AWS Certified Developer - Associate
Storage
EFS
In this lesson, we explore Amazon's Elastic File System (EFS), a robust file storage service that supports the Network File System (NFS) protocol. With EFS, any application that uses NFS can seamlessly integrate with this service.
EFS allows you to create a file system that can be remotely mounted by Amazon EC2 Linux instances and other compute services. Remember that EFS supports only Linux-based EC2 instances and is not compatible with Windows.
Note
Amazon EFS supports mounting the same file system on multiple EC2 instances concurrently, making it ideal for sharing data across various instances.
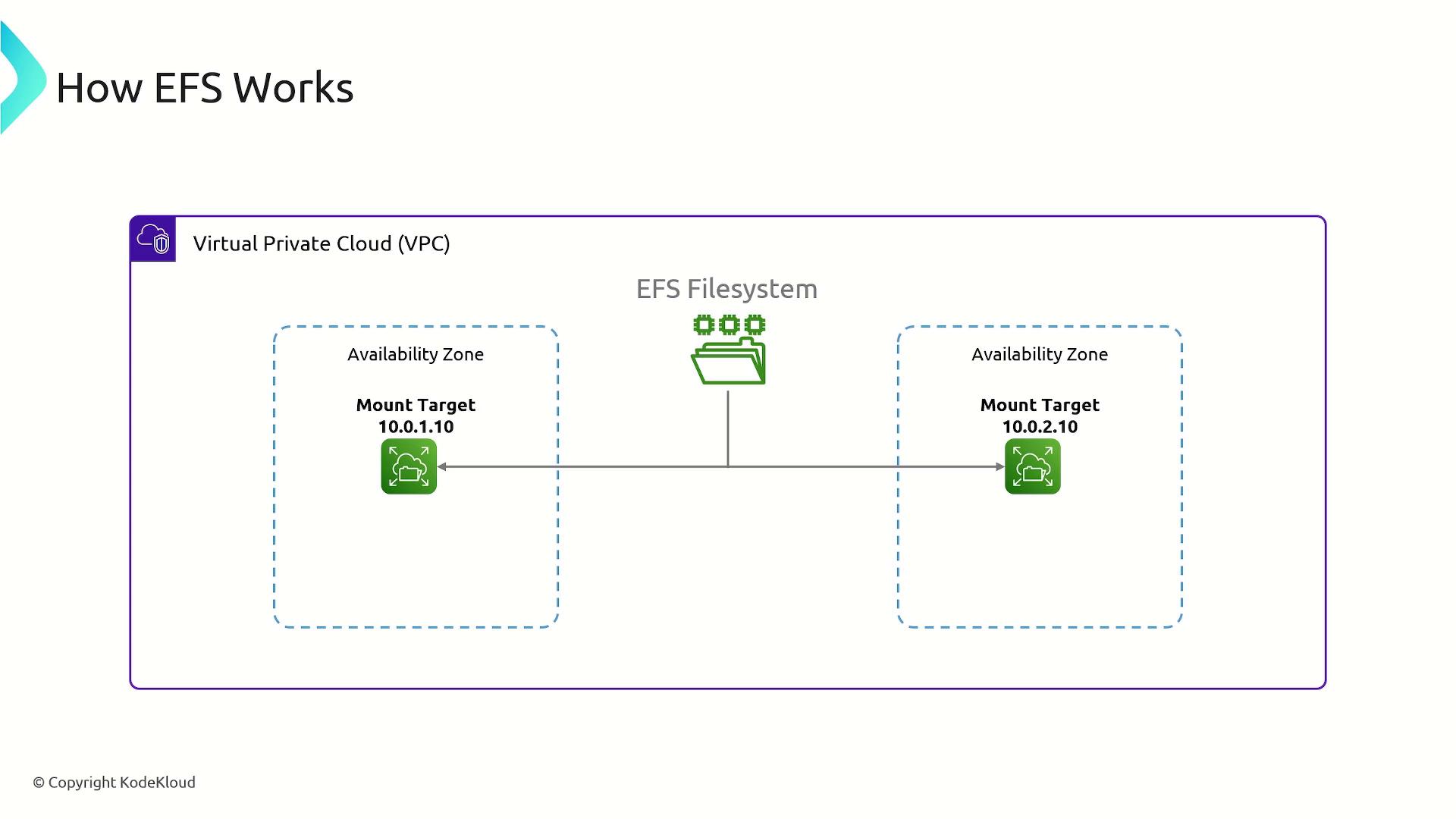
To deploy an EFS file system, you must launch it within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Inside the VPC, the file system becomes accessible through mount targets. When you create an EFS file system, you designate specific subnets for these mount targets, and each one is assigned an IP address. EC2 instances connect to the EFS file system using the IP address of the chosen mount target. For high availability, it is advisable to create mount targets in multiple availability zones.
Storage Classes
EFS offers two main storage class families to cater to different needs:
Standard Storage Classes:
This family includes EFS Standard and EFS Standard Infrequent Access, offering multi-AZ resilience, durability, and high availability.One Zone Storage Classes:
This family features EFS One Zone and EFS One Zone Infrequent Access, delivering cost savings by storing data in a single availability zone.

Performance and Throughput Modes
In addition to varying storage classes, you can configure EFS to optimize performance for your workloads. Two primary configuration areas are available:
File System Performance Modes:
These modes affect metadata operations:- General Purpose: Optimized for latency-sensitive applications such as web applications, content management systems, home directories, and general file serving.
- Max I/O: Supports higher aggregate throughput and operations per second, albeit with increased latencies for file system operations.
Throughput Modes:
These modes determine how data throughput is managed:- Bursting Throughput: The default mode that automatically scales with the size of your file system, offering performance bursts when required.
- Provisioned Throughput: Allows you to set a fixed throughput independent of file system capacity, ensuring consistent performance.

Setting Up EFS on an Amazon EC2 Linux Instance
To set up EFS, begin by installing the Amazon EFS utilities on your EC2 instance. Depending on your package manager, you might use one of the following commands. The example below demonstrates installation using the dnf package manager:
$ sudo dnf -y install amazon-efs-utils
Dependencies resolved.
==================================================================================================================================
Package Architecture Version Repository Size
==================================================================================================================================
Installing:
amazon-efs-utils noarch 1.35.0-1.amzn2023 amazonlinux 56 k
Installing dependencies:
stunnel x86_64 5.58-1.amzn2023.0.2 amazonlinux 156 k
Transaction Summary
==================================================================================================================================
Install 2 Packages
Total download size: 212 k
Installed size: 556 k
Downloading Packages:
(1/2): amazon-efs-utils-1.35.0-1.amzn2023.noarch.rpm 550 kB/s | 56 kB 00:00
(2/2): stunnel-5.58-1.amzn2023.0.2.x86_64.rpm 1.0 MB/s | 156 kB 00:00
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 866 kB/s | 212 kB 00:00
Running transaction check
After installing the utilities, mount the EFS file system to your desired directory. Replace "efs:id" with the actual file system ID from the AWS Console and specify the mount point:
$ sudo mount.efs efs:id /directory
Summary of Amazon EFS
Amazon EFS is a powerful file system storage service that:
- Uses the NFS protocol to seamlessly integrate with supporting applications.
- Is compatible with Linux-based EC2 instances and permits simultaneous mounts on multiple instances.
- Is deployed within a VPC using mount targets, with each mount target providing an essential IP address for connectivity.
- Offers two primary storage class families (Standard and One Zone) along with configurable performance and throughput modes.
- Functions similarly to a traditional file system mounting process, but unlike block storage (e.g., EBS volumes), it cannot be booted.

Watch Video
Watch video content