AWS Certified Developer - Associate
Application Integrations
SNS Overview
This article explores AWS’s Simple Notification Service (SNS), a robust cloud messaging service that functions like a digital postal system. SNS enables publishers to send notifications that are simultaneously delivered to multiple subscribers, making it a cornerstone in event-driven architectures.
How SNS Works
AWS SNS leverages a publish/subscribe model that simplifies message distribution. Here’s an overview of the process:
- A producer (or publisher) sends a message to an SNS topic.
- The SNS topic acts as a communication channel, similar to a "radio frequency."
- All subscribers listening to that topic receive the message.
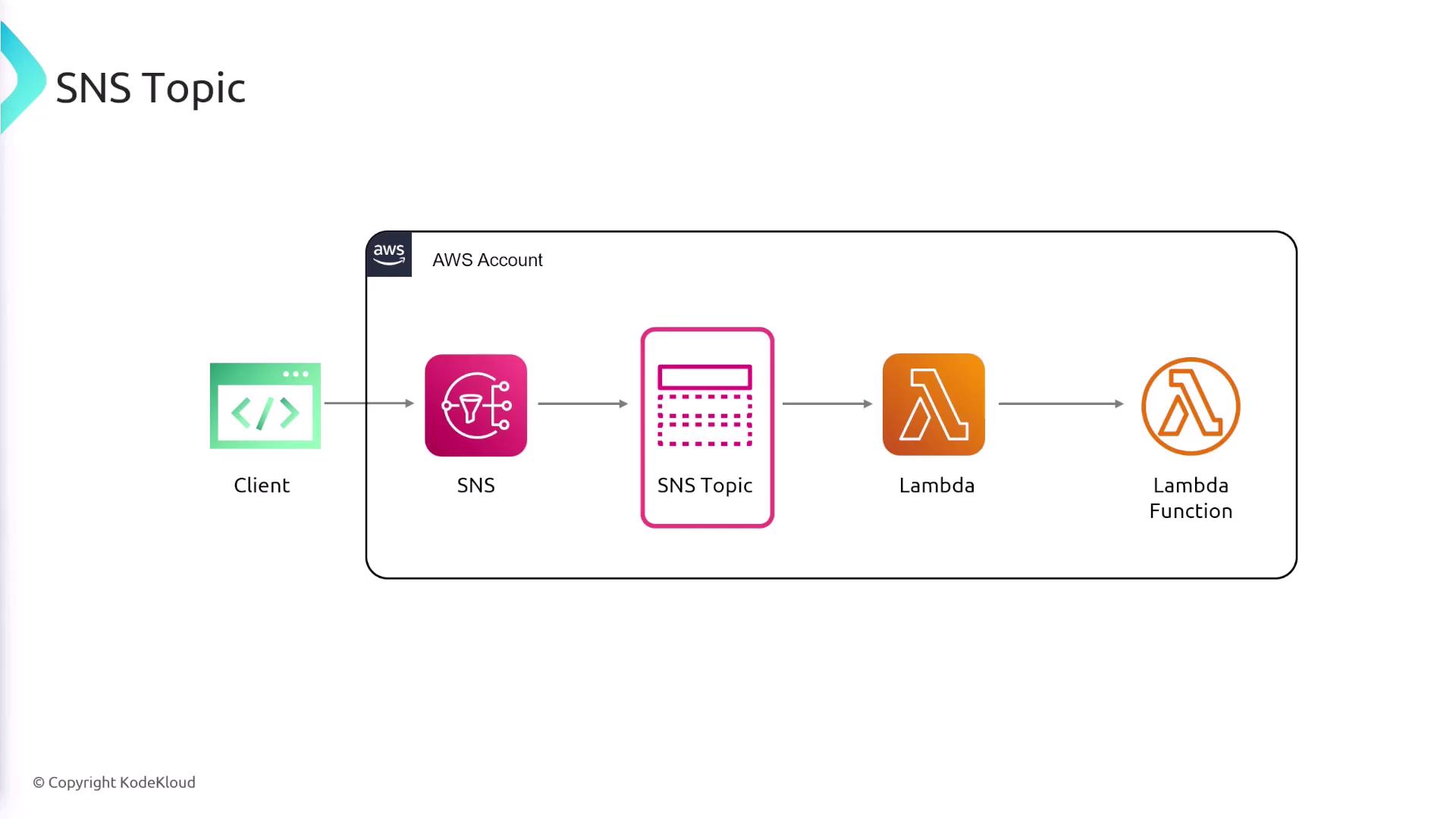
How it Works
When a message is published, only subscribers who have signed up for that specific topic will process it. This facilitates event-based communication across different system components. For example, a new user registration could trigger both a welcome email and a verification process.
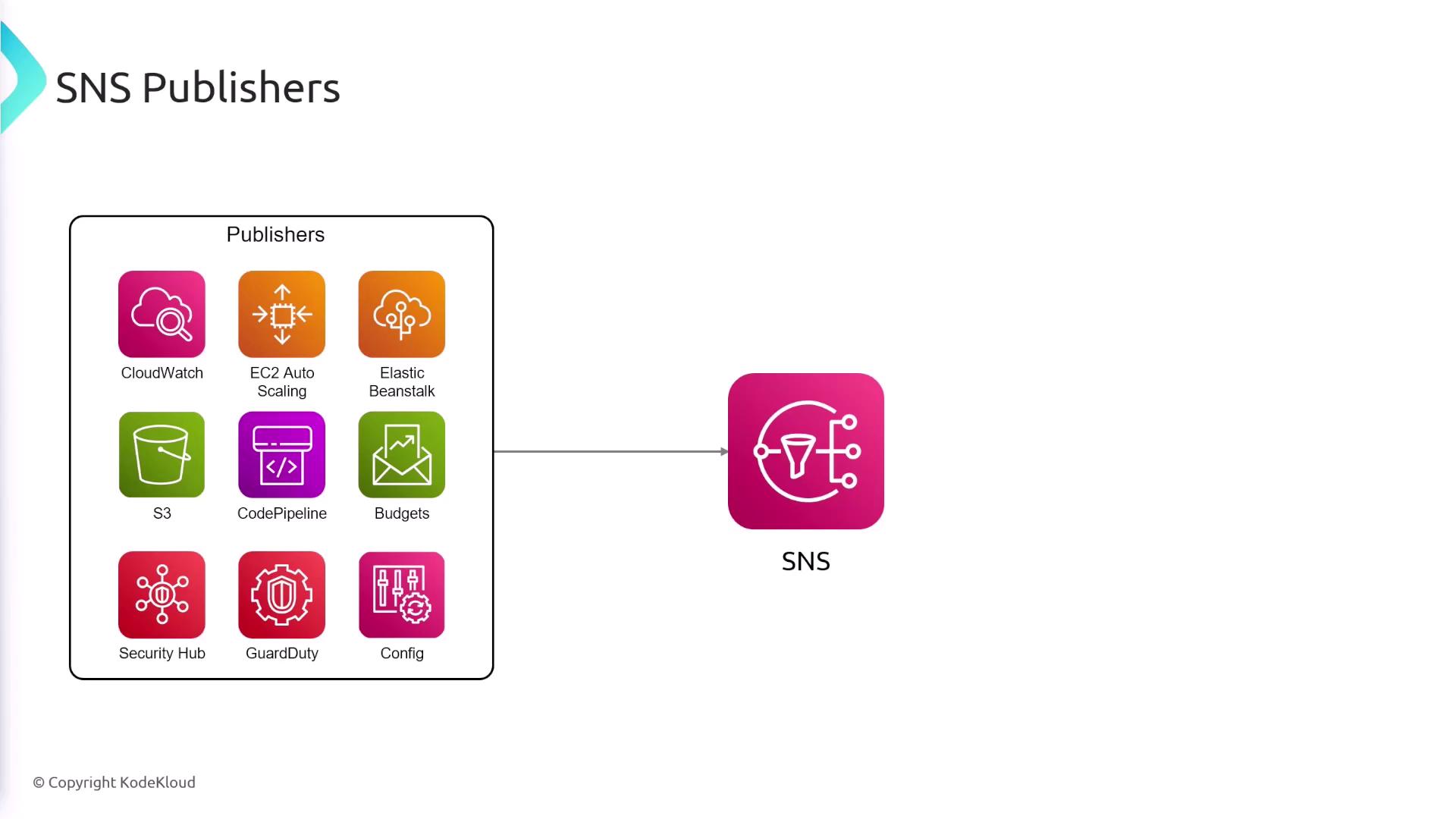
Publishers in SNS
SNS supports a variety of publishers, including several AWS services. Common examples include:
- CloudWatch alarms
- EC2 instances
- Elastic Beanstalk
- S3 events
- CodePipeline, among others
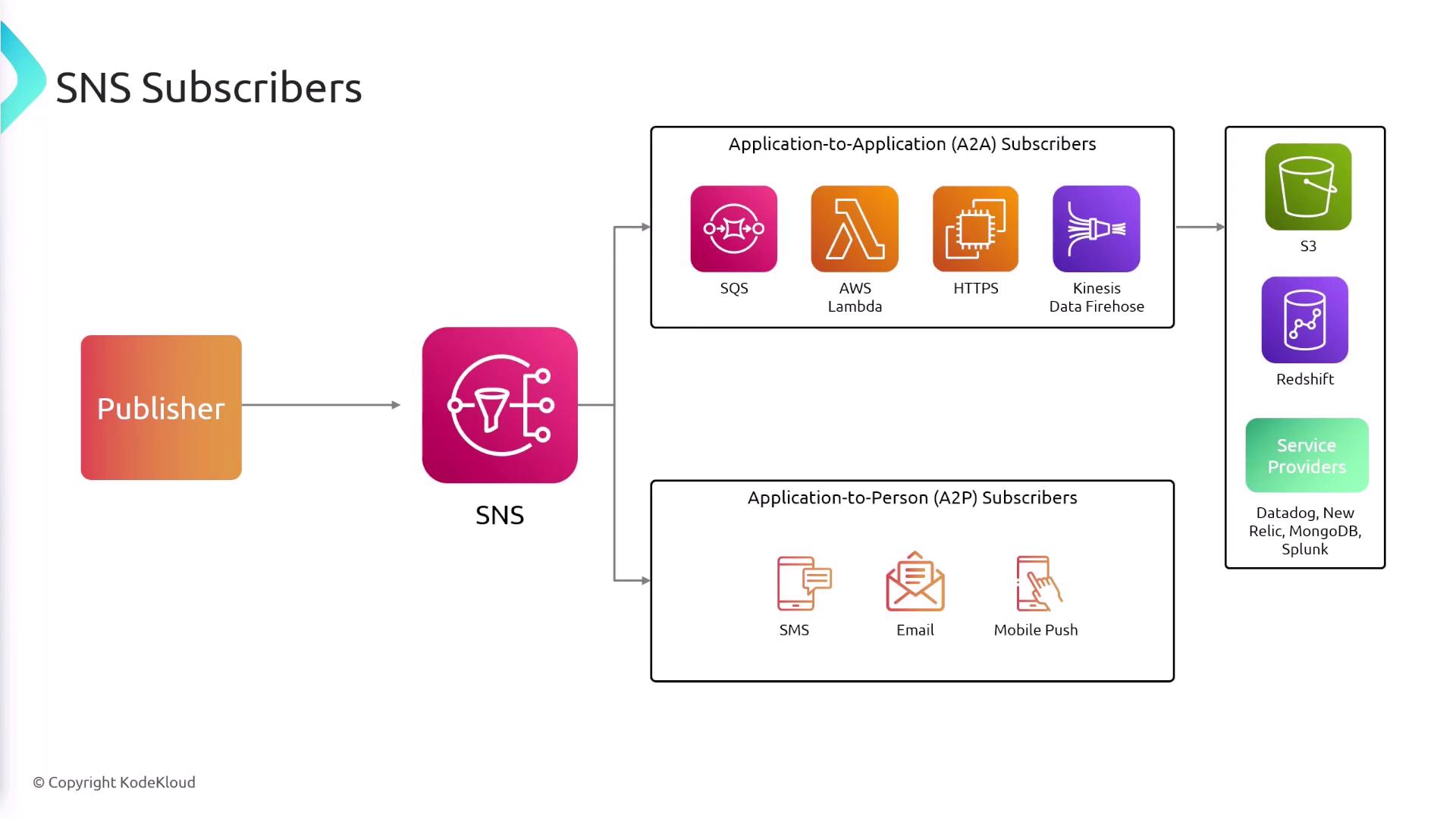
Subscribers in SNS
SNS offers flexible options for subscribers. Typical subscribers include:
- SQS queues
- Lambda functions
- HTTP endpoints
- EC2 instances
- Kinesis Data Firehose
In addition to these, SNS can deliver notifications via SMS, email, or mobile push notifications.
Fan-Out Architecture with SNS and SQS
SNS can be paired with SQS to implement a fan-out architecture, where a single SNS message is replicated across multiple endpoints. This approach allows different processing tasks to be executed concurrently by distinct SQS queues.
Consider a scenario inspired by video streaming platforms:
- When a user uploads a video, the video metadata is published to an SNS topic.
- One SQS queue processes tasks such as video format conversion (e.g., 4K or 1080p).
- Another SQS queue handles the generation of video thumbnails.
This architecture ensures multiple downstream processes react independently to a single event, thereby enhancing system scalability.
Access Control with SNS Resource Policies
SNS resource policies are critical for enforcing security and controlling access. These policies define which entities can publish or subscribe to a topic. For instance, you might restrict publishing permissions only to a specific IAM role.
Below is an example policy that permits only a designated role to publish messages to an SNS topic:
{
"Sid": "AllowSpecificRoleToPublish",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/SpecificPublishingRole"
},
"Action": "SNS:Publish",
"Resource": "arn:aws:sns:us-west-2:123456789012:MySNSTopic",
"Condition": {
"ArnEquals": {
"aws:SourceArn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/SpecificPublishingRole"
}
}
}
Security Reminder
It is crucial to configure SNS resource policies correctly to prevent unauthorized access and ensure that only trusted entities can interact with your SNS topics.
Summary
AWS SNS is a versatile and scalable messaging service designed to distribute messages efficiently to multiple subscribers. Its ability to integrate with various AWS services and external systems makes it an essential tool for building event-driven architectures. By leveraging SNS for secure and rapid message delivery, organizations can ensure that notifications reach the appropriate endpoints reliably.
For additional resources on AWS services and best practices, visit the AWS Documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content