AWS Certified SysOps Administrator - Associate
Domain 4 Security and Compliance
Multi Account in AWS Strategies
Welcome to this lesson on multi-account strategies in AWS. In this guide, we discuss methods to manage multiple AWS accounts while ensuring robust security and compliance across your organization.
When managing multiple accounts, implementing proper operational security controls is essential despite the inherent complexity. One of the key mechanisms to achieve this is the use of Service Control Policies (SCPs). SCPs help enforce specific restrictions—for example, allowing more flexibility in development accounts while applying stricter controls on production environments.
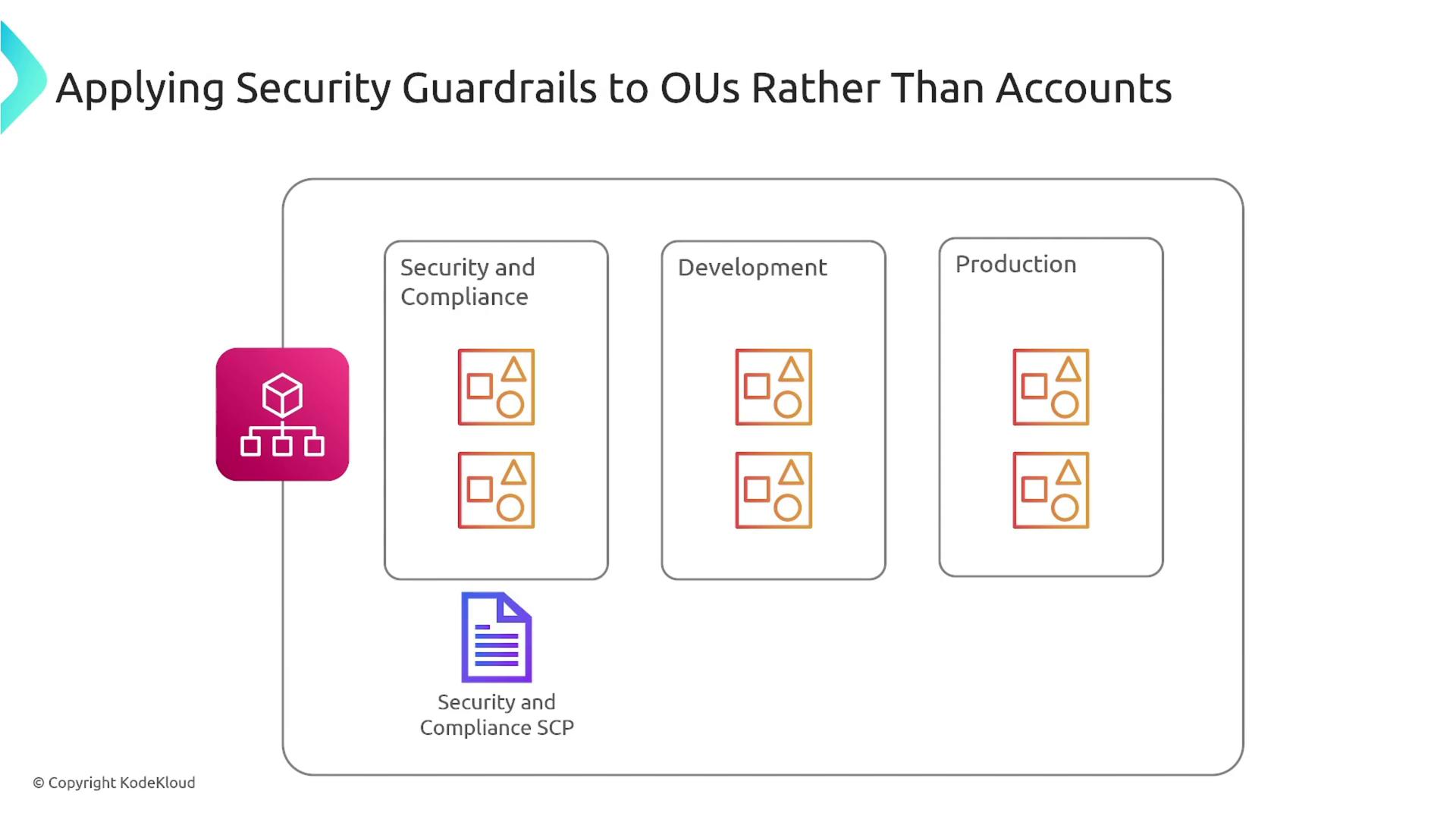
As illustrated above, production environments are typically locked down with even tighter controls. SCPs play a central role in managing multiple accounts that are grouped within organizational units such as development, production, and security/compliance.
It is crucial to avoid building deeply nested organizational trees. Instead, aim for a flat structure. For example, design production accounts consistently across subsidiaries, and apply similar principles to development accounts. Keeping the structure simple minimizes unnecessary complexity and enhances agility.
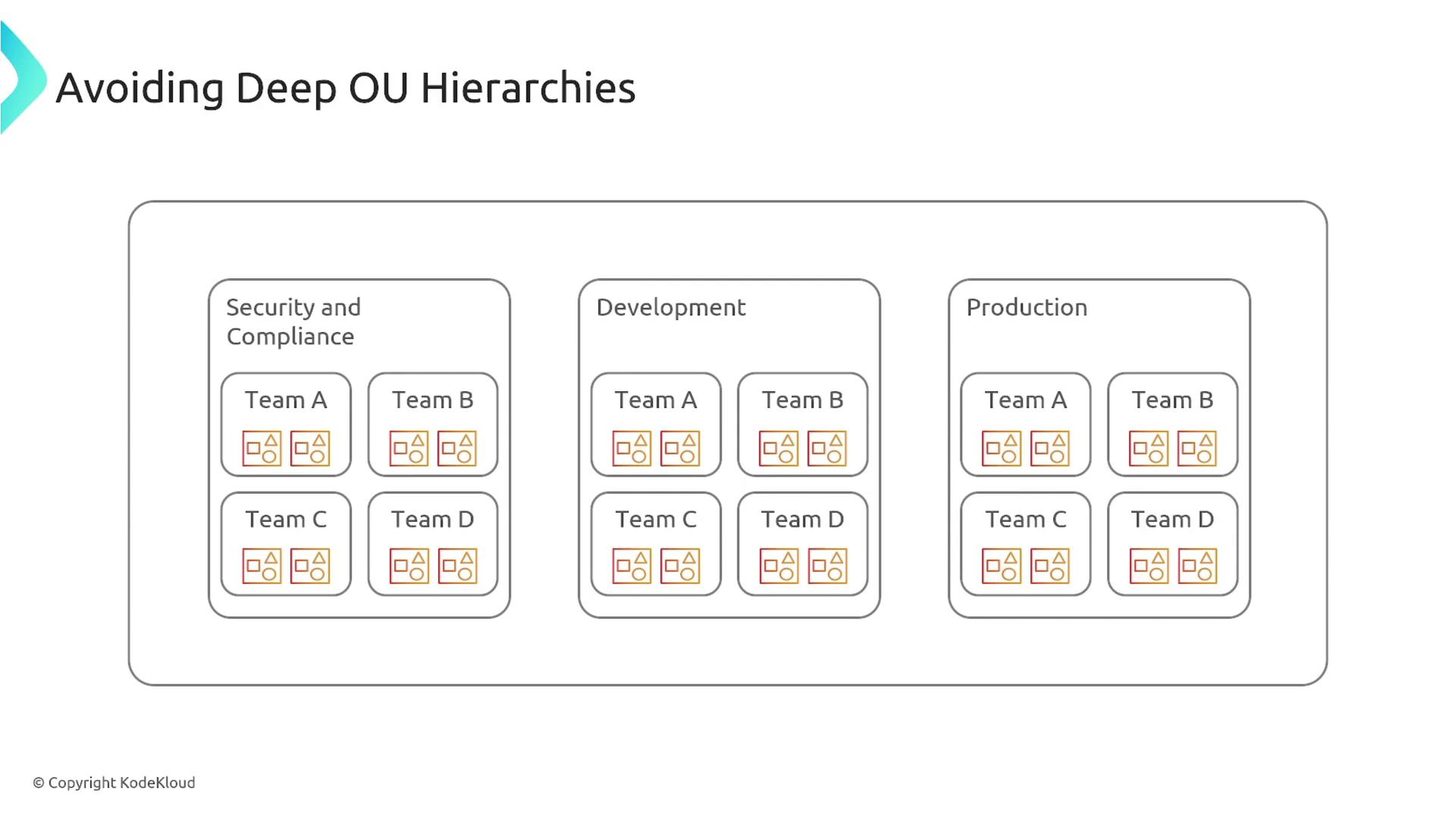
Start small with AWS Organizations and gradually expand your organizational units as needed. In many large enterprises, maintaining a flat hierarchy has proven effective. For instance, a Fortune 50 company managed 750 AWS accounts by organizing them into distinct units for production, development, QA, highly sensitive workloads, and even an experimental environment for data science initiatives.
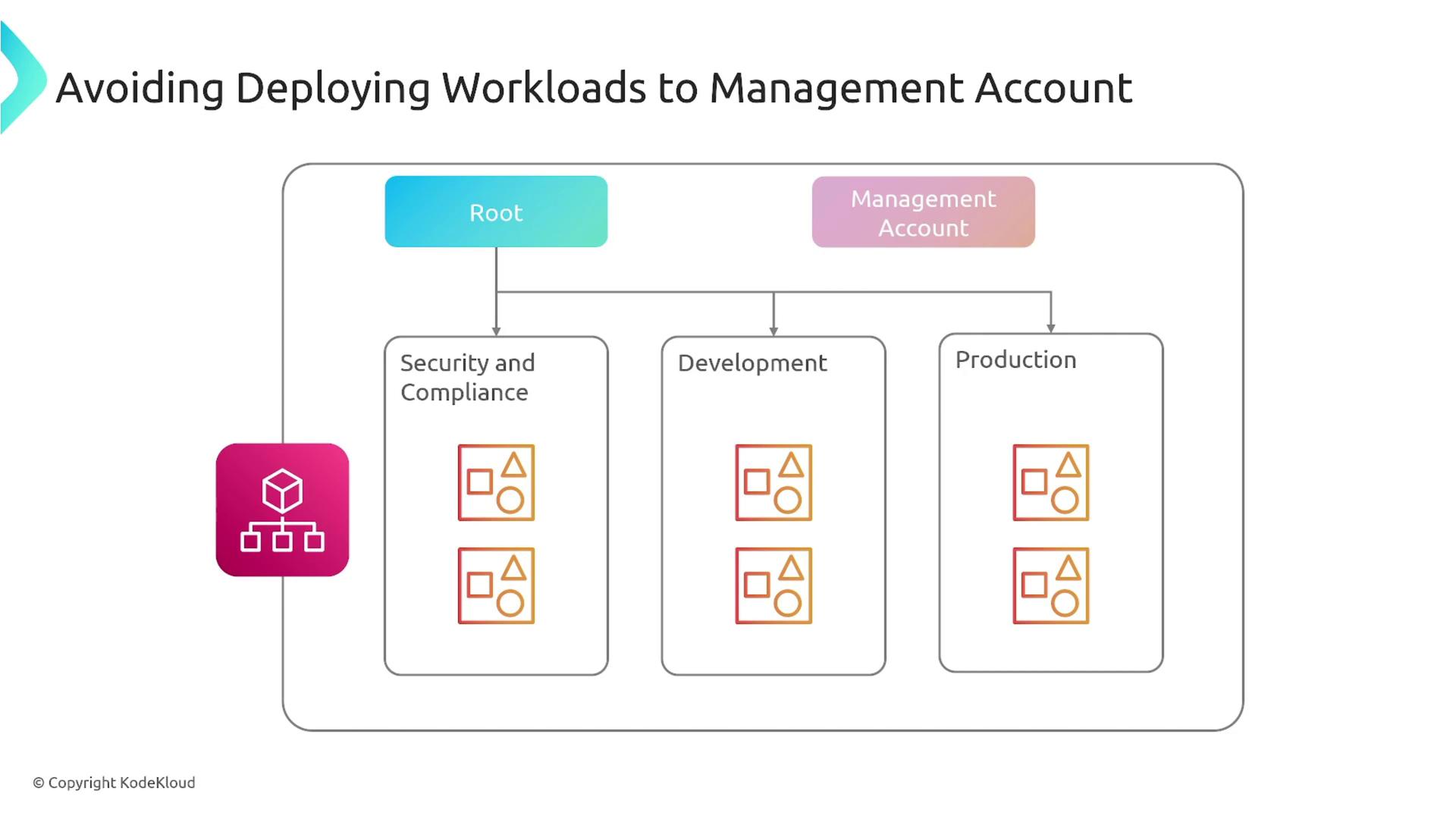
Every organization has a management account that is essential for billing, control, and defining SCPs and policies. This account acts as the root or foundation of your organizational structure, ensuring that policies applied at the root cascade to all underlying accounts.
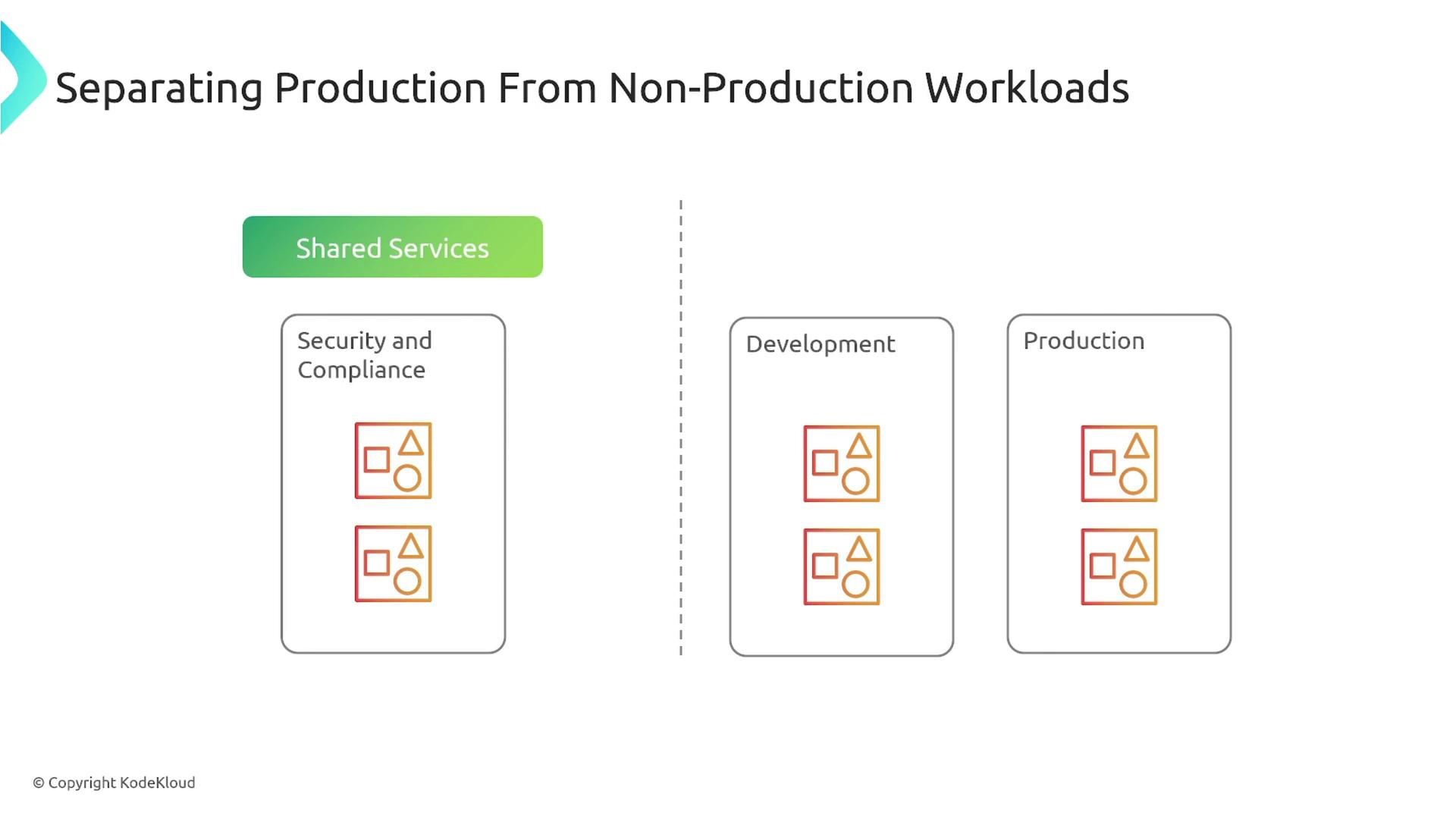
Best Practice
A recommended best practice is to separate non-production and production environments. For example, designate shared services accounts for security and compliance separate from accounts dedicated to software delivery. Additionally, you can segment development accounts into areas like QA, staging, and UAT to minimize impact from potential issues.
Automation can further streamline the management of multiple AWS accounts. Tools such as AWS Control Tower enable you to set up an account factory that automatically creates and configures accounts with the necessary SCPs and resource configurations. This automated setup helps enforce multi-factor authentication across all accounts and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
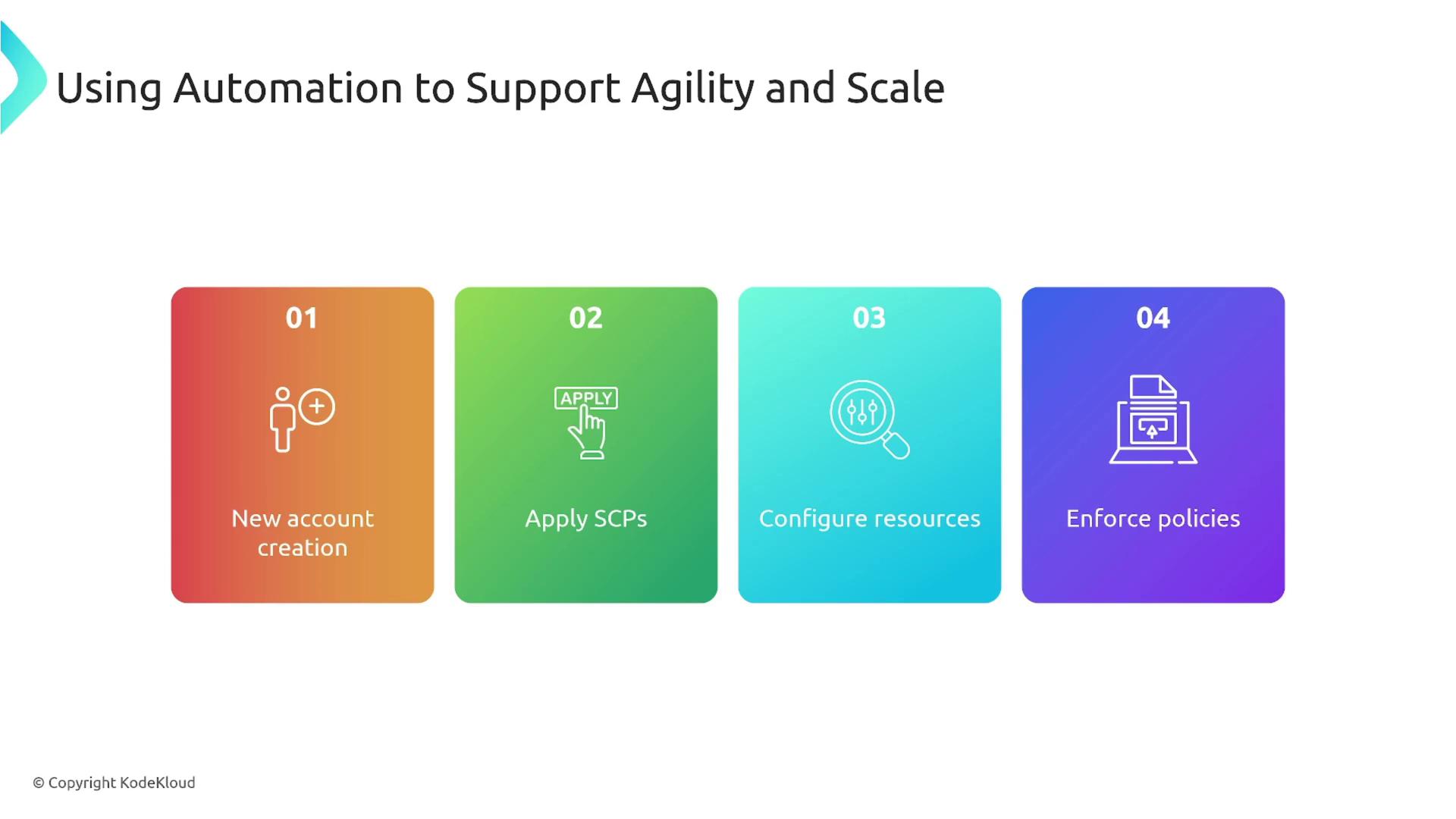
Another important aspect is managing access within accounts. A common strategy involves differentiating between regular user accounts for day-to-day operations and elevated "breaking glass" access reserved for emergency situations. This approach, similar to using sudo in Linux, ensures that full administrative privileges are only activated under strictly monitored conditions.
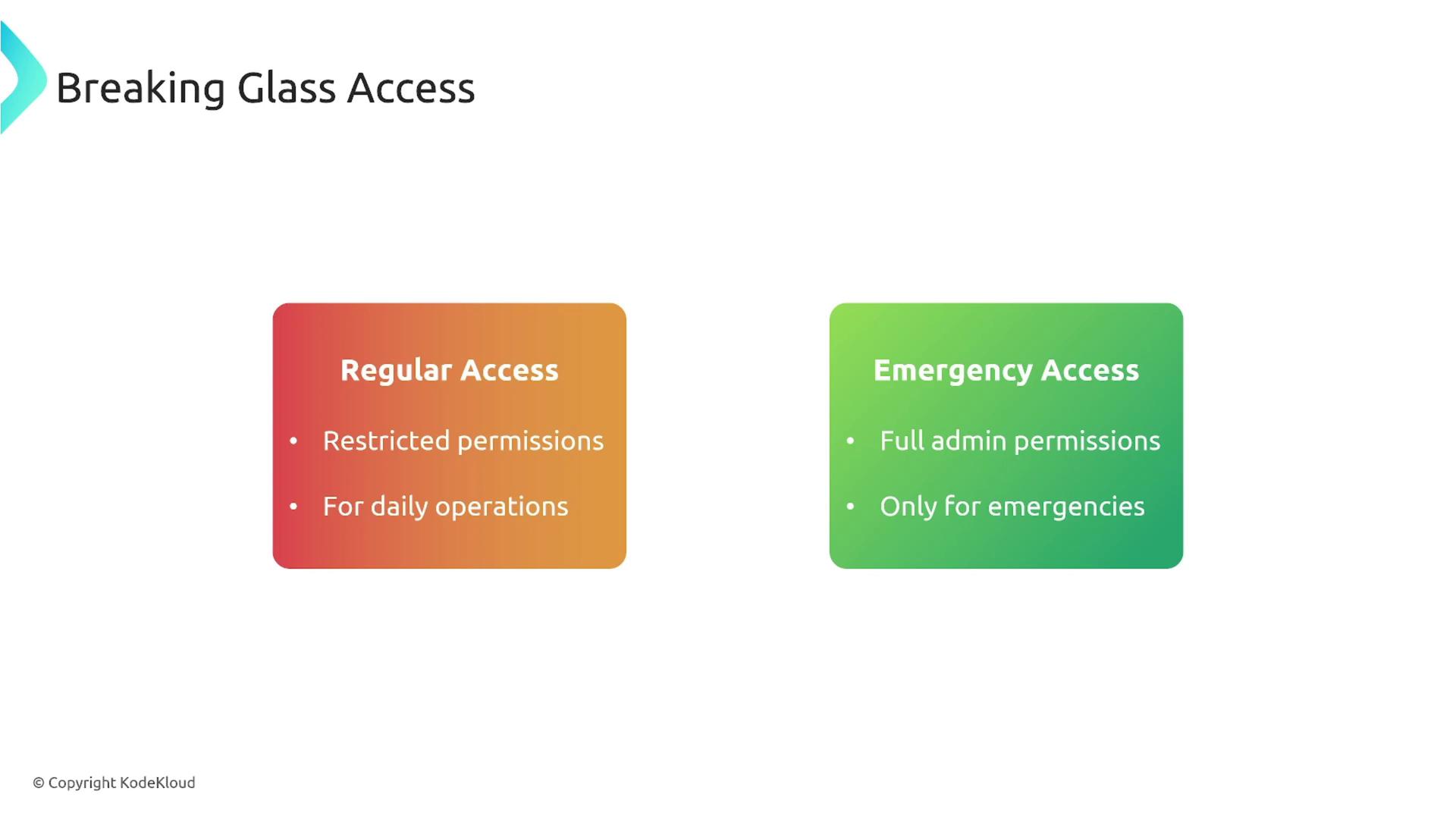
In summary, implementing multi-account strategies in AWS involves:
- Keeping organizational structures simple and flat.
- Applying SCPs systematically across various environments.
- Leveraging automation tools like AWS Control Tower to enhance security and scalability.
- Using access management strategies to balance daily operations with emergency needs.
These practices not only enforce necessary security policies but also provide a scalable approach to efficiently manage a large number of AWS accounts.
Thank you for reading this lesson on multi-account strategies in AWS.
Watch Video
Watch video content