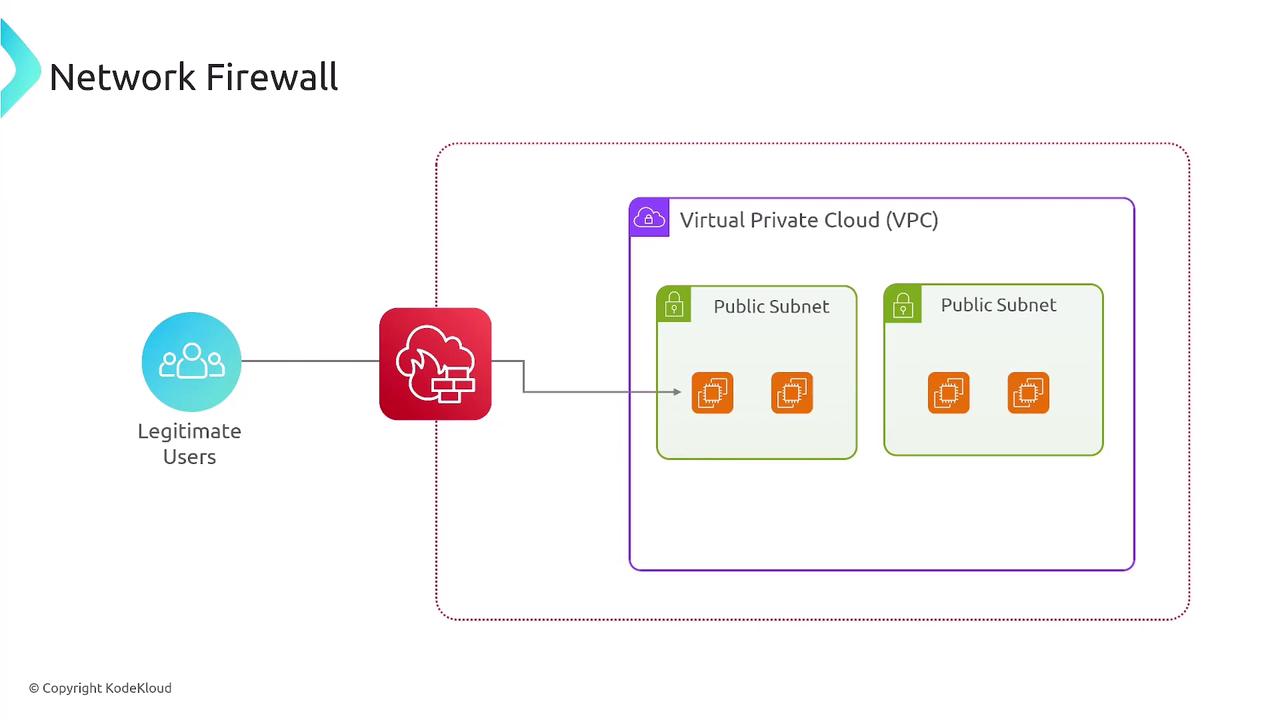
How AWS Network Firewall Works
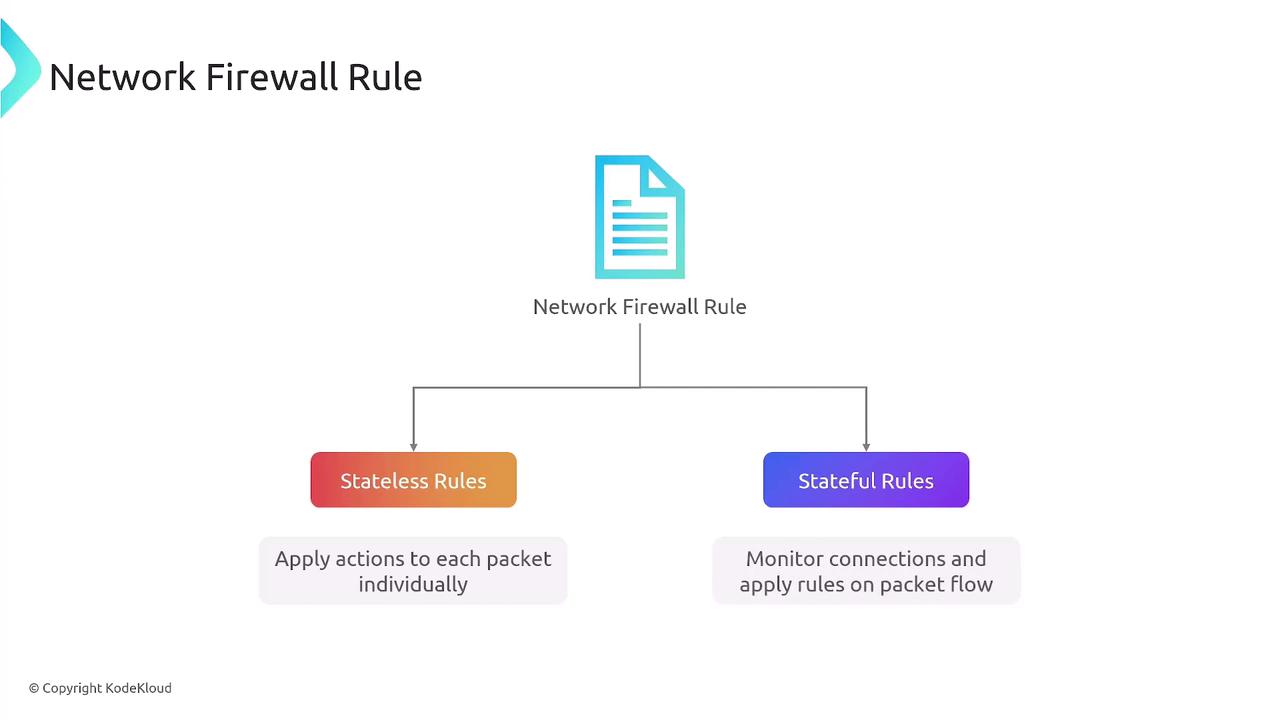
The AWS Network Firewall Service operates based on rules that filter traffic by IP, port, protocol, or specific patterns. These rules are structured into rule groups, which are then aggregated into a firewall policy. This policy is enforced on a network firewall instance to determine if traffic should be allowed, dropped, or alerted.There are two types of firewall rules:
- Stateless rules: Evaluate each network packet individually, similar to traditional network access control lists.
- Stateful rules: Monitor ongoing connections to track packet dialogs, ensuring that established sessions (e.g., web traffic) are properly managed.
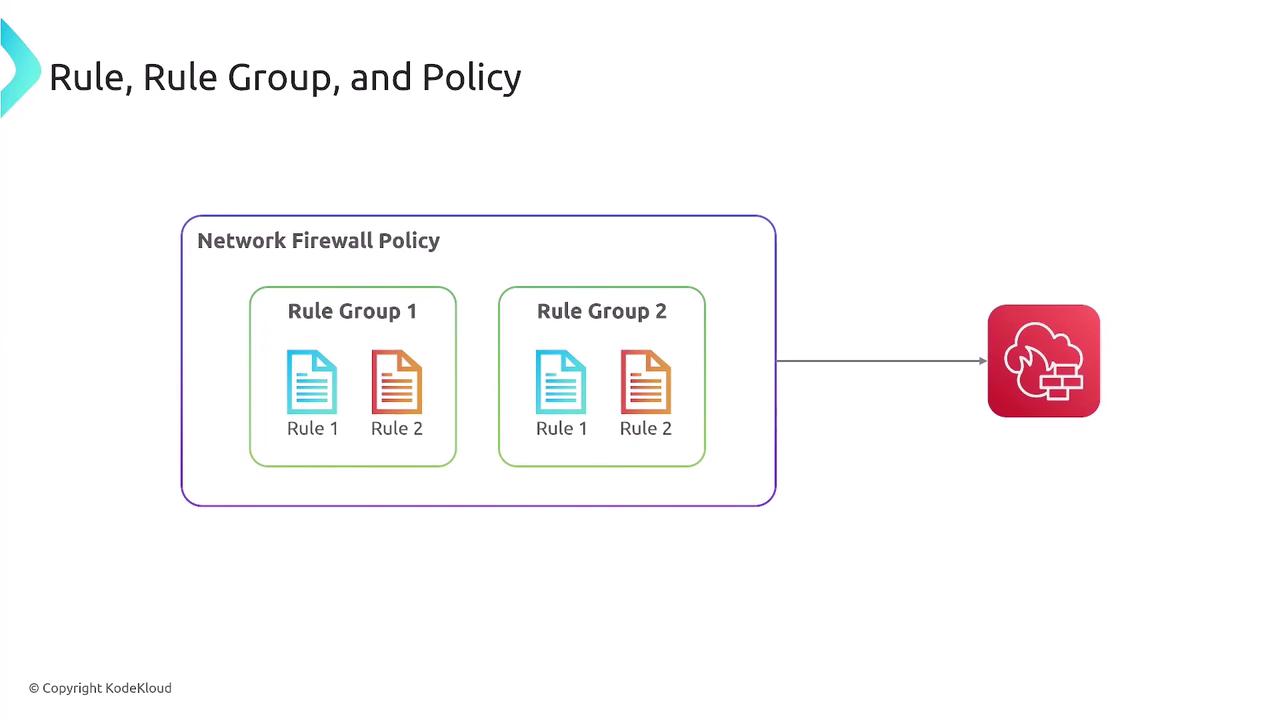
Rule Groups and Firewall Policies
Rule groups, which are collections of individual rules, are combined to create a comprehensive firewall policy. This policy is then applied to a network firewall instance, streamlining traffic filtering with both default actions and custom configurations.

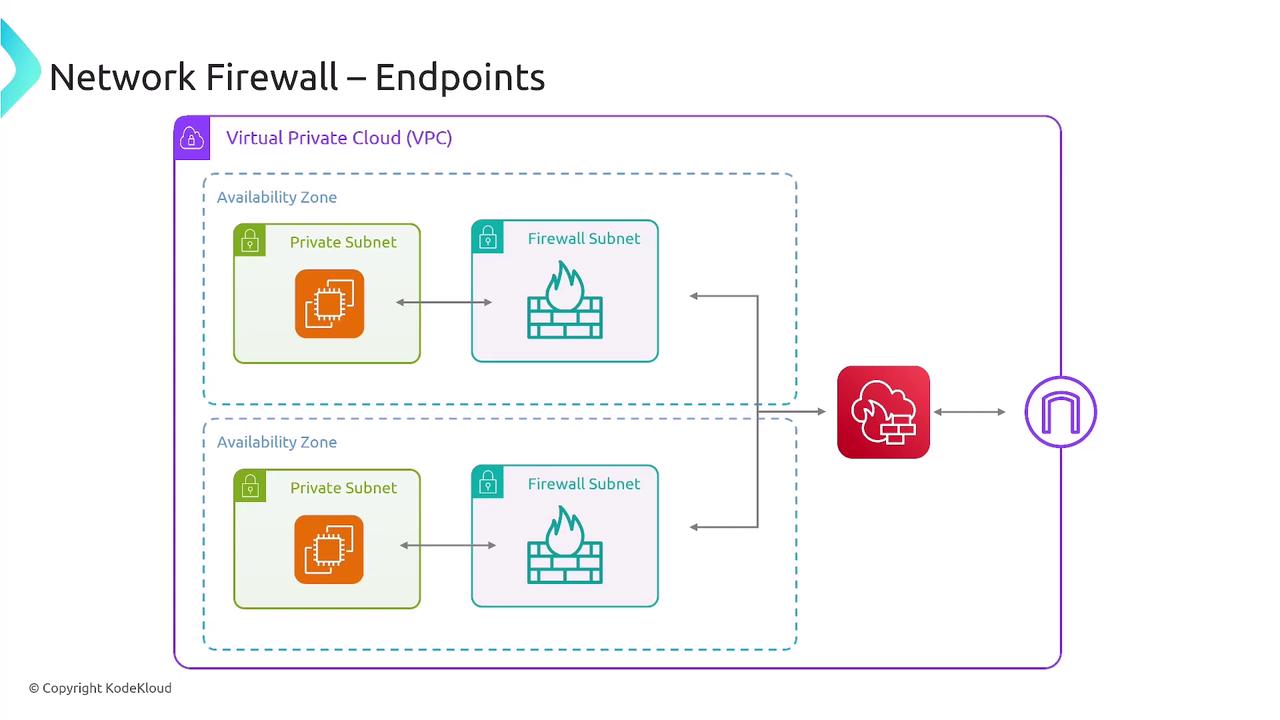
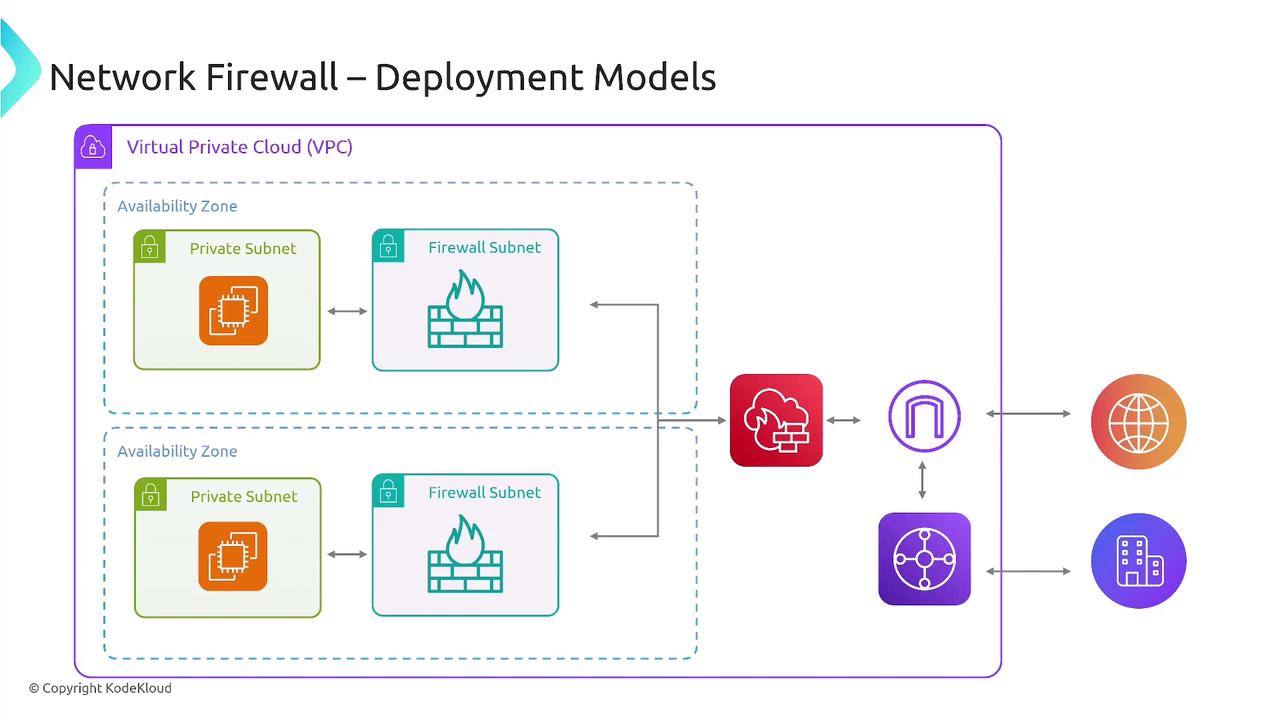
VPC Routing and Firewall Deployment
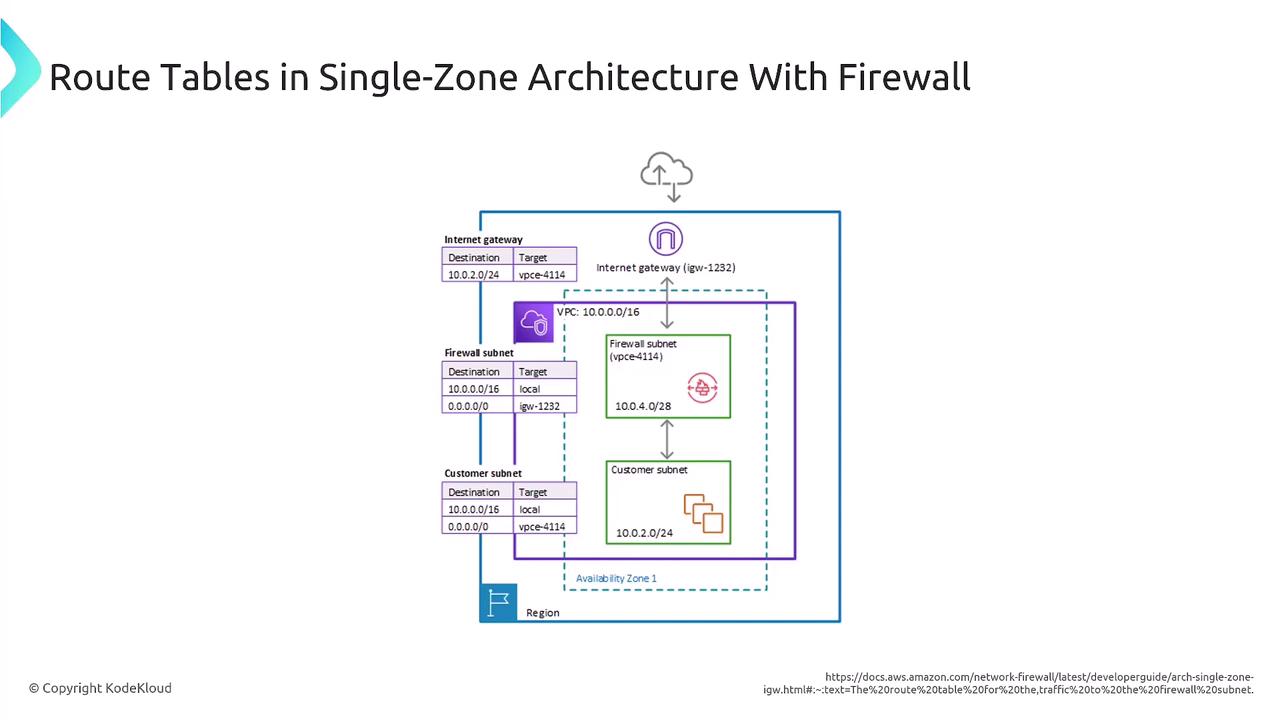
When deploying a network firewall, it is vital to update your VPC route tables to ensure traffic (both inbound and outbound) is appropriately routed through the firewall subnet. For instance, incoming traffic from the internet is first inspected by the firewall before being forwarded to the private subnet if allowed.
Choosing Between Stateless and Stateful Rule Engines
Selecting the appropriate rule engine is crucial depending on your traffic inspection needs. Stateless rules process traffic rapidly without session tracking, while stateful rules provide deeper packet inspection by tracking connection states. Depending on your configuration, you can implement actions such as passing, dropping, or alerting.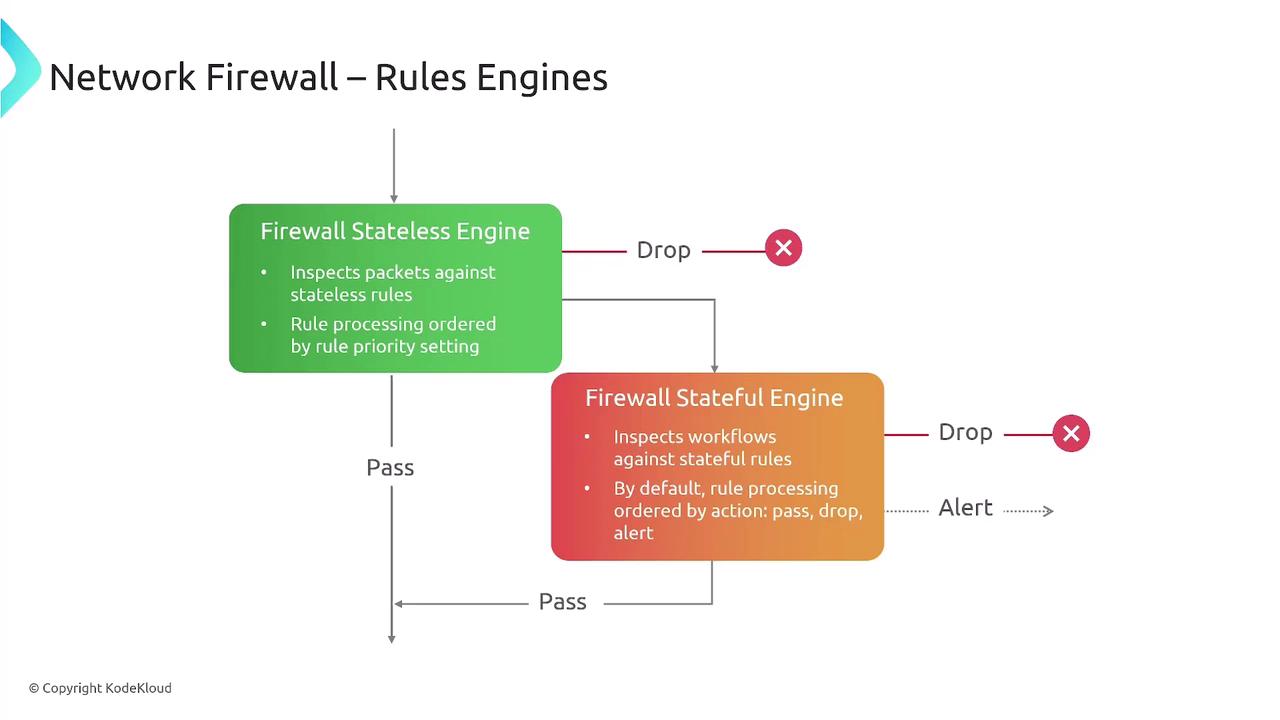
Centralized Security with AWS Firewall Manager
Managing multiple firewall configurations across an organization can be complex. Manual management of firewall rule sets may lead to inconsistencies, increased complexity, slower threat response times, and compliance challenges. AWS Firewall Manager provides a centralized solution to manage these configurations across all accounts in your AWS Organization.
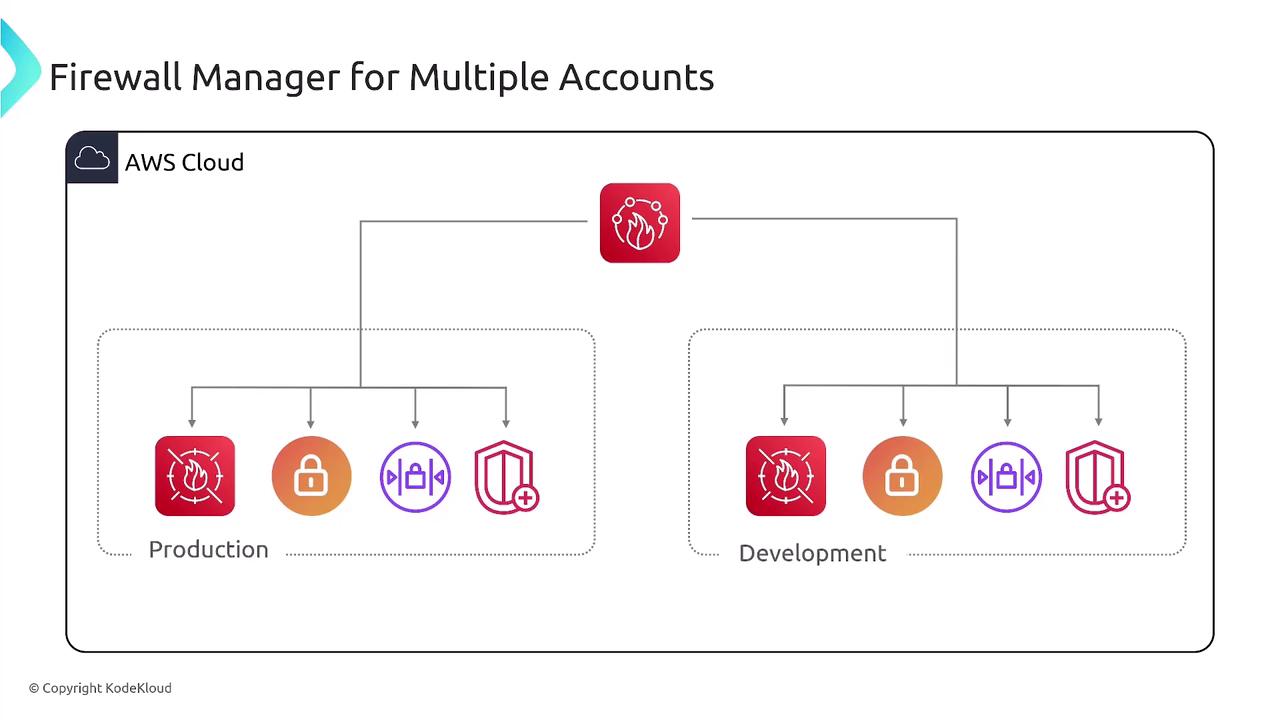
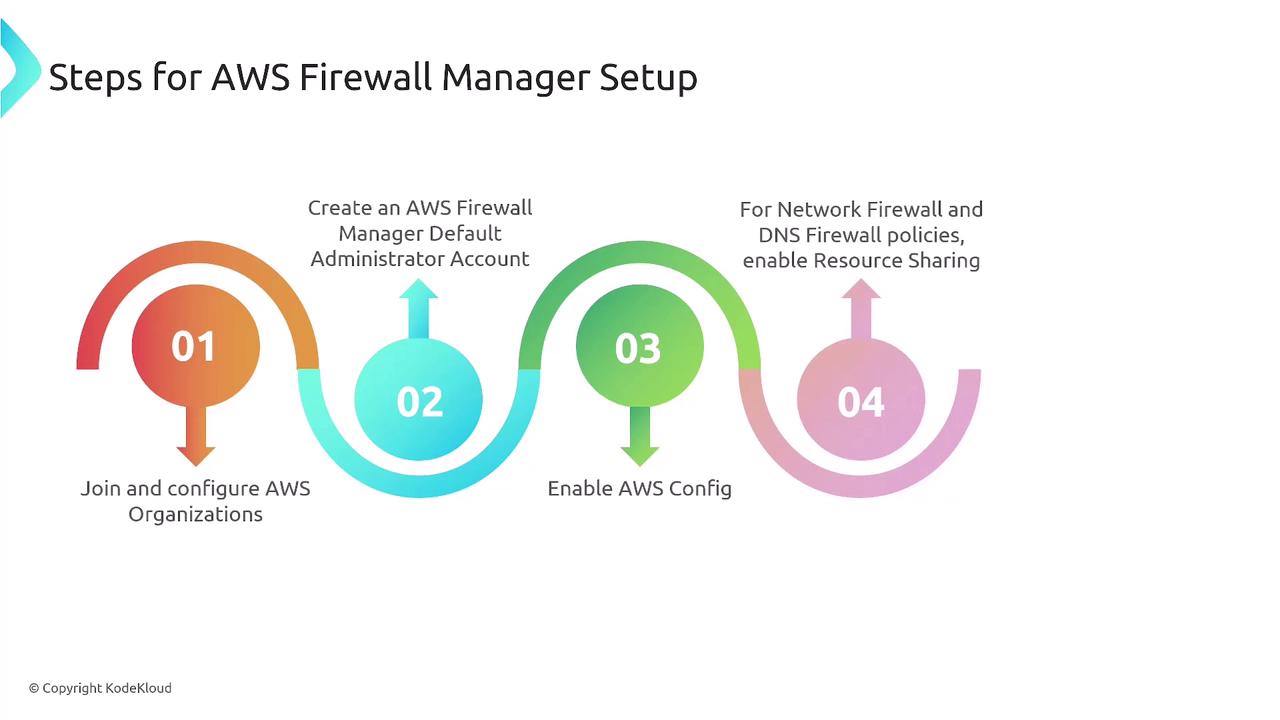
Prerequisites for AWS Firewall Manager
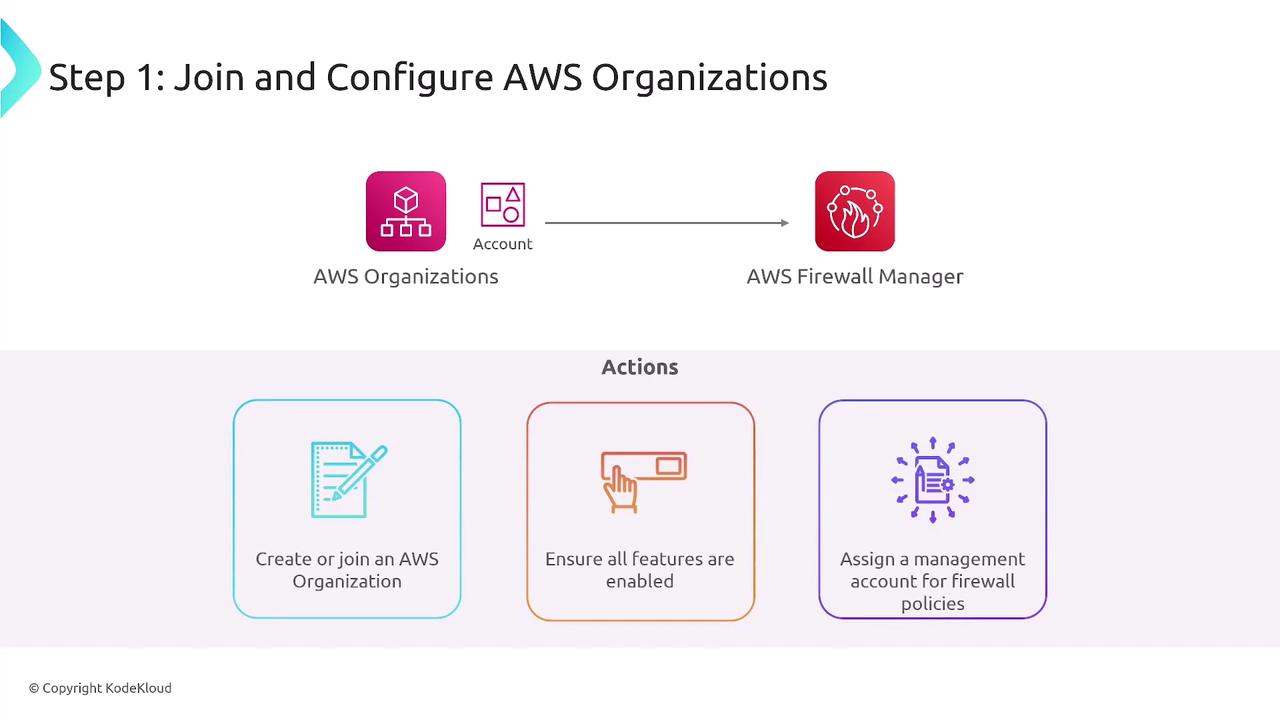
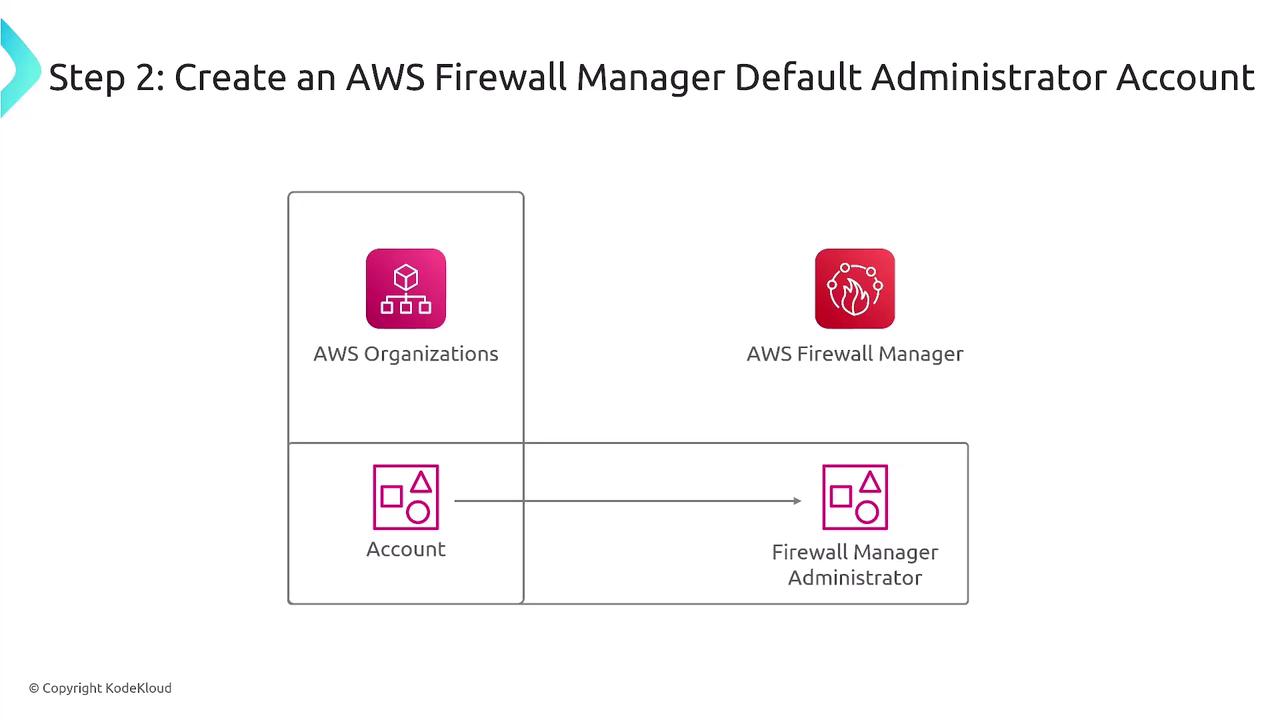
To ensure smooth operation of Firewall Manager, the following prerequisites must be met:- Join or create an AWS Organization and designate a management account specifically for Firewall Manager.
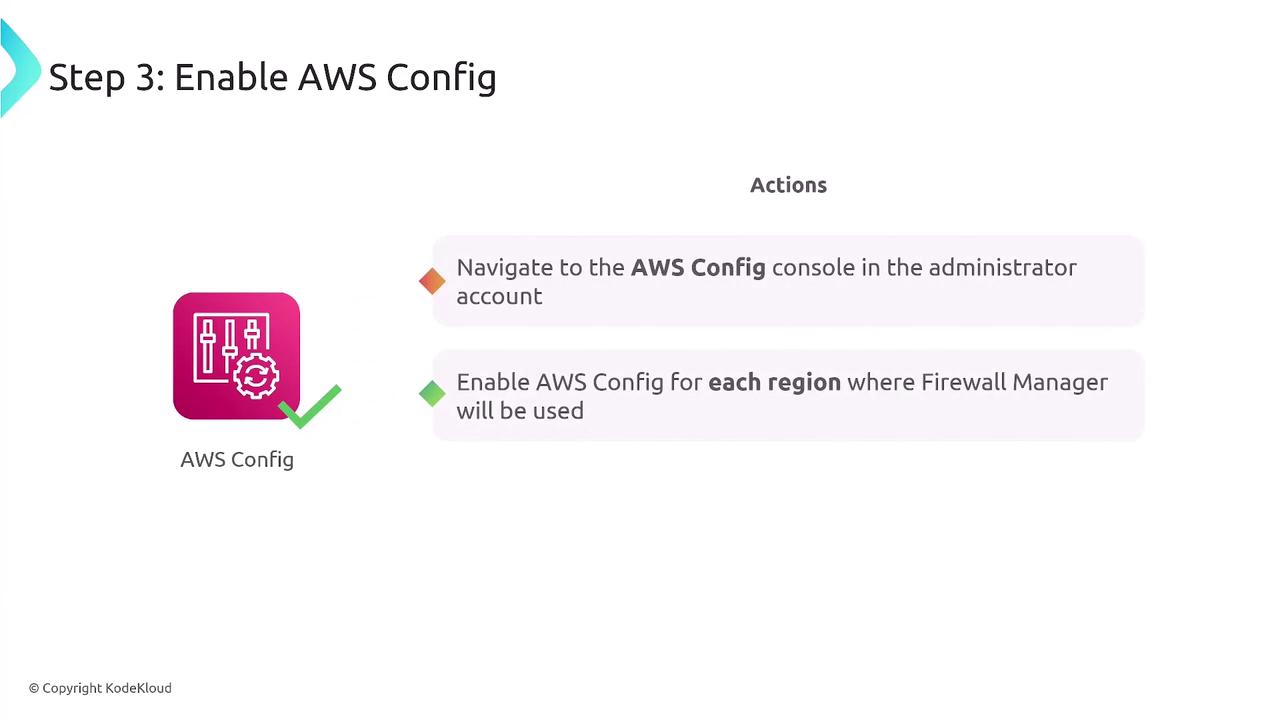
- Enable AWS Config in every region where you plan to operate the service, ensuring continuous tracking of configuration changes.
- Use the AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM) to share firewall resources among member accounts.
- Enable Firewall Manager in each active region.