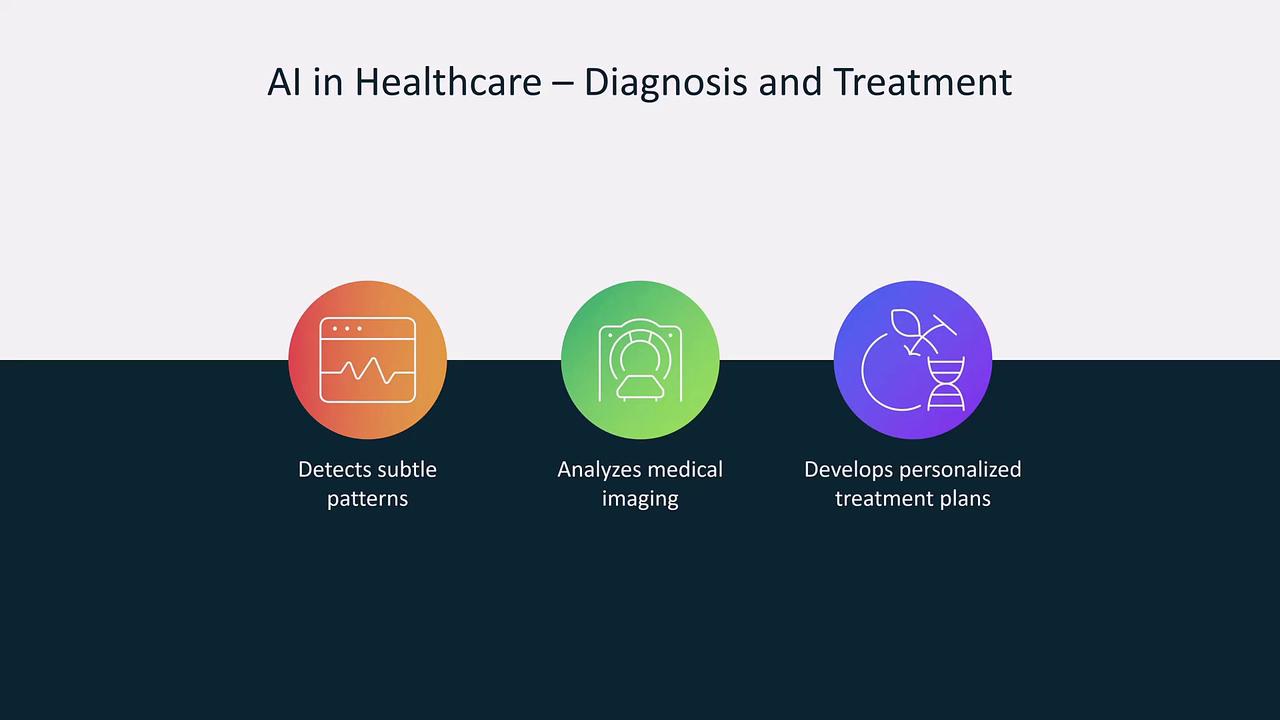
AI significantly impacts healthcare by assisting with medical diagnostics, analyzing X-rays, and predicting patient outcomes through efficient processing of large datasets.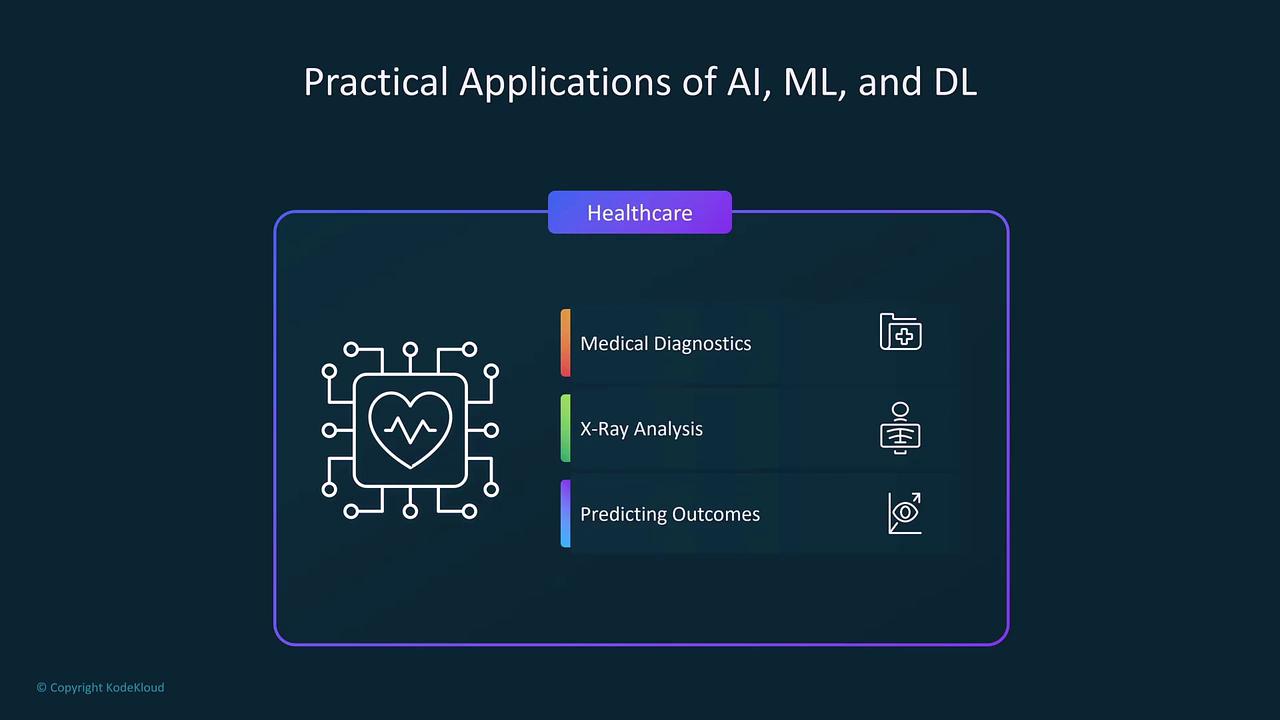
AI-driven diagnostics are transforming patient care by providing early detection and personalized treatment recommendations.
AI in Finance
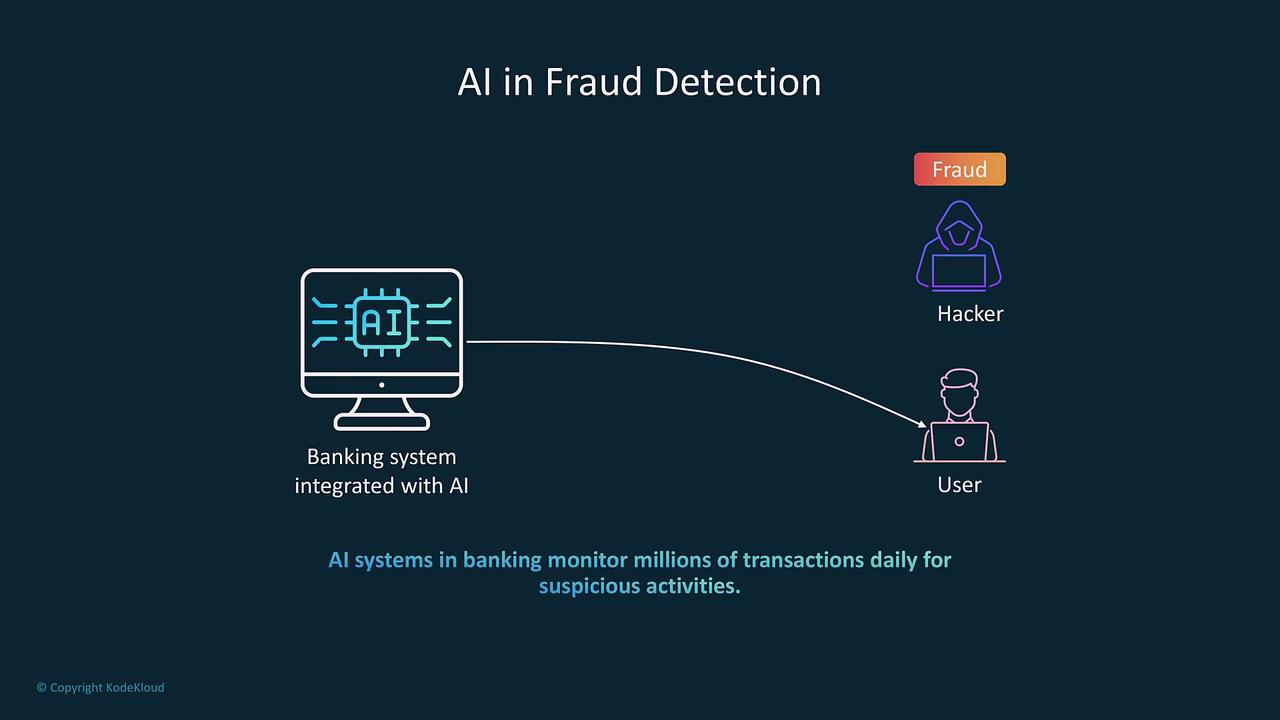
While AI is designed to assist rather than completely replace human intervention, it plays a vital role in fields like fraud detection and personalized financial advice. By automating repetitive tasks and identifying anomalies in transaction data, AI ensures enhanced consistency and speed in financial operations.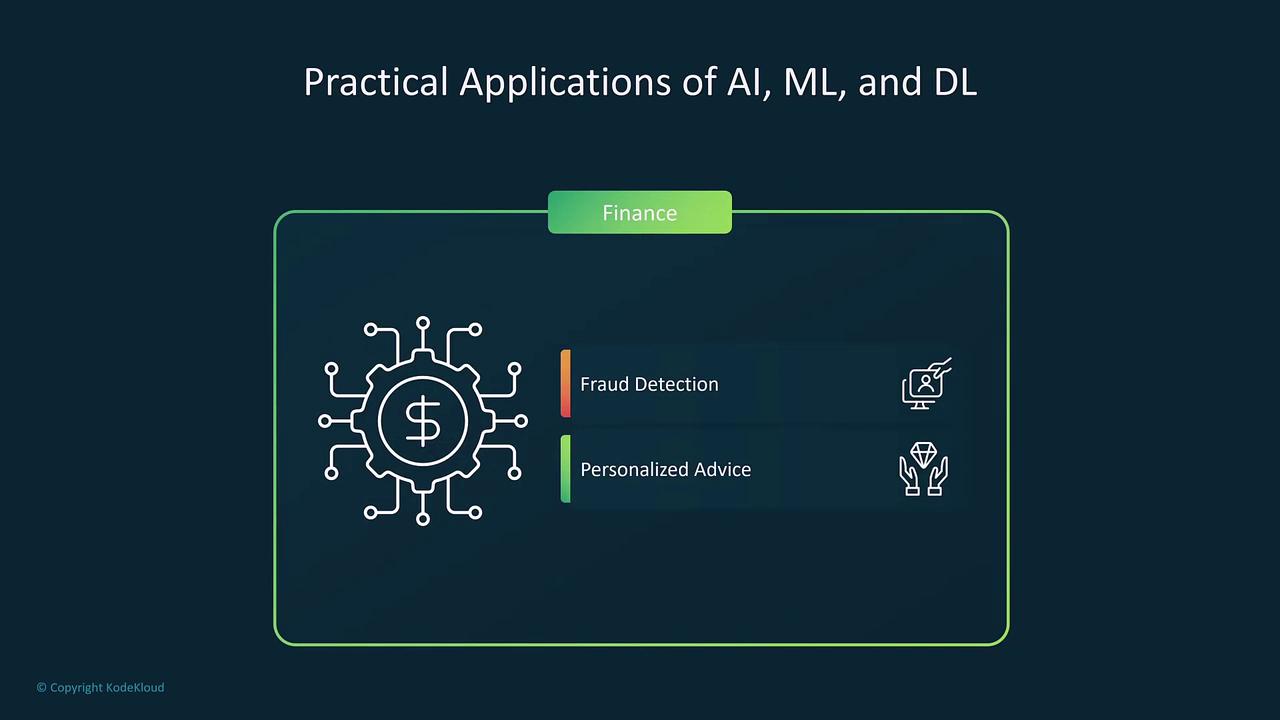
AI in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, AI enhances operational efficiency by detecting defects, performing predictive maintenance, and assisting with capacity planning. These capabilities not only improve product quality but also streamline production processes.
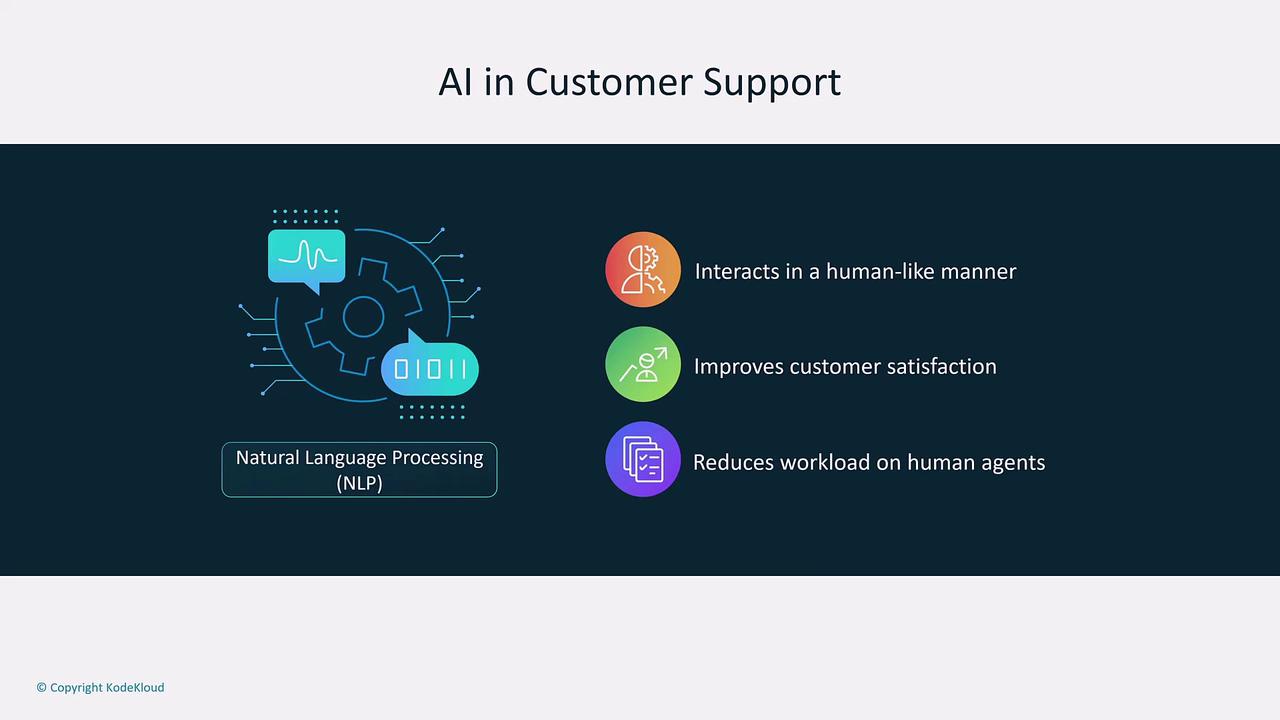
Enhancing Customer Service with AI
Customer service automation employs AI-powered chatbots to handle routine inquiries about account balances, shipping statuses, and refund requests. Utilizing natural language processing (NLP), these chatbots interact in a human-like manner, streamlining support and allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Predictive Maintenance and Demand Forecasting
Predictive maintenance is another key application where AI analyzes data from IoT sensors embedded in machinery to predict failures and schedule maintenance during planned downtimes. This proactive method minimizes unexpected equipment failures and unnecessary costs, benefiting industries from manufacturing to aviation. Beyond maintenance, AI-driven demand forecasting utilizes historical sales data and consumer trends to accurately predict inventory requirements and optimize supply chains.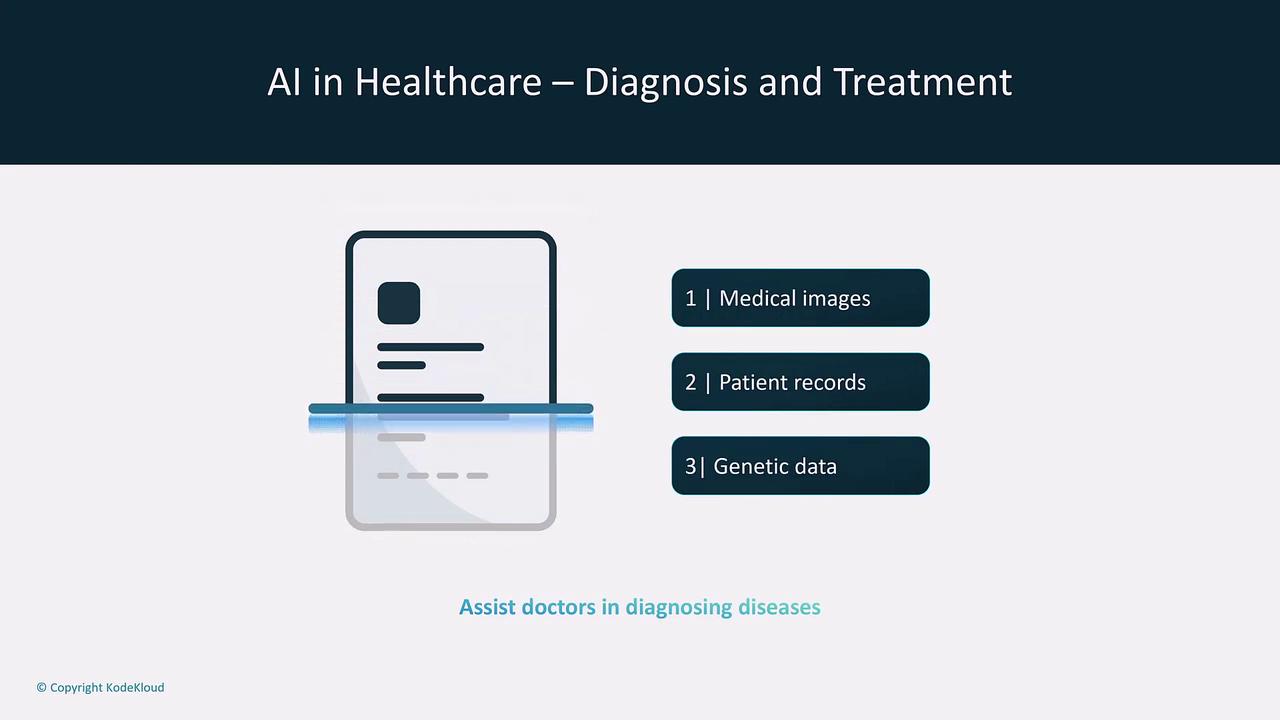

AI in Autonomous Vehicles and Agriculture
Autonomous vehicles showcase AI in action by analyzing data from sensors, cameras, radars, and road conditions to navigate complex environments in real time. For example, Tesla’s autopilot system uses AI for obstacle detection, traffic signal recognition, and autonomous parking.
AI in Daily Life
From personal virtual assistants and streaming services to online shopping recommendations, AI enhances daily life by providing accurate suggestions based on past behavior, streamlining customer interactions, and improving device interoperability.
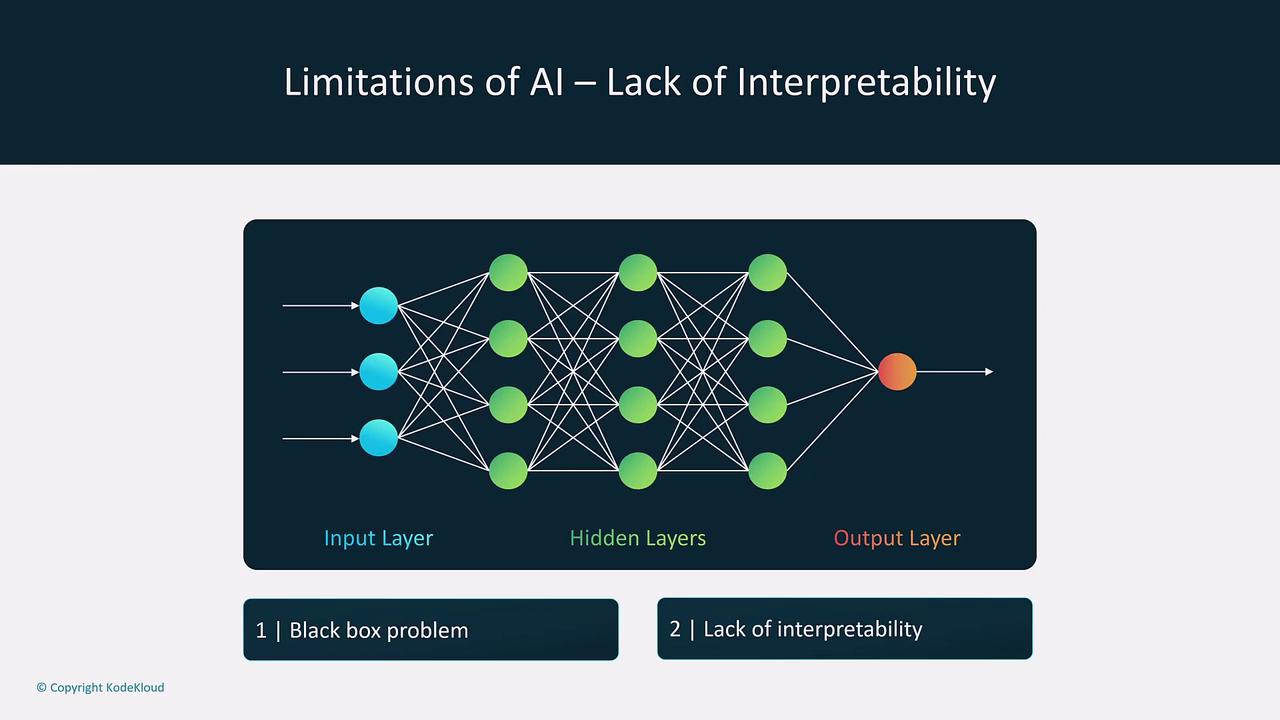
Challenges and Limitations of AI
Despite its benefits, integrating AI presents challenges. The significant computational power required for training models, along with the necessary resources for data storage, cloud services, and skilled personnel, must be carefully considered.When implementing AI solutions, be aware of limitations such as the “black box” problem, potential biases, and hallucinations in outputs. Transparency and accountability are crucial, especially in sensitive areas.
Final Thoughts
AI, ML, and deep learning offer transformative capabilities across sectors. By enhancing efficiency, reducing errors, and boosting customer experiences, AI becomes an indispensable tool for modern businesses. However, successful implementation hinges on aligning the right technology with the specific use case while considering the inherent challenges.